391
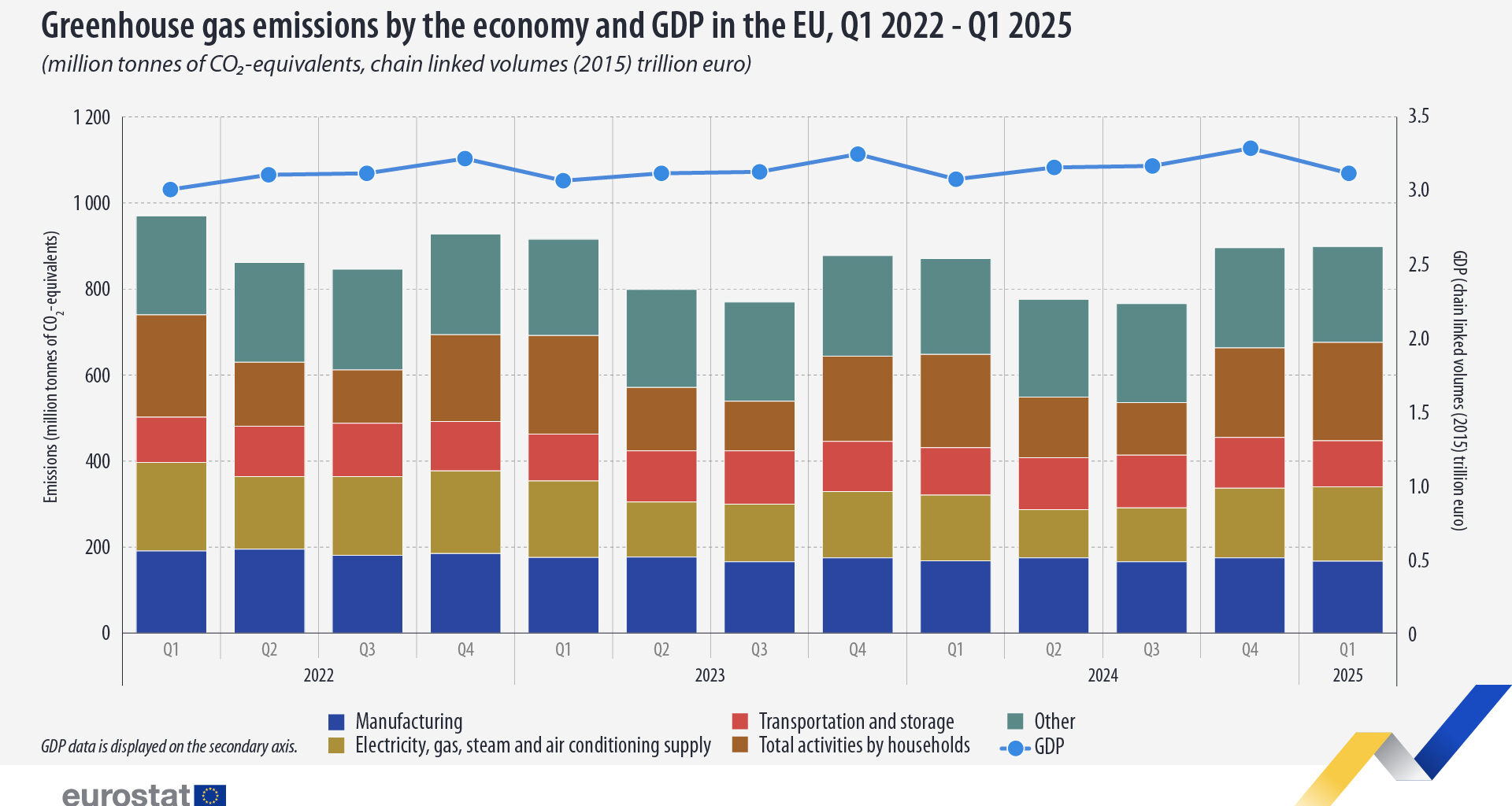
At the same time, the EU’s GDP increased by 1.2% in the first quarter of 2025, compared with the same quarter of 2024.
This information comes from data on quarterly estimates of greenhouse gas emissions by economic activity published by Eurostat.
The 2 economic sectors responsible for the largest year-on-year increases were electricity, gas, steam and air conditioning supply (+13.6%) and households (+5.6%). Three sectors decreased their emissions, namely manufacturing (-0.2%), transportation and storage (-2.9%) and agriculture, forestry and fishing (-1.4%).
In the first quarter of 2025, compared with the same quarter of 2024, increases in greenhouse gas emissions were estimated for 20 EU countries, while decreases were estimated for the remaining 7 countries.
6 countries (Bulgaria, Czechia, Cyprus, Poland, Hungary and Greece) were estimated to have increased their emissions by more than 5%.
The largest reductions in greenhouse gases were estimated for Malta (-6.2%), Finland (-4.4%) and Denmark (-4.3%). Out of the 7 EU countries that registered decreases in greenhouse gas emissions, 3 also recorded a decline in their GDP (Estonia, Latvia and Luxembourg). The other 4 EU countries (Denmark, Finland, Malta and Sweden) were estimated to have decreased emissions while growing their GDP.