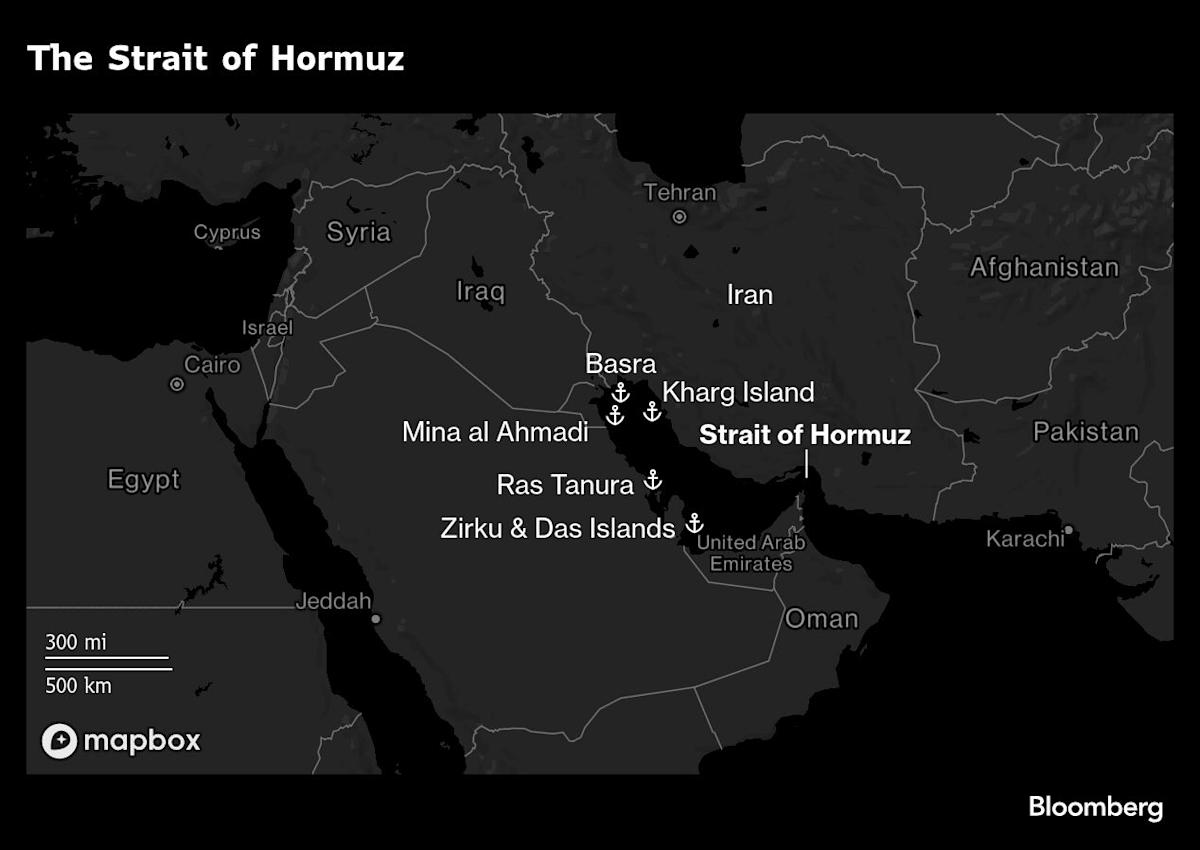
(Bloomberg) — US airstrikes on Iranian nuclear facilities are sharpening the focus on one option Iran has yet to really deploy in the conflict: disrupting regional oil trade, especially through the critical Strait of Hormuz.
Most Read from Bloomberg
Iran has over the years threatened multiple times to shut the strait — a narrow stretch of water through which a fifth of the world’s oil supply flows each day. But in practice, Tehran has numerous less-drastic options at its disposal to calibrate a response that hurts its enemies while limiting the impact on allies like China, its biggest oil buyer.
Follow Bloomberg’s live blog on the US strikes
A full closure of Hormuz for more than a few hours or days is a nightmare scenario that many observers think improbable. It would choke off flows and spike crude prices — JPMorgan & Co. analysts said by almost 70% — fueling global inflation and weighing heavily on growth.
Up to Friday, oil shipping from the region, and indeed through Hormuz, had been relatively unscathed by the conflict. Shipments from Iran itself have surged, and oil tanker activity through the Strait of Hormuz remained largely steady. Still, Greece’s shipping ministry on Sunday advised the nation’s vessel owners to review the use of the strait.
If it chooses to target oil in its retaliation against the US strikes, Iran’s coastline onto Hormuz gives Tehran an array of options, from lower-impact harassing of ships in the region, to the more extreme alternatives: attacking tankers with drones, mines or bombs to the point that the strait becomes impassable for commercial trade.
“If Iran were to decide to begin to take action in the Straits of Hormuz, there’s a wide range of things that can look like,” Daniel Sternoff, non-resident fellow at the Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy, said on the center’s podcast before the US attack happened. “We can kind of draw a huge set of scenarios and unknowns which have all sorts of consequences.”
Iran may also ultimately avoid actions that impede oil flows — recent history is littered with examples where supply threats came to nothing.
In whatever it does, Tehran will have to weigh the possibility of retaliation against its own energy infrastructure and the possibility that it could upset China if flows got disrupted. It will also have to consider the potential for retaliation against its own shipments, another important source of oil for China.