Germany’s dominance in pharmaceutical exports is one of the defining features of the global life sciences economy. In 2024, Germany remained the largest exporter of medicinal and pharmaceutical products in the European Union and one of the top three in the world, competing with the United States and Switzerland. According to Germany export data and the Pharmaceutical export data of Germany, the total value of Germany pharmaceutical exports reached $124.21 billion in 2024, a 4% increase from the previous year. According to the latest Germany pharmaceutical export data, Germany exported pharmaceuticals worth $77.42 billion in the first 7 months of 2025.
Germany is the largest pharmaceutical exporter in the world, as per the global trade data. Pharmaceuticals are the 4th largest exported product category of Germany. The German pharmaceutical sector is renowned for producing high-quality medications, vaccines, and medical equipment, as well as for having robust research capacity. Germany has strengthened its position in the global healthcare industry by establishing itself as a hub for medical innovation. Major biotech and pharmaceutical firms like Bayer AG are present, which helps explain the nation’s impressive export results.
Germany’s pharmaceutical exports reached new heights in 2024-25, reinforcing its position as a cornerstone of global healthcare supply chains. The reasons behind this leadership go far beyond mere scale. Germany’s success stems from a unique combination of industrial capability, research excellence, regulatory strength, and strategic geography. The data from 2024–25 reveals how these factors continue to pay off, and what challenges Germany faces as the world’s demand for high-quality, innovative medicines evolves. In this article, we will explore Germany’s pharmaceutical export data, focusing on the top export destinations, key export trends, and market insights.
Germany Pharmaceutical Exports by Country: Where Does Germany Export Pharmaceuticals?
Germany is a prominent global player in the pharmaceutical industry, with a robust export market spanning various countries worldwide. Among the top destinations for Germany’s pharmaceutical exports are the United States, France, the United Kingdom, and China. These countries exhibit a high demand for Germany’s pharmaceutical products, known for their quality and innovation. With a reputation for high-quality products and cutting-edge research, Germany continues to be a top exporter of pharmaceuticals to countries all around the world. The top 10 export destinations for German pharmaceutical exports, as per the data on Germany pharmaceutical exports by country and Germany shipment data for 2024-25, include:
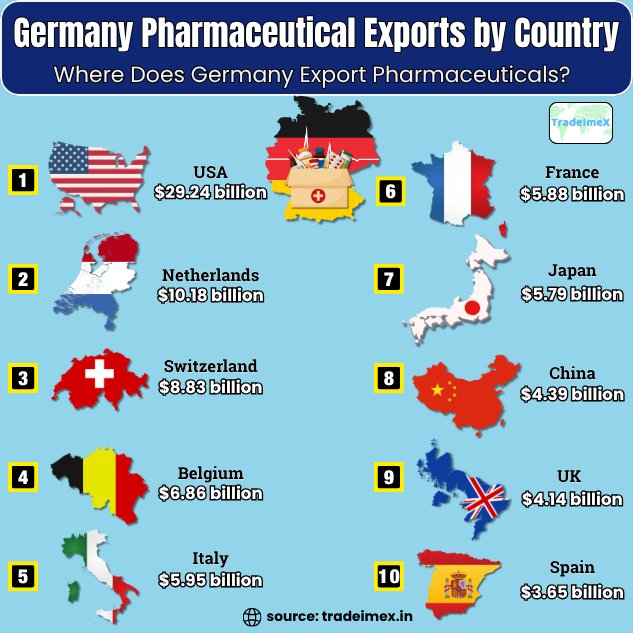
1. USA: $29.24 billion (23.5%)
The United States stands as the largest importer of pharmaceutical products from Germany, accounting for a significant portion of Germany’s pharmaceutical exports, as per the data on Germany pharmaceutical exports to the US. With a strong demand for innovative medications and healthcare products, the US market remains a crucial destination for German pharmaceutical companies.
2. Netherlands: $10.18 billion (8.2%)
The Netherlands is another key market for Germany’s pharmaceutical exports, serving as a gateway to the European market, as per the data on Germany pharmaceutical exports to the Netherlands by HS code. The proximity and strong trade relations between the two countries make the Netherlands an attractive destination for German pharmaceutical companies looking to expand their reach within the region.
