Introduction: Powering the Future with Smart Grids
As the world shifts toward cleaner, more resilient, and more efficient energy systems, smart grids have emerged as a vital component of this transformation. Designed to modernize the way electricity is produced, delivered, and consumed, smart grids integrate advanced communication technologies, automation, and data analytics into traditional power infrastructure. This enables real-time monitoring, improved reliability, reduced energy losses, and better integration of renewable energy sources. With growing electricity demands, aging power grids, and an urgent need to cut emissions, countries around the globe are turning to smart grid technologies as a sustainable and strategic solution.
What is Driving the Rapid Growth of the Smart Grid Market?
According to the Persistence Market Research report, the global smart grid market is projected to experience tremendous growth over the next several years. The market size is expected to be valued at approximately US$ 52 billion in 2025 and is estimated to soar to US$ 154.1 billion by 2032. This remarkable expansion reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.8% during the forecast period of 2025 to 2032. This growth trajectory is being driven by a confluence of factors, including increasing energy demand, climate change concerns, government policies promoting renewable integration, and rapid digitalization of the power sector.
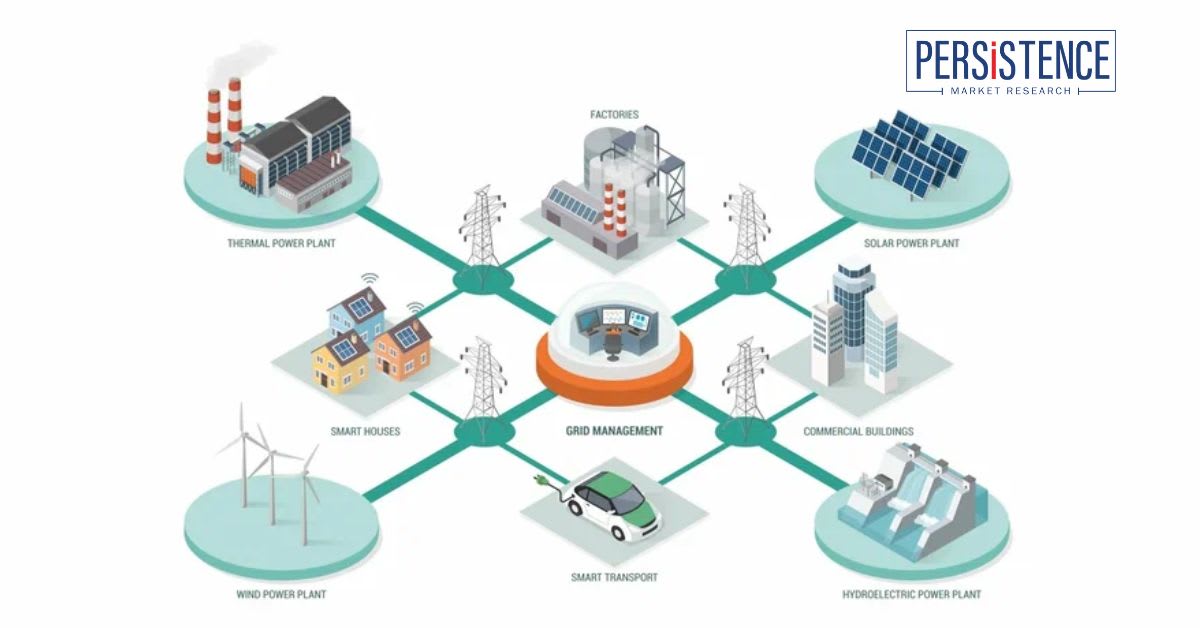
What is a Smart Grid and Why is it Important for the Future of Energy?
A smart grid is an electricity network that uses digital technology to monitor and manage the flow of energy from generation to consumption. Unlike traditional grids, smart grids facilitate two-way communication between utility providers and consumers, enabling real-time data exchange and automation. This is crucial for integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind, reducing outages, improving energy efficiency, and enabling demand-side management. Smart grids are essential for the transition to sustainable energy systems, as they support decarbonization goals, improve grid reliability, and empower consumers with better control over their energy use.
Key Market Drivers: Digitalization, Decarbonization, and Decentralization
Three fundamental trends are propelling the smart grid market forward: digitalization, decarbonization, and decentralization. First, digitalization is enabling utilities to harness big data, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) to enhance grid performance. From smart meters to AI-driven predictive maintenance, digital tools are transforming the way electricity networks operate.
Second, the global decarbonization push is encouraging countries to shift away from fossil fuels and toward renewable sources. Smart grids are essential in this transition, as they help manage the variable output of renewables, balance supply and demand, and maintain grid stability.
