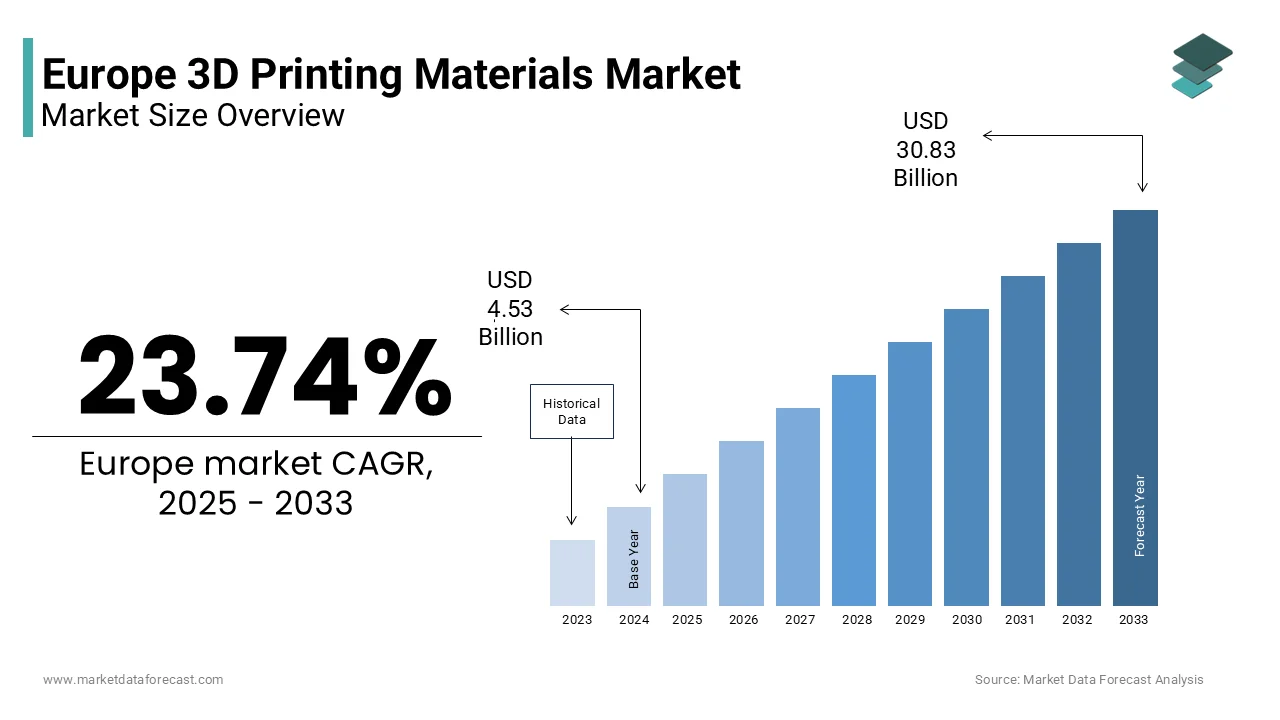
The Europe 3D printing materials market was valued at USD 4.53 billion in 2024, is expected to reach USD 5.61 billion in 2025, and is projected to surge to USD 30.83 billion by 2033, expanding at a CAGR of 23.74% during 2025–2033. Market growth is fueled by strong adoption of additive manufacturing across aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and industrial sectors, along with increasing demand for lightweight components, rapid prototyping, and advanced materials such as composites and high-performance polymers. Supportive government initiatives, expanding industrial automation, and growing investments in Industry 4.0 technologies further accelerate regional market expansion.
Key Market Trends
Rising adoption of additive manufacturing in aerospace and automotive to reduce weight, improve efficiency, and streamline production.
Growing use of advanced polymers, composites, and metal powders for high-strength, high-precision applications.
Increasing penetration of 3D printing in healthcare for implants, dental devices, and personalized medical solutions.
Expansion of industrial-scale 3D printing supported by automation, robotics, and digital manufacturing ecosystems.
Continuous innovation by material suppliers to introduce sustainable, recyclable, and bio-based 3D printing materials.
Segmental Insights
By Technology
The fused deposition modeling (FDM) segment dominated the Europe 3D printing materials market in 2024 with a 37.7% share, driven by its cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and suitability for prototyping and functional parts.