3. Switzerland: $8.83 billion (7.1%)
Switzerland is renowned for its high standards in the pharmaceutical industry, making it an ideal market for German pharmaceutical exports. With a focus on innovation and quality, Swiss consumers value German-made pharmaceutical products, further solidifying Switzerland’s position as a top destination for Germany’s exports.
4. Belgium: $6.86 billion (5.5%)
Belgium serves as a strategic location for German pharmaceutical companies due to its central location within Europe. The country’s strong healthcare system and favorable business environment make it an attractive market for German pharmaceutical exports, contributing significantly to Germany’s overall export numbers.
5. Italy: $5.95 billion (4.8%)
Italy is a key player in the European pharmaceutical market, with a growing demand for German-made healthcare products. The country’s strong focus on research and development in the pharmaceutical sector makes it an important destination for Germany’s pharmaceutical exports, further strengthening the trade relations between the two nations.
6. France: $5.88 billion (4.7%)
France is a major importer of pharmaceutical products from Germany, with a diverse healthcare market that offers opportunities for German companies to expand their reach. The country’s robust regulatory framework and focus on healthcare innovation make it a valuable market for German pharmaceutical exports.
7. Japan: $5.79 billion (4.7%)
Japan stands as a key market for Germany’s pharmaceutical exports, with a sizable demand for high-quality healthcare products. The strong partnership between the two countries and Japan’s emphasis on technological advancements in the pharmaceutical industry make it a lucrative destination for German pharmaceutical companies.
8. China: $4.39 billion (3.5%)
China’s growing healthcare market presents ample opportunities for German pharmaceutical companies to increase their exports. The country’s focus on expanding its pharmaceutical industry and improving healthcare standards makes it an attractive market for Germany’s pharmaceutical products, driving growth in export numbers.
9. United Kingdom: $4.14 billion (3.3%)
Despite recent challenges in trade relations, the United Kingdom remains an essential market for Germany’s pharmaceutical exports. The strong historical ties between the two countries and the UK’s healthcare market demand for innovative products make it a key destination for German pharmaceutical companies.
10. Spain: $3.65 billion (2.9%)
Spain rounds out the list of top destinations for Germany’s pharmaceutical exports, with a growing demand for high-quality healthcare products. The country’s focus on research and development in the pharmaceutical sector and its strategic location within Europe make it an attractive market for German pharmaceutical companies.
Germany’s Pharmaceutical Export Data (2024–25)
Export Value and Growth
In 2024, Germany’s exports of medicinal and pharmaceutical products outside the European Union were valued at approximately $74.7 billion. Within the EU, Germany exported a similar magnitude, bringing total pharmaceutical exports to well over $124 billion when both intra-EU and extra-EU trade are combined.
This represents a year-on-year growth of around 12–13%, a pace that outperformed the overall EU average for pharmaceutical exports. It also reflects a strong rebound after minor slowdowns seen during 2022–23 when global supply chains were under stress due to energy costs and post-pandemic normalization.
Germany’s pharmaceutical exports account for roughly 15–17% of total global pharmaceutical trade, depending on how international re-exports (like those via Belgium and the Netherlands) are counted. Within Europe, Germany alone contributes more than one-fifth of all EU pharmaceutical exports.
Trade Surplus and Global Share
The EU as a whole ran a record trade surplus of about $213 billion in pharmaceuticals in 2024, and Germany contributed the single largest national share to that figure. Germany’s pharmaceutical trade surplus, exports minus imports, was about $49.5 billion, reflecting the country’s role as both a producer and a hub for high-value medicine exports.
Germany is also one of the world’s largest importers of pharmaceutical inputs and finished products, importing around $25 billion worth of medicines from outside the EU in 2024. These imports often consist of specialized drugs, research materials, and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) used in domestic production and re-export.
Key Export Markets
The United States remains Germany’s single largest export destination, accounting for roughly 35–40% of Germany’s extra-EU pharmaceutical exports, or around $27–30 billion in 2024. Other major markets include:
Switzerland – Approximately $8.8 billion
United Kingdom – Around $6.6 billion
China and Japan – Together, around $7.7 billion
Canada, Brazil, and Australia – Growing but smaller shares
Intra-EU exports remain very strong as well. France, the Netherlands, Italy, and Austria are major partners, not only for finished medicines but also for intermediates and raw materials.
