Deep Dive delves into hot issues in Hong Kong and mainland China. Our easy-to-understand articles provide context to grasp what’s happening, while our questions help you craft informed responses. Check sample answers at the end of the page.
Rare earth minerals are crucial for many technologies, from smartphones to electric vehicles and weapons.
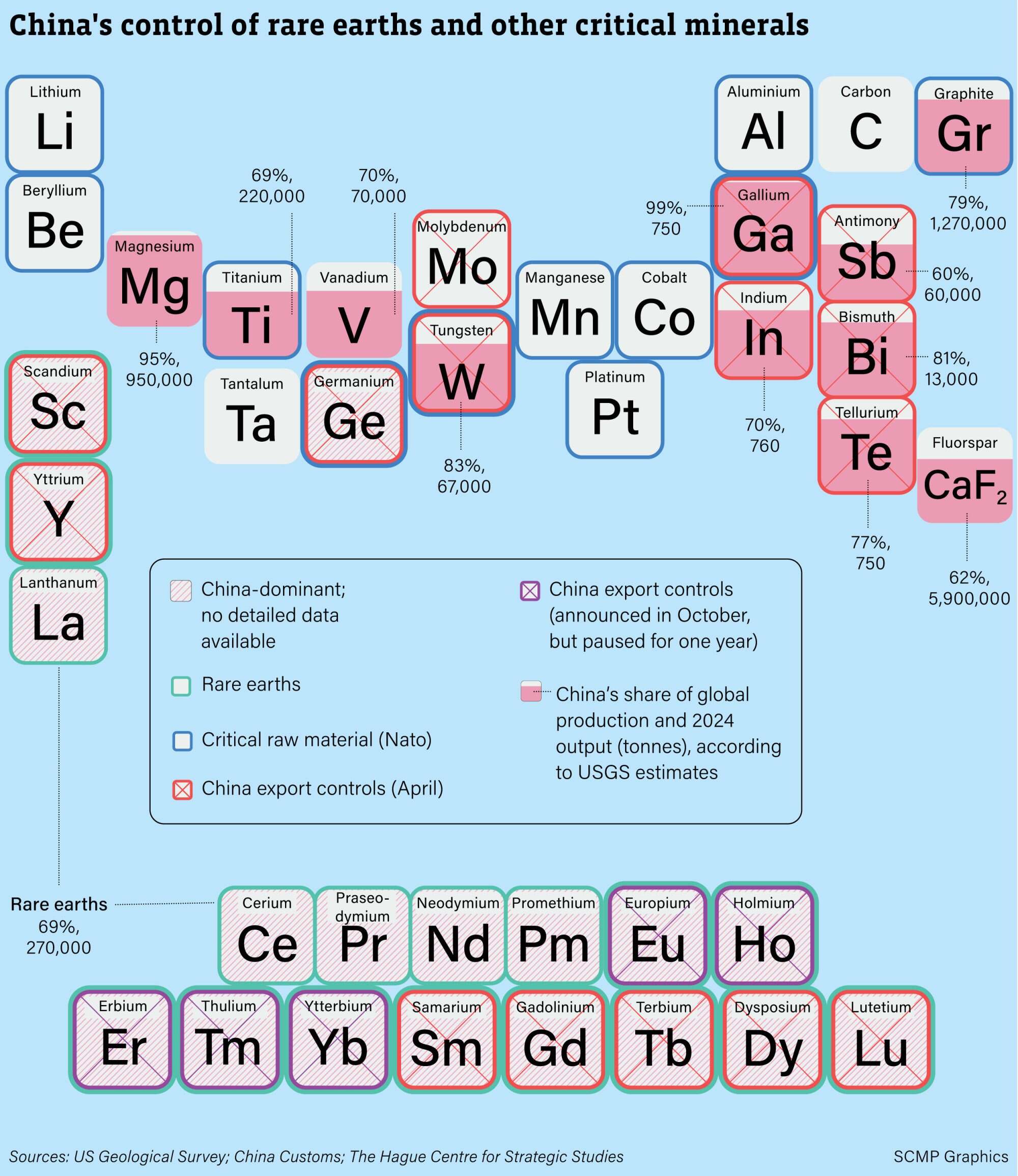
China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of rare earths and the magnets they are used for. In 2024, its reserves held about 44 million tonnes of rare earth minerals. Besides rare earths, China also has an edge in most other critical minerals. For example, China controls 98.8 per cent of global output of refined gallium.