By End User Industry
The aerospace and defense segment led the market in 2024, accounting for 33.8% of the regional share, supported by demand for lightweight components, rapid prototyping, and performance-critical parts.
Regional Insights
Germany was the largest market, contributing 28.5% of Europe’s 3D printing materials market share in 2024, backed by strong industrial manufacturing, automotive leadership, and advanced engineering capabilities.
France held the second-largest share in 2024, supported by the country’s aerospace sector, government-backed innovation initiatives, and expanding industrial adoption.
Other key contributors include the UK, Italy, and Netherlands, driven by growing digital manufacturing ecosystems and wider use of additive solutions across industries.
Competitive Landscape
The Europe 3D printing materials market is highly competitive, with global and regional players focusing on material innovation, performance optimization, and expanding their industrial-grade product portfolios. Companies are investing in advanced polymers, composites, metal powders, and sustainable material alternatives to meet rising industry demand. Strategic collaborations, acquisitions, and partnerships with OEMs, aerospace firms, and manufacturing hubs are strengthening market presence across Europe.
Prominent players include Formlabs, EOS, ENVISIONTEC US LLC, American Elements, Höganäs AB, UltiMaker, Carbon Inc., KRAIBURG TPE GmbH, Covestro AG, Markforged, Stratasys, ExOne, Arkema, 3D Systems, Evonik Industries AG, Materialise, BASF SE, Sandvik AB, and Solvay.
Europe 3D printing materials Market Size
The Europe 3D printing materials market size was valued at USD 4.53 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 30.83 billion by 2033 from USD 5.61 billion in 2025, growing at a CAGR of 23.74%.
3D printing materials are consumables, including polymers, metals, ceramics and composites that are specifically engineered for additive manufacturing processes across industrial, medical, aerospace and consumer sectors. Unlike conventional raw materials, these substances are formulated to meet stringent rheological, thermal and mechanical criteria dictated by layer-by-layer fabrication technologies such as fused deposition modelling, selective laser sintering and direct metal laser melting. According to the European Commission, thousands of European enterprises utilise additive manufacturing in some capacity, with Germany, France and Italy leading industrial adoption. European manufacturers consumed significant volumes of 3D printing polymers and metal powders in 2023, which reflects robust material throughput beyond prototyping. According to the European Space Agency, a growing share of newly designed satellite components now incorporates additively manufactured parts requiring certified high-performance alloys in 2024. Furthermore, the European Medicines Agency noted that hospitals across the EU use 3D printed biocompatible materials for surgical guides and dental implants. These institutional and industrial integrations indicate that 3D printing materials have transitioned from experimental inputs to mission-critical enablers of advanced manufacturing sovereignty in Europe.
MARKET DRIVERS Expansion of Industrial Additive Manufacturing in Aerospace and Automotive Sectors
The deepening integration of 3D printing into high-value European industrial supply chains is primarily driving the 3D printing materials market growth in Europe. In aerospace, Airbus reported in 2023 that its A350 XWB aircraft contains over one thousand additively manufactured titanium and Inconel components per unit. This shift reduces part counts and cuts weight, directly enhancing fuel efficiency. Similarly, BMW Group confirmed that its iFACTORY initiative deployed hundreds of metal 3D printers across European plants in 2023 using aluminium and steel powders to produce lightweight jigs, fixtures and end-use parts. The automotive sector accounted for a significant share of industrial metal powder consumption in Europe during 2023. The European Clean Aviation Joint Undertaking allocated 220 million euros in 2024 specifically for additive manufacturing of net-zero propulsion components requiring novel high-temperature alloys. These strategic industrial commitments transform 3D printing materials from auxiliary supplies into core enablers of decarbonization performance and supply chain resilience across Europe’s advanced manufacturing base.
