Automation accelerates Japan’s EV shift
Increased automation in assembly lines has led to a rise in industrial robot installation, according to trade body.
AI generated, Adobe Firefly
An 11% increase in automated manufacturing robots was driven by diversification in drivetrains and wider commitment to EV assembly, IFR reports
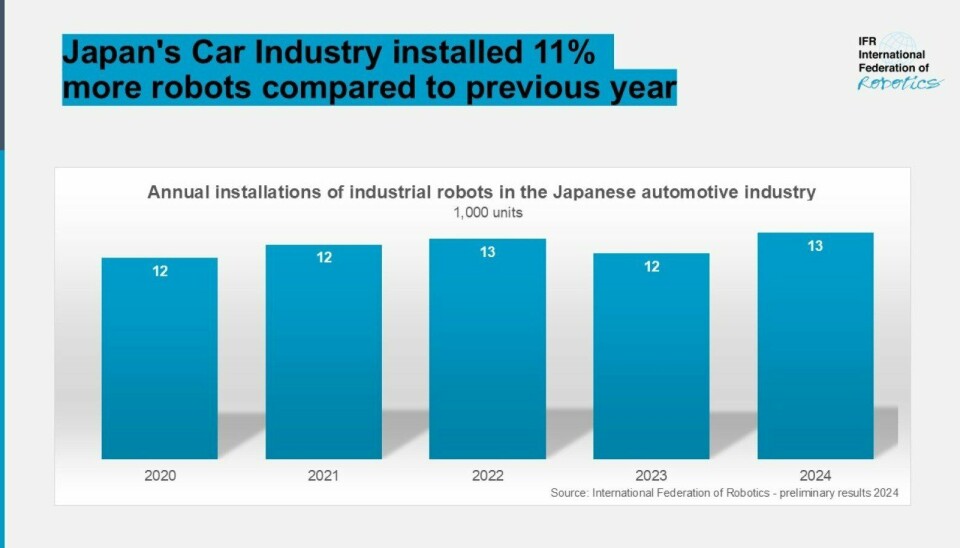
Since 2020, installation of industrial robots across the auto industry in Japan has fluctuated but reached a new peak in 2024
International Federation of Robots
The installation of industrial robots within Japanese automotive manufacturing plants rose by 11% in 2024, according to preliminary statistics from the International Federation of Robotics (IFR).
The IFR is a not-for-profit member organisation representing technology, automation and software companies across a variety of sectors.
It reported that a total of 13,000 robots were installed across sites in Japan, the highest number since 2020.
Global statistics for 2024 have not yet been released, but worldwide installations of industrial robots in the automotive sector fell between 2022 and 2023, dropping from 136,112 to 135,461.
The automotive industry accounted for approximately 25% of annual robotic installations in Japan, second only to the electronics sector.
The increase was caused by a wider move across Japanese automakers to expand manufacturing capabilities for battery and fuel cell electric vehicles, as well as increased interest in hydrogen-fuelled combustion engines.
Earlier this year, for example, Mazda announced a new EV would begin production at its Hofu plant in Yamaguchi. Last year, other Japanese OEMs Nissan, Honda, and Mitsubishi entered into agreements to collectively explore next-gen EVs.
Learn more about how automation can be applied across the supply chain
Audi’s supply chain in 2033 and beyond: Designed to combine logistics, automation and people
Automated robots would help with the assembly of a more diversified portfolio of vehicles and drivetrains, the IFR suggested.
Takayuki Ito, president of the IFR, commented that the increased usage of robotics across Japanese manufacturing “characterises modern industrial workplaces”.
“Japan is the world’s predominant robot manufacturing country representing 38% of global robot production,” he added. “In terms of factory automation, Japan’s automotive industry ranked fourth worldwide with a robot density of 1,531 robots per 10,000 employees in 2023. This is ahead of the United States and Germany only behind Slovenia, Korea and Switzerland.”