Meanwhile, the US is a major importer of rare earths. These are needed for the country’s defence, energy, electronic, smartphone and electric vehicles industries.
The US relies on China for 70 per cent of its rare earths and 99 per cent of its heavy rare earths, according to a report published November 13 by a US-based think tank, the Council on Foreign Relations.
After US President Donald Trump imposed sweeping new tariffs on Chinese goods in April, Beijing tightened export restrictions on several key minerals. China’s exports of rare earth magnets slowed over the following months, sparking concern among Western manufacturers.
In early October, China announced more export controls related to rare earths. This expanded the scope of the previous restrictions. Analysts said the country was trying to fight off US attempts at getting a better position in the critical minerals supply chain.
But in late October, Trump and President Xi Jinping met in South Korea and reached an agreement. For one year, China would suspend the rare earth export controls it announced earlier that month.
Trump’s administration later said it hoped to secure a finalised deal on rare earths with China by Thanksgiving. This is a US holiday that falls on November 27.
With Beijing’s export restrictions, the US Department of Defence faces a growing risk to military readiness and supply chain security. China’s control in critical minerals has given the country the power to negotiate with the US amid Trump’s tariffs.
These minerals are required for various American advanced weapon systems. This includes precision-guided missiles, fighter jets, naval warships and submarines.
More than 80 per cent of the US weapons system supply chains reportedly incorporate antimony, gallium or germanium.
Staff writers
Question prompts:
List THREE uses of rare earth minerals.
Why did China tighten export restrictions on critical minerals?
How have China’s export controls on rare earths affected its negotiations with the US? Explain using News, Glossary and your own knowledge.
Graphic
Question prompts:
Which rare earth minerals are currently subject to China’s export controls?
According to the chart, which critical mineral is most dominated by China? How does this benefit China?
Glossary
rare earth minerals: a category of critical minerals used to make magnets that are crucial to vehicles, electronics and weapons. In their periodic table order, the 17 metallic elements are scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium.
tariffs: taxes on imported goods. Tariffs are paid to local governments by firms bringing in foreign goods.
refined gallium: a highly pure metal produced as a by-product from the refining of other metals. It is used in electric vehicles, solar power and the displays and batteries for devices such as laptops and phones.
Sample answers
News:
1. defense technologies, such as advanced weapon systems, precision-guided missiles, fighter jets, naval warships, submarines, and radar systems / renewable energy, such as electric vehicles / high-tech industries, including smartphones and electronics
2. China imposed stricter export controls in response to US tariffs on Chinese goods / to use its rare earths supply as a bargaining chip while negotiating with the US about its tariffs on Chinese goods / to strengthen its near-monopoly over the rare earth sector / to counter US efforts to establish its own supply chain for critical minerals (any one)
3. China’s export controls on critical minerals strengthened its bargaining power. Since the US heavily relies on Chinese rare earths for its defence, technology, and renewable energy, China’s restrictions threaten to disrupt US national security. This puts the US in a vulnerable position. China can use its dominance in critical minerals to counterbalance US geopolitical pressure. This is forcing the US to reconsider its dependency on Chinese minerals. (accept all reasonable answers)
Graphic
1. Samarium (Sm), Gadolinium (Gd), Terbium (Tb), Dysposium (Dy), Lutetium (Lu), Yttrium (Y) and Scandium (Sc)
2. China has the highest share of global production in gallium (99 per cent). By restricting these exports, China can strengthen its bargaining power in its trade war negotiations with the United States, as more than 80 per cent of the US weapons system supply chains reportedly incorporate antimony, gallium or germanium.
