Cohen J, Onunaku N, Clothier S, Poppe J. Helping young children succeed: Strategies to promote early childhood social and emotional development. Denver: National Conference of State Legislatures; 2005.
Kessler RC, Amminger GP, Aguilar-Gaxiola S, Alonso J, Lee S, Ustün TB. Age of onset of mental disorders: a review of recent literature. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2007;20:359–64.
Banerjee R, McLaughlin C, Cotney J, Roberts L, Peereboom C. Promoting emotional health, well-being and resilience in primary schools. Wales: Public Policy Institute of Wales; 2016.
Reinke WM, Stormont M, Herman KC, Puri R, Goel N. Supporting children’s mental health in schools: Teacher perceptions of needs, roles, and barriers. Sch Psychol Q. 2011;26:1–13.
Bonell C, Humphrey N, Fletcher A, Moore L, Anderson R, Campbell R. Why schools should promote students’ health and wellbeing. BMJ. 2014;348:g3078.
Goesling B. A practical guide to cluster randomized trials in school health research. J Sch Health. 2019;89:916–25.
Langford R, Bonell CP, Jones HE, Pouliou T, Murphy SM, Waters E, et al. The WHO Health Promoting School framework for improving the health and well-being of students and their academic achievement. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;2014:CD008958.
Axford N, Bjornstad G, Clarkson S, Ukoumunne OC, Wrigley Z, Matthews J, et al. The effectiveness of the KiVa bullying prevention program in Wales, UK: results from a pragmatic cluster randomized controlled trial. Prev Sci. 2020;21:615–26.
Bonell C, Allen E, Warren E, McGowan J, Bevilacqua L, Jamal F, et al. Effects of the Learning Together intervention on bullying and aggression in English secondary schools (INCLUSIVE): a cluster randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;392:2452–64.
Connolly P, Miller S, Kee F, Sloan S, Gildea A, McIntosh E, et al. A cluster randomised controlled trial and evaluation and cost-effectiveness analysis of the Roots of Empathy schools-based programme for improving social and emotional well-being outcomes among 8-to 9-year-olds in Northern Ireland. Public Health Research. 2018;6(4).
Ford T, Hayes R, Byford S, Edwards V, Fletcher M, Logan S, et al. The effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of the Incredible Years Teacher Classroom Management programme in primary school children: results of the STARS cluster randomised controlled trial. Psychol Med. 2019;49:828–42.
Humphrey N, Barlow A, Wigelsworth M, Lendrum A, Pert K, Joyce C, et al. A cluster randomized controlled trial of the Promoting Alternative Thinking Strategies (PATHS) curriculum. J Sch Psychol. 2016;58:73–89.
Kidger J, Turner N, Hollingworth W, Evans R, Bell S, Brockman R, et al. An intervention to improve teacher well-being support and training to support students in UK high schools (the WISE study): A cluster randomised controlled trial. PLoS Med. 2021;18:e1003847.
Stallard P, Sayal K, Phillips R, Taylor JA, Spears M, Anderson R, et al. Classroom based cognitive behavioural therapy in reducing symptoms of depression in high risk adolescents: pragmatic cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2012;345:e6058.
Stallard P, Skryabina E, Taylor G, Phillips R, Daniels H, Anderson R, et al. Classroom-based cognitive behaviour therapy (FRIENDS): a cluster randomised controlled trial to Prevent Anxiety in Children through Education in Schools (PACES). Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1:185–92.
Campbell MJ, Walters S. How to Design, Analyse and Report Cluster Randomised Trials in Medicine and Health Related Research. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons; 2014.
Donner A, Klar N. Design and Analysis of Cluster Randomization Trials in Health Research. Chichester: Wiley; 2000.
Eldridge SM, Kerry S. A Practical Guide to Cluster Randomised Trials in Health Services Research. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 2012.
Hayes R, Moulton L. Cluster Randomised Trials. Florida: CRC Press; 2009.
Murray DM. Design and Anaylsis of Group-Randomized Trials. New York: Oxford University Press; 1998.
Parker K, Nunns M, Xiao Z, Ford T, Ukoumunne OC. Characteristics and practices of school-based cluster randomised controlled trials for improving health outcomes in pupils in the UK: a methodological systematic review. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2021;21:152.
Eldridge SM, Ukoumunne OC, Carlin JB. The intra-cluster correlation coefficient in cluster randomised trials: a review of definitions. Int Stat Rev. 2009;77:378–94.