Third, decentralization of energy systems—through the rise of distributed energy resources like rooftop solar, battery storage, and microgrids—is creating a more complex energy landscape. Smart grid technologies enable the efficient management and integration of these distributed sources into the wider grid infrastructure.
Advanced Technologies Transforming the Smart Grid Landscape
The smart grid market is being shaped by a range of emerging technologies that are unlocking new capabilities and efficiencies. Smart meters, for instance, allow utilities and consumers to track electricity usage in real time, enabling more accurate billing and consumption awareness. Distribution automation systems detect and isolate faults on the grid to minimize outages and improve response times.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are also playing pivotal roles. These technologies help forecast energy demand, identify potential equipment failures, and optimize load balancing. Blockchain technology, though in its early stages, is being explored for peer-to-peer energy trading, enhancing transparency and trust in decentralized systems.
Furthermore, the growing integration of electric vehicles (EVs) is catalyzing the need for intelligent grid infrastructure. Smart grids support EV charging infrastructure through demand response programs and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies, ensuring grid reliability while accommodating increased electricity usage.
Regional Analysis: North America and Asia Pacific Lead the Charge
Geographically, North America remains a leader in smart grid development, particularly the United States and Canada. Federal and state-level initiatives, robust investments in grid modernization, and a high penetration of renewable energy are driving growth in this region. The U.S. Department of Energy, for example, continues to invest heavily in grid resilience and smart grid pilot projects.
Asia Pacific, however, is expected to witness the fastest growth during the forecast period. Countries such as China, India, Japan, and South Korea are investing massively in smart grid infrastructure to meet rising electricity demand, improve energy access, and integrate large-scale renewables. China, in particular, has emerged as a powerhouse, with aggressive smart grid rollout strategies, smart substation deployments, and government-led innovation initiatives.
Europe is also seeing significant progress, with the EU’s Green Deal and climate targets promoting smart energy solutions. Advanced smart meter deployment programs and cross-border grid integration projects are helping the region move closer to a unified and intelligent energy market.
Challenges in Smart Grid Deployment
Despite the promising outlook, several challenges must be addressed to realize the full potential of smart grids. One of the primary hurdles is the high initial capital investment required for infrastructure modernization, including advanced metering systems, automation devices, and communication networks. For many utilities—especially in developing economies—this poses a significant barrier.
Cybersecurity is another critical concern. As power grids become more digital and interconnected, they also become more vulnerable to cyber threats. Ensuring robust security protocols, encryption, and real-time monitoring systems is essential to protect grid assets and customer data.
Additionally, regulatory and policy fragmentation across regions can slow down smart grid deployment. Uniform standards, supportive regulations, and incentives are crucial to foster innovation and market expansion.
Emerging Trends: From Smart Cities to Energy-as-a-Service
The smart grid market is increasingly aligning with broader technological and social trends. One such trend is the rise of smart cities, where integrated digital infrastructure supports transportation, energy, water, and waste systems. In these urban environments, smart grids serve as the backbone for efficient energy management, clean mobility, and real-time service delivery.
Another emerging trend is Energy-as-a-Service (EaaS), where businesses and consumers outsource their energy needs to service providers who manage everything from generation and storage to optimization and maintenance. Smart grid technologies are crucial enablers of EaaS, providing the data and control needed to deliver customized, subscription-based energy solutions.
Demand-side management (DSM) is also gaining momentum. With real-time pricing, automated controls, and user incentives, DSM helps balance energy use during peak hours, reduce costs, and support grid resilience.
Future Outlook: A Transformative Decade Ahead
Looking ahead, the smart grid market is set for a transformative decade. Innovations in edge computing, digital twins, 5G connectivity, and cloud platforms are expected to revolutionize how energy systems are monitored and managed. Increased collaboration between energy companies, technology providers, and policymakers will further accelerate adoption.
With the global smart grid market forecasted to grow from US$ 52 billion in 2025 to US$ 154.1 billion by 2032 at a CAGR of 16.8%, the pace of innovation and investment will be critical. As nations pursue their decarbonization goals, smart grids will play a central role in creating cleaner, more adaptive, and customer-centric energy ecosystems.
Conclusion: Smart Grids Are the Foundation of Energy Modernization
The smart grid market represents the cornerstone of the future energy landscape. By enabling more flexible, efficient, and sustainable electricity systems, smart grids are not only enhancing power delivery but also transforming the way we interact with energy. As technology continues to evolve and climate concerns take center stage, the integration of smart grid solutions will be instrumental in achieving global energy security, sustainability, and resilience.
Explore the Latest Trending “Exclusive Article” @