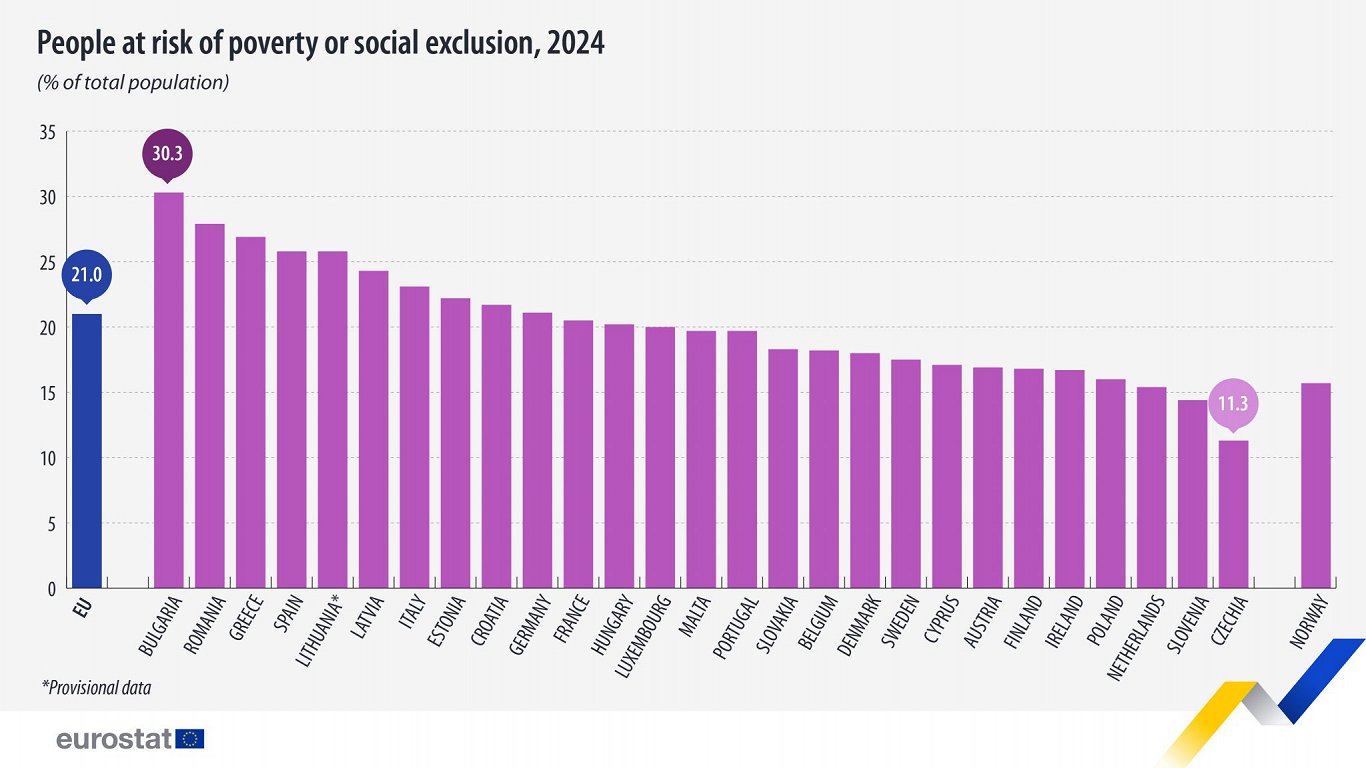
In 2024, 93.3 million people in the EU (21.0% of the population) were at risk of poverty or social exclusion, which means they lived in households experiencing at least 1 of 3 poverty and social exclusion risks: risk of poverty, severe material and social deprivation, and living in a household with very low work intensity.
Compared with 2023, there was a slight decrease of 0.3 percentage points across Europe (21.3% of the population, 94.6 million people).
The highest values were reported in Bulgaria (30.3%), Romania (27.9%), Greece (26.9%), Spain and Lithuania (both 25.8%).
Latvia’s figure was 24.3%, meaning that 449,000 people are classified as being at risk of poverty or social exclusion out of a population of 1.9 million.
On the other hand, the lowest shares were recorded in Czechia (11.3%), Slovenia (14.4%), the Netherlands (15.4%), Poland (16.0%) and Ireland (16.7%). Estonia did best among the Baltic states with a rate of 22.2%.
Select text and press Ctrl+Enter to send a suggested correction to the editor
Select text and press Report a mistake to send a suggested correction to the editor
Tell us about a mistake