Rutterford C, Taljaard M, Dixon S, Copas A, Eldridge S. Reporting and methodological quality of sample size calculations in cluster randomized trials could be improved: a review. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:716–23.
Campbell MK, Piaggio G, Elbourne DR, Altman DG. CONSORT 2010 statement: extension to cluster randomised trials. BMJ. 2012;345: e5661.
Dong N, Reinke WM, Herman KC, Bradshaw CP, Murray DW. Meaningful effect sizes, intraclass correlations, and proportions of variance explained by covariates for planning two- and three-level cluster randomized trials of social and behavioral outcomes. Eval Rev. 2016;40:334–77.
Hale DR, Patalay P, Fitzgerald-Yau N, Hargreaves DS, Bond L, Görzig A, et al. School-level variation in health outcomes in adolescence: analysis of three longitudinal studies in England. Prev Sci. 2014;15:600–10.
Hedberg EC. Academic and behavioral design parameters for cluster randomized trials in kindergarten: an analysis of the Early Childhood Longitudinal Study 2011 Kindergarten Cohort (ECLS-K 2011). Eval Rev. 2016;40:279–313.
Sellström E, Bremberg S. Is there a “school effect” on pupil outcomes? A review of multilevel studies. Journal of epidemiology and community health. J Epidemiol Comm Health. 2006;60:149–55.
Shackleton N, Hale D, Bonell C, Viner RM. Intraclass correlation values for adolescent health outcomes in secondary schools in 21 European countries. SSM – Popul Health. 2016;2:217–25.
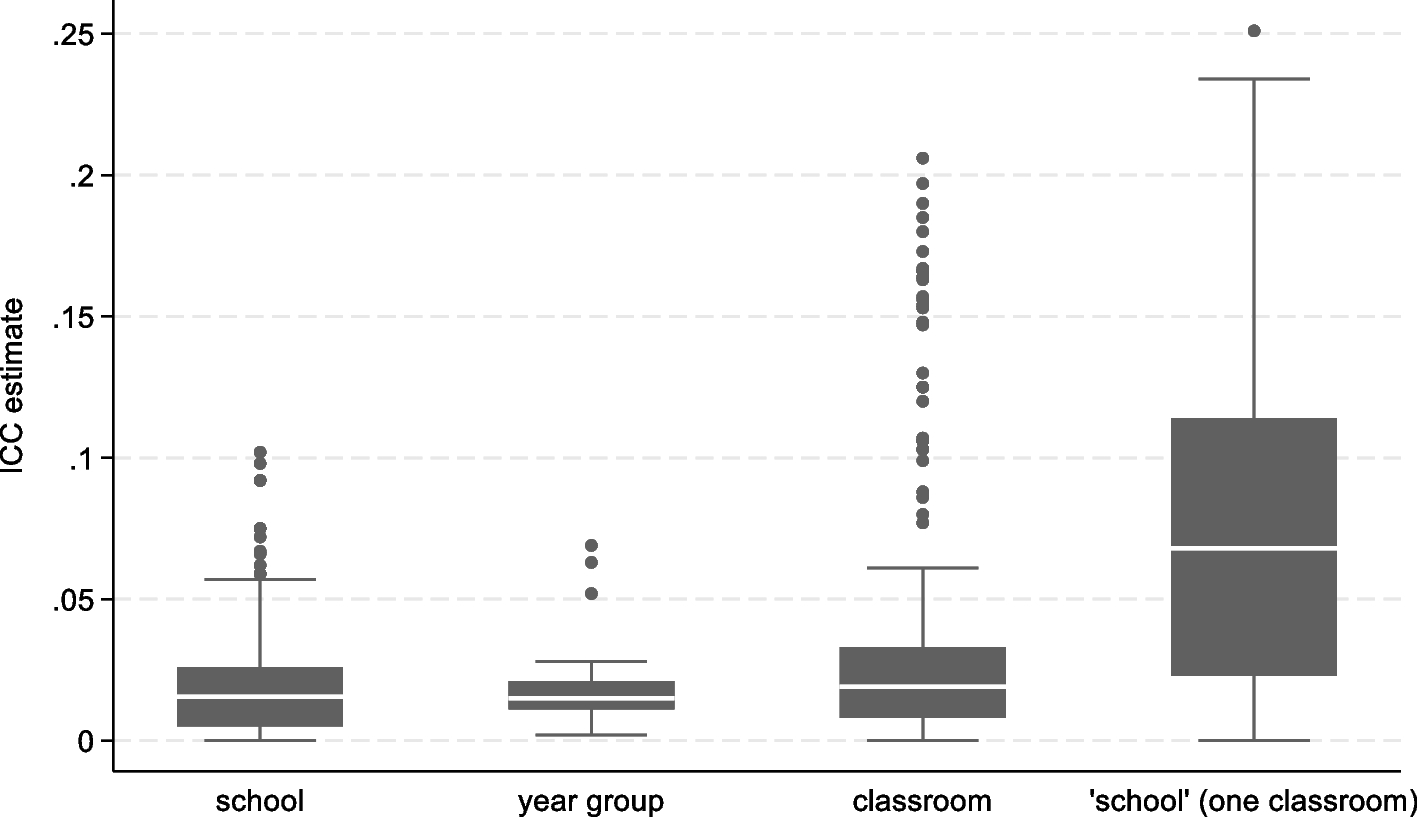
Parker K, Nunns M, Xiao Z, Ford T, Ukoumunne OC. Intracluster correlation coefficients from school-based cluster randomized trials of interventions for improving health outcomes in pupils. J Clin Epidemiol. 2023;158:18–26.