Germany Pharmaceutical Exports in the Last 10 Years: Yearly German Pharmaceutical Export Data
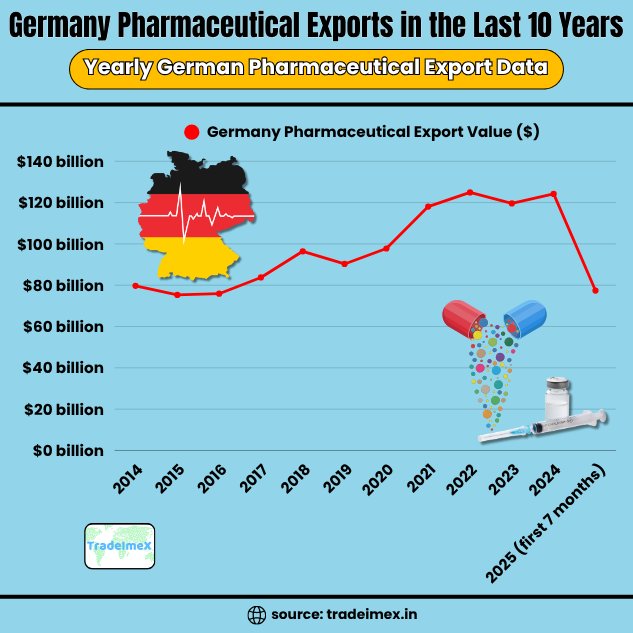
Year of Exports
Germany Pharmaceutical Export Value ($)
2014
$79.70 billion
2015
$75.29 billion
2016
$75.89 billion
2017
$83.76 billion
2018
$96.42 billion
2019
$90.29 billion
2020
$97.77 billion
2021
$118.06 billion
2022
$124.93 billion
2023
$119.60 billion
2024
$124.21 billion
2025 (first 7 months)
$77.42 billion
Top Pharmaceutical Products Exported by Germany: Germany Pharmaceutical Exports by HS Code
Germany’s top pharmaceutical products contribute significantly to the country’s pharmaceutical exports by HS Code. These high-quality pharmaceutical goods showcase Germany’s strong presence in the global market, reflecting the nation’s expertise and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. The leading pharmaceutical exports of Germany in 2024-25 include:
Medicaments consisting of mixed or unmixed products (HS code 3004): $67.19 billion
Human blood, animal blood, & antisera (HS code 3002): $49.26 billion
Pharmaceutical preparations & products of subheadings 3006.10.10 to 3006.93.00 (HS code 3006): $3.58 billion
Wadding, gauze, & bandages (HS code 3005): $1.06 billion
Medicaments consisting of two or more constituents (HS code 3003): $627.31 million
Dried glands & other organs (HS code 3001): $157.56 million
Structure of the German Pharmaceutical Industry
Industry Size and Employment
Germany’s pharmaceutical industry is among the largest in the world. As of 2024:
Total industry turnover: About $66 billion
Employment: Over 145,000 direct employees, plus an estimated 350,000 in related sectors (chemicals, logistics, healthcare services)
Number of manufacturers: Over 600 pharmaceutical companies, including global giants and mid-sized innovators
The country’s manufacturing capacity covers the full value chain, from chemical synthesis of active ingredients to finished dosage forms and biopharmaceutical production. The integration of the chemical and pharmaceutical sectors gives Germany a distinctive advantage in producing both traditional small-molecule drugs and advanced biologics.
Research and Development Spending
R&D is the backbone of Germany’s pharmaceutical competitiveness. In 2023, German pharmaceutical companies invested roughly $10.6 billion in research and development, representing around 16% of total industry revenue. This ratio is among the highest in the world.
German firms file hundreds of new pharmaceutical patents annually with the European Patent Office, ranking the country in the top three globally for pharmaceutical and biotechnology patents. The focus areas for R&D include:
Oncology and immunotherapy
Rare diseases and gene therapies
mRNA technology (following BioNTech’s success)
Neuroscience and chronic disease treatments
Germany’s R&D strength is amplified by its network of research institutions, universities, and biotech clusters, most notably in Munich, Berlin-Brandenburg, Heidelberg, and North Rhine-Westphalia.
