Take a look at the essential events, concepts, terms, quotes, or phenomena every day and brush up your knowledge. Here’s your UPSC current affairs knowledge nugget for today on IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
(Relevance: International reports and organisations, especially the International Monetary Fund, form a crucial part of the UPSC CSE syllabus. Previously, various questions have been asked with regard to the IMF and its facilities and reports. Thus, knowing about it and its recently released report becomes important.)
Why in the news?
On July 29, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) released the latest update of its World Economic Outlook (WEO). The WEO is the IMF’s benchmark publication as it provides a comprehensive picture of the global economy as well as details of individual countries. In this context, knowing about the WEO, its highlights becomes important.
Key Takeaways :
1. The IMF releases the WEO twice every year, in April and October, apart from updating it twice — in January and July. The document released on 29th July is the July update to the WEO released in April.
2. The broader message of updated WEO is captured by its title— “Global Economy: Tenuous Resilience amid Persistent Uncertainty”. There are two main takeaways for the state of the global economy.
3. First, the global economy has proven to be resilient, albeit tenuous, and second, the outlook is plagued by persistent uncertainty.
4. Despite all upheavals (such as the Covid-19 pandemic, the Russia-Ukraine conflict, and the tariff onslaught unleashed by the second Trump Administration), the global economy has managed to continue growing. That is the meaning of resilience.
Story continues below this ad
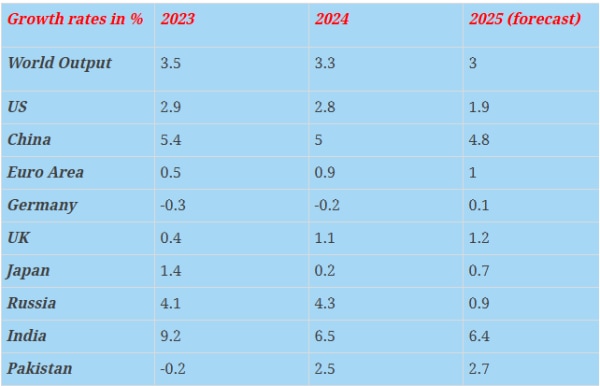
5. According to the latest update by the IMF, “Global growth is projected at 3.0 percent for 2025 and 3.1 percent in 2026. The forecast for 2025 is 0.2 percentage points higher than that in the reference forecast of the April 2025 World Economic Outlook (WEO) and 0.1 percentage points higher for 2026.”
6. However, this resilience is “tenuous” (that is, unstable or with weak foundations). That’s because, while the tariff situation isn’t as bad as it appeared in April when US President Donald Trump first announced them on Liberation Day, it is not as if there is enough clarity about the eventual tariff rates.
7. Another big downside risk comes from the geopolitical tensions (such as the ones in the Middle East and Ukraine), which could “disrupt global supply chains and push commodity prices up”.
Growth data of individual countries
1. The US, from where most of the policy uncertainty is emanating at present, is expected to lose growth momentum in 2025, as against the past two years. By the end of 2025, US GDP would be close to $31 trillion. In 2026, the US growth is expected to slow down even further to just 1.2%.
Story continues below this ad
 Source: IMF
Source: IMF
2. In sharp contrast, China, which is the main economic threat to the US, is expected to slow down only marginally and still manage to grow at a respectable rate of 4.8% for an economy with an annual GDP of over $19 trillion.
3. India continues to be a bright spot in the global economy. It is expected to grow 6.4% in 2025. While this rate is substantially slower than 2023, the fact is that by growing at over 6% in a world where competing economies are struggling to grow even at one-third that rate, India is fast bridging the gap and ensuring that it overtakes one developed economy after another, at least in terms of total GDP.
BEYOND THE NUGGET: About the International Monetary Fund
1. Set up in 1945 , the IMF works to achieve sustainable growth and prosperity for all of its 191 member countries. It does so by supporting economic policies that promote financial stability and monetary cooperation, which are essential to increase productivity, job creation, and economic well-being.
2. It has three critical missions:
(i) Furthering international monetary cooperation,
(ii) Encouraging the expansion of trade and economic growth, and
(iii) Discouraging policies that would harm prosperity.
Story continues below this ad
3. According to official website of IMF, “Unlike development banks, the IMF does not lend for specific projects. Instead, the IMF provides financial support to countries hit by crises to create breathing room as they implement policies that restore economic stability and growth. It also provides precautionary financing to help prevent crises.”
4. Board of Governors is the highest decision-making body of the IMF. It normally meets once a year. It consists of one governor and one alternate governor for each member country. The governor is appointed by the member country and is usually the minister of finance or the governor of the central bank.
5. All powers of the IMF are vested in the Board of Governors. The Board of Governors may delegate to the Executive Board all except certain reserved powers.
6. As per the IMF, the Executive Board is responsible for conducting the day-to-day business of the IMF. It is composed of 25 Directors, who are elected by member countries or by groups of countries, and the Managing Director, who serves as its Chairman.
Story continues below this ad
01Where does IMF get its money?
IMF funds come from three sources: member quotas, multilateral and bilateral borrowing agreements. Quotas are the IMF’s main source of financing, wherein each member of the IMF is assigned a quota, based broadly on its relative position in the world economy.
02Who is the Managing Director of IMF?
Kristalina Georgieva has been serving as Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund since October 1, 2019. She began her second term on October 1, 2024.
03What are special drawing rights (SDRs)?
The IMF lends money to the economies in peril in the form of Special Drawing Rights (SDRs), which is a basket of five currencies — US dollar, Euro, Chinese Yuan, Japanese Yen and British Pound. It can be executed in the form of loans, cash, bonds, or stock purchases.
04What is the Global Financial Stability Report?
Released by the IMF, the Global Financial Stability Report provides an assessment of the global financial system and markets and addresses emerging market financing in a global context.
It focuses on current market conditions, highlighting systemic issues that could pose a risk to financial stability and sustained market access by emerging market borrowers. It draws out the financial ramifications of economic imbalances highlighted by the IMF’s World Economic Outlook.
Post Read Questions
(1) “Rapid Financing Instrument” and “Rapid Credit Facility” are related to the provisions of lending by which one of the following? (UPSC CSE 2022)
(a) Asian Development Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
(d) World Bank
(2) ‘Global Financial Stability Report’ is prepared by the (UPSC CSE 2016)
(a) European Central Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) International Bank for Reconstruction and Development
(d) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development
Answer key
1. (b) 2. (b)
(Sources: ExplainSpeaking: Key takeaways from IMF’s latest World Economic Outlook on India, the US, and the world, Knowledge Nugget: Why IMF, its Bailouts, and Extended Fund Facility (EFF) should be in focus for your UPSC Exam)
Subscribe to our UPSC newsletter. Stay updated with the latest UPSC articles by joining our Telegram channel – Indian Express UPSC Hub, and follow us on Instagram and X.
Story continues below this ad
🚨 Click Here to read the UPSC Essentials magazine for July 2025. Share your views and suggestions in the comment box or at manas.srivastava@indianexpress.com🚨