Bonell C, Jamal F, Harden A, Wells H, Parry W, Fletcher A. Systematic review of the effects of schools and school environment interventions on health: evidence mapping and synthesis. Public Health Research. 2013;1(1).
Hemming K, Eldridge S, Forbes G, Weijer C, Taljaard M. How to design efficient cluster randomised trials. BMJ. 2017;358: j3064.
James J, Thomas P, Cavan D, Kerr D. Preventing childhood obesity by reducing consumption of carbonated drinks: cluster randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2004;328:1237.
Giles M, McClenahan C, Armour C, Millar S, Rae G, Mallett J, et al. Evaluation of a theory of planned behaviour–based breastfeeding intervention in Northern Irish schools using a randomized cluster design. Br J Health Psychol. 2014;19:16–35.
Kuyken W, Ball S, Crane C, Ganguli P, Jones B, Montero-Marin J, et al. Effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of universal school-based mindfulness training compared with normal school provision in reducing risk of mental health problems and promoting well-being in adolescence: the MYRIAD cluster randomised controlled trial. Evid Based Ment Health. 2022;25:99–109.
Norris E, Dunsmuir S, Duke-Williams O, Stamatakis E, Shelton N. Physically active lessons improve lesson activity and on-task behavior: A cluster-randomized controlled trial of the “Virtual Traveller” Intervention. Health Educ Behav. 2018;45:945–56.
Rutterford C, Copas A, Eldridge S. Methods for sample size determination in cluster randomized trials. Int J Epidemiol. 2015;44:1051–67.
Fazzari MJ, Kim MY, Heo M. Sample size determination for three-level randomized clinical trials with randomization at the first or second level. J Biopharm Stat. 2014;24:579–99.
Teerenstra S, Moerbeek M, van Achterberg T, Pelzer BJ, Borm GF. Sample size calculations for 3-level cluster randomized trials. Clin Trials. 2008;5:486–95.
Webster-Stratton C, Reid MJ. The Incredible Years parents, teachers, and children training series: A multifaceted treatment approach for young children with conduct problems. In: Weisz JR, Kazdin AE, editors. Evidence-based psychotherapies for children and adolescents. 3rd ed. New York: Guilford Press; 2018. p. 122–41.
Goodman R. Psychometric properties of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2001;40:1337–45.
Allwood M, Allen K, Price A, Hayes R, Edwards V, Ball S, et al. The reliability and validity of the pupil behaviour questionnaire: a child classroom behaviour assessment tool. Emot Behav Diffic. 2018;23:361–71.
Allen K, Marlow R, Parker C, Rodgers L, Ukoumunne OC, Chan Seem E, et al. ‘How I Feel About My School’: the construction and validation of a method of wellbeing at school for primary school children. Clin Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2018;23:25–41.
Salmivalli C, Kärnä A, Poskiparta E. Counteracting bullying in Finland: The KiVa program and its effects on different forms of being bullied. Int J Behav Dev. 2011;35:405–11.
Olweus D. The Revised Olweus Bully / Victim Questionnaire. Bergen: University of Bergen; 1996.
Kärnä A, Voeten M, Little TD, Poskiparta E, Alanen E, Salmivalli C. Going to scale: a nonrandomized nationwide trial of the KiVa antibullying program for grades 1–9. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2011;79:796–805.
Barrett P. Friends for Life – Group leaders’ manual for children. Bowen Hills: Australian Academic Press; 2004.