Why Germany Leads the World in Pharmaceutical Exports
1. Deep Industrial Integration
Germany’s pharmaceutical dominance is built on a tightly integrated industrial base. The country’s powerful chemical sector provides a steady supply of intermediates, excipients, and APIs. Unlike many nations that depend heavily on imported raw materials, Germany maintains partial self-sufficiency in key inputs.
This vertical integration reduces vulnerability to global supply disruptions and allows for tight quality control throughout production. It also supports flexible manufacturing, enabling firms to respond quickly to global demand shifts, such as the surges seen during COVID-19 and in new vaccine production.
2. Advanced Manufacturing and Quality Standards
Germany’s manufacturing facilities are globally recognized for precision, safety, and efficiency. Production is governed by Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) standards, with continuous monitoring and automation across plants. German facilities are frequent reference sites for regulatory bodies such as the U.S. FDA and European Medicines Agency (EMA).
Pharmaceutical exports from Germany are often high-value, specialized products, oncology drugs, biologics, vaccines, and innovative therapies, rather than low-margin generics. This emphasis on quality over quantity drives profitability and reinforces Germany’s image as a supplier of trusted, premium medicines.
3. Regulatory Excellence and Reputation
Germany has one of the most robust pharmaceutical regulatory environments in the world. The Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices (BfArM) and Paul-Ehrlich-Institut (PEI) oversee approvals, clinical trials, and pharmacovigilance.
This regulatory credibility enhances Germany’s export reputation. Many non-EU countries automatically recognize or fast-track approvals for drugs registered in Germany or the broader EU, giving German firms a competitive export advantage.
4. Research Collaboration and Cluster Model
Germany’s success in pharmaceutical exports is also linked to its innovation clusters, regional ecosystems where universities, biotech startups, and major pharmaceutical corporations collaborate. Examples include:
Munich and Martinsried: Biotech and immunology hub
Heidelberg: Cancer research and genomics
Berlin-Brandenburg: Digital health and life sciences innovation
Frankfurt/Mainz: Home to BioNTech and several vaccine producers
These clusters combine academic research with industrial application, enabling rapid translation of discoveries into exportable pharmaceutical products.
5. Strategic Geography and Infrastructure
Located in the heart of Europe, Germany enjoys logistical advantages unmatched by most countries. Its rail, highway, and port infrastructure allows rapid transport to European partners and global shipping hubs. Air freight capacity, particularly in Frankfurt, one of the world’s leading pharmaceutical logistics airports, ensures temperature-controlled, reliable distribution worldwide.
This infrastructure was crucial during the pandemic when Germany became a central distribution node for vaccines across Europe and beyond.
6. Skilled Workforce and Technical Training
Germany’s dual education system ensures a steady pipeline of skilled professionals, from lab technicians and chemists to process engineers and quality controllers. Pharmaceutical training programs are closely aligned with industry needs, and the country’s universities produce a continuous stream of graduates in life sciences and chemical engineering.
This human capital underpins Germany’s high manufacturing standards and capacity for innovation.
7. Government Support and Policy Stability
Germany’s government views the pharmaceutical industry as a strategic pillar of its economy. Policies supporting R&D tax incentives, public funding for biotech startups, and infrastructure investment all sustain the country’s global competitiveness.
In 2024, the German government reiterated its commitment to strengthening domestic pharmaceutical production to ensure supply security, particularly in essential medicines and vaccine technologies. These initiatives not only support domestic healthcare resilience but also expand export capacity.
Global and Domestic Challenges
Germany’s dominance is not without headwinds. Several structural and global factors could challenge its leadership if not managed effectively.
1. Supply Chain Dependencies
Despite its strong manufacturing base, Germany still relies on imported raw materials and APIs, especially from China and India. Around 60–70% of the world’s API production occurs in Asia, meaning that even Germany’s advanced facilities can face bottlenecks if supply lines are disrupted. The government has acknowledged this risk and is incentivizing domestic API production through targeted subsidies.
