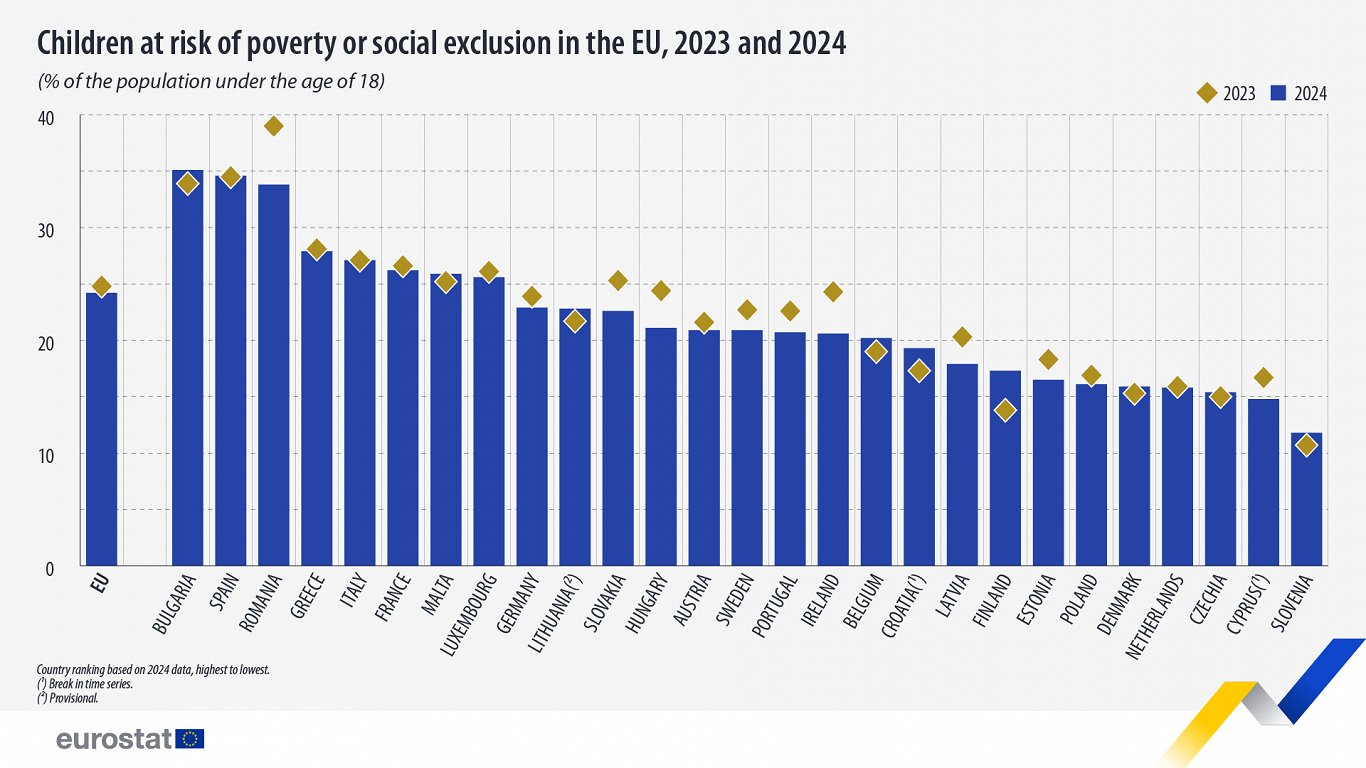
Latvia does fairly well in comparison with its EU peers, with a figure of 17.9% – a significant improvement on the 20.3% figure it recorded in 2023. A decade ago in 2015, Latvia’s figure was way higher at 30.7%, and the subsequent years have seen a gradual improvement.
Estonia’s figure in 2024 was 16.5% and Lithuania’s was a provisional 22.8%, putting Latvia in the middle of the Baltic states.
At the country level, in 2024, the highest values were reported in Bulgaria (35.1%), Spain (34.6%) and Romania (33.8%). In contrast, Slovenia (11.8%), Cyprus (14.8%) and Czechia (15.4%) registered the lowest shares.
Compared with 2023, Romania registered the largest decrease in the share of children at risk of poverty or social exclusion in 2024, -5.2 pp, followed by Ireland (-3.7 pp) and Hungary (-3.3 pp). On the other hand, Finland (+3.5 pp), Croatia (+2.0 pp), Bulgaria and Belgium (both +1.2 pp) observed the largest increases.
Select text and press Ctrl+Enter to send a suggested correction to the editor
Select text and press Report a mistake to send a suggested correction to the editor
Tell us about a mistake