Sandín B, Chorot P, Valiente RM, Chorpita BF. Development of a 30-item version of the Revised Child Anxiety and Depression Scale. Revista de Psicopatología y Psicología Clínica. 2010;15:165–78.
Chorpita BF, Tracey SA, Brown TA, Collica TJ, Barlow DH. Assessment of worry in children and adolescents: an adaptation of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire. Behav Res Ther. 1997;35:569–81.
Rosenberg M. Society and the adolescent self-image. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2015.
Furber G, Segal L. The validity of the Child Health Utility instrument (CHU9D) as a routine outcome measure for use in child and adolescent mental health services. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015;13:22.
Shochet IM, Ham D. Universal school-based approaches to preventing adolescent depression: past findings and future directions of the Resourceful Adolescent Program. Int J Ment Health Promot. 2004;6:17–25.
Angold A, Costello EJ, Messer SC, Pickles A, Winder F, Silver D. The development of a short questionnaire for use in epidemiological studies of depression in children and adolescents. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res. 1995;5:237–49.
Schniering CA, Rapee RM. Development and validation of a measure of children’s automatic thoughts: the children’s automatic thoughts scale. Behav Res Ther. 2002;40:1091–109.
Goodenow C. The psychological sense of school membership among adolescents: Scale development and educational correlates. Psychol Sch. 1993;30:79–90.
Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Appl Psychol Meas. 1977;1:385–401.
Tennant R, Hiller L, Fishwick R, Platt S, Joseph S, Weich S, et al. The Warwick-Edinburgh Mental Well-being Scale (WEMWBS): development and UK validation. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2007;5:63.
Gioia GA, Isquith PK, Guy SC, Kenworthy L. BRIEF-2: Behavior rating inventory of executive function. Florida: Psychological Assessment Resources Lutz; 2015.
Chorpita BF, Yim L, Moffitt CE, Umemoto LA, Francis SE. Assessment of symptoms of DSMIV anxiety and depression in children: A Revised Child Anxiety And Depression Scale. Behav Res Ther. 2000;38:835–55.
Spier E. Alaska School Climate and Connectedness Survey: 2016 Statewide Report. California: American Institutes for Research; 2016.
Greco LA, Baer RA, Smith GT. Assessing mindfulness in children and adolescents: development and validation of the Child and Adolescent Mindfulness Measure (CAMM). Psychol Assess. 2011;23:606–14.
StataCorp. Stata Statistical Software: Release 18. College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC; 2023.
Gulliford MC, Ukoumunne OC, Chinn S. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community-based surveys and intervention studies: data from the Health Survey for England 1994. Am J Epidemiol. 1999;149:876–83.
Siddiqui O, Hedeker D, Flay BR, Hu FB. Intraclass correlation estimates in a school-based smoking prevention study: outcome and mediating variables, by sex and ethnicity. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;144:425–33.
Collishaw S, Goodman R, Ford T, Rabe-Hesketh S, Pickles A. How far are associations between child, family and community factors and child psychopathology informant-specific and informant-general? J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2009;50:571–80.
Stone LL, Otten R, Engels RC, Vermulst AA, Janssens JM. Psychometric properties of the parent and teacher versions of the strengths and difficulties questionnaire for 4- to 12-year-olds: a review. Clin Child Fam Psychol Rev. 2010;13:254–74.
van den Heuvel M, Jansen D, Stewart RE, Smits-Engelsman BCM, Reijneveld SA, Flapper BCT. How reliable and valid is the teacher version of the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire in primary school children? PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0176605.
Department for Education. Behaviour in Schools: Advice for headteachers and school staff. In: Education Df, editor. 2022.
Bradshaw CP, Waasdorp TE, Debnam KJ, Johnson SL. Measuring school climate in high schools: a focus on safety, engagement, and the environment. J Sch Health. 2014;84:593–604.
Kidger J, Araya R, Donovan J, Gunnell D. The effect of the school environment on the emotional health of adolescents: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2012;129:925–49.
Bonell C, Parry W, Wells H, Jamal F, Fletcher A, Harden A, et al. The effects of the school environment on student health: a systematic review of multi-level studies. Health Place. 2013;21:180–91.
Diedrichs PC, Atkinson MJ, Steer RJ, Garbett KM, Rumsey N, Halliwell E. Effectiveness of a brief school-based body image intervention ‘Dove Confident Me: Single Session’when delivered by teachers and researchers: Results from a cluster randomised controlled trial. Behav Res Ther. 2015;74:94–104.