2. Cost Pressures
High labor costs, energy prices, and environmental regulations increase the cost of production in Germany compared with Asian competitors. This limits the profitability of exporting low-margin products such as generics. As a result, Germany focuses primarily on high-value, patented, or specialty pharmaceuticals where quality outweighs cost.
3. Global Competition
Countries like Ireland, Belgium, Switzerland, and the U.S. have become formidable competitors in high-value pharmaceutical exports. Ireland, for instance, benefits from favorable tax structures that attract multinationals, while Switzerland’s pharmaceutical giants (like Roche and Novartis) dominate in biologics. Germany’s challenge is to remain competitive in innovation and production efficiency, not just scale.
4. Regulatory and Pricing Pressures
Both at home and abroad, pharmaceutical pricing is under scrutiny. In Germany, strict pricing regulations and health insurance negotiations can compress domestic margins. Internationally, export markets are increasingly imposing reference pricing and reimbursement restrictions.
5. R&D Risks
Drug discovery is inherently risky. Only about one in every 5,000 drug candidates reaches the market. With R&D costs rising, companies face long lead times and uncertain payoffs. Sustaining innovation pipelines demands continual reinvestment and government support.
Outlook for 2025 and Beyond
Continued Export Growth
All available indicators suggest that Germany’s pharmaceutical exports will continue to grow in 2025, albeit at a slightly slower pace than the 2024 surge. Export growth of 6–8% is projected, driven by new product launches and rising global demand for biologics and specialty medicines.
Expansion of Biopharma and mRNA Capabilities
Following BioNTech’s global success, Germany has become a magnet for biopharmaceutical and mRNA technology investment. Several new manufacturing sites and research centers are being built, expanding capacity for advanced biologics, vaccines, and gene therapies. These developments will solidify Germany’s position in the next generation of pharmaceutical exports.
Supply Chain Localization
To reduce dependency on foreign API suppliers, Germany is pursuing greater localization of critical drug ingredients. This is supported by EU-wide strategies to build resilience in pharmaceutical supply chains. Over time, this shift could strengthen Germany’s export independence and stability.
Sustainability and Green Production
The German pharmaceutical sector is also investing in sustainable production, reducing carbon emissions and chemical waste. As global buyers increasingly demand sustainable sourcing, this environmental focus could become another competitive differentiator for German exports.
Emerging Markets and Diversification
While the U.S. and EU remain core markets, German pharmaceutical firms are expanding exports to Asia, Latin America, and the Middle East, where healthcare spending is rising rapidly. Countries like China, Japan, and Brazil are expected to account for a growing share of German pharmaceutical exports in the coming years.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
Germany’s leadership in pharmaceutical exports in 2024–25 is the result of a powerful and deliberate combination of innovation, industrial excellence, and global trust. The numbers speak for themselves: nearly $75 billion in extra-EU pharmaceutical exports, more than $132 billion total, and a trade surplus exceeding $49 billion in this sector alone. Behind these figures lies a national system that integrates advanced science, precision manufacturing, skilled talent, and robust infrastructure. Germany’s pharmaceutical ecosystem, from BioNTech’s groundbreaking mRNA vaccines to Bayer’s chemical and biological research, is designed not just for domestic supply but for global leadership.
As the world’s demand for medicines continues to grow with aging populations, emerging diseases, and expanding healthcare access, Germany’s role as a trusted pharmaceutical supplier will remain central. Yet, maintaining this leadership will require vigilance: diversifying supply chains, managing costs, embracing sustainable production, and pushing the boundaries of medical innovation. If it succeeds in these areas, Germany is likely to remain the world’s pharmaceutical export powerhouse well beyond 2025, shaping not only the European economy but also the future of global health.
For more insights on the latest Germany import-export data, or to search live data on Germany pharmaceutical exports by country, visit TradeImeX. Contact us at info@tradeimex.in for customized trade reports, import-export database, and market insights.
Disclaimer: TradeImeX provides global trade database, including import-export data of 100+ countries and customized data report. We do NOT buy or sell any products. For purchasing or selling inquiries, please contact the actual importers/exporters listed in our database reports.