Regulatory Push for Sustainable and Circular Material Innovations
The stringent environmental policies of Europe are accelerating demand for recyclable bio bio-based, and low-carbon 3D printing materials, which is further boosting the 3D printing materials market growth in Europe. The European Chemicals Agency classified several conventional photopolymer resins as substances of very great concern in 2023, which is prompting a rapid shift toward certified sustainable alternatives. Bio-derived polymers such as polylactic acid from European corn starch now represent a growing share of polymer material consumption in non-industrial 3D printing applications. Closed-loop recycling systems in Dutch additive manufacturing hubs have recovered and reprocessed substantial volumes of thermoplastic waste into certified filament meeting ISO 17296 standards. Furthermore, the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan mandates that by 202,5 all publicly funded manufacturing projects must demonstrate material recyclability, which is a directive directly impacting Horizon Europe-funded initiatives in Belgium and Sweden. Companies like BASF and Arkema have responded by launching plant-based polyamides and chemically recyclable thermosets compliant with REACH and Ecolabel criteria. This regulatory ecosystem not only reduces environmental impact but also creates a competitive advantage for material suppliers aligned with Europe’s green industrial strategy.
MARKET RESTRAINTS High Cost and Limited Availability of Certified Metal and Composite Materials
The elevated price and constrained supply of qualified advanced materials remain significant restraints to broader adoption across European industries, which is primarily hampering the regional market growth. Aerospace-grade titanium powder remains significantly more expensive than commodity aluminium alloys, creating a major cost barrier. This challenge is compounded by limited domestic production, with a large share of Europe’s speciality metal powders imported from abroad. Certification further restricts availability as materials used in medical or aerospace applications require extensive validation under standards such as ASTM F3301 and ISO 13485, which is a process that can take many months. Only a limited number of European material suppliers currently hold full aerospace material certification for nickel-based superalloys. Additionally, composite filaments reinforced with carbon or glass fibre often lack batch-to-batch consistency, which leads to print failures. These economic and technical bottlenecks delay production scaling and deter small and medium enterprises from adopting high-performance additive manufacturing despite its strategic benefits.
Lack of Standardisation in Material Testing and Performance Data
The absence of harmonised testing protocols for 3D printing materials across Europe creates uncertainty in mechanical reliability and hinders cross-border industrial adoption. As per the European Committee for Standardisation, a minority of polymer and metal materials used in additive manufacturing had fully aligned EN ISO performance datasets in 2023. This fragmentation forces manufacturers to conduct redundant in-house validation, which increases time to market and development costs. As per Germany’s Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing, identical polyether ether ketone filament from different suppliers exhibited notable variation in tensile strength due to unstandardized annealing processes. In the medical sector, the lack of unified biocompatibility data delayed regulatory approval for multiple novel dental resins in 2023, according to the European Dental Association. Furthermore, national testing bodies in Italy, Spain and Poland use divergent methodologies for fatigue and creep resistance, which complicates pan-European certification. Until material properties are consistently characterised and documented under a single metrological framework, end users remain hesitant to deploy 3D printed parts in safety-critical applications despite technological readiness.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES Growth of Distributed Digital Inventory and On-Demand Spare Parts Production
The shift toward digital warehousing and on-demand spare parts manufacturing is a notable opportunity for the European 3D printing materials market. Rolls-Royce confirmed in 2024 that it maintains digital inventories for legacy aircraft components, which eliminates physical storage and enables on-demand from certified metal powders. Similarly, Siemens Energy established facilities that produce turbine repair parts using recycled metal powders, which reduces lead times. The European Defence Agency advanced additive logistics, enabling NATO forces to 3D print certified spare parts at forward bases using pre-qualified material cartridges. This model could reduce European military logistics costs significantly. Civilian applications are also expanding with Deutsche Bahn printing thousands of train interior components from flame-retardant polymers compliant with DIN 5510 standards. This transition from physical stockpiles to digital blueprints dramatically increases material turnover and creates recurring demand for certified consumables across transportation, energy and defence.
Rise of Biofabrication and Patient-Specific Medical Implants
The clinical adoption of 3D printed patient-specific medical devices is unlocking high-value opportunities for biocompatible and resorbable materials in Europe’s healthcare system and for the European market. As per the European Society of Radiology, many major European hospitals now use 3D printed surgical guides and anatomical models for pre-operative planning. In recent years, French hospitals have implanted thousands of custom cranial plates fabricated from PEEK and bioactive glass composites meeting ISO 10993 biocompatibility standards. The UK’s National Health Service launched initiatives in 2024 to scale production of patient-matched orthopaedic and dental implants using certified titanium and zirconia powders. Furthermore, the European Union’s Horizon Europe program funded multiple biofabrication projects focused on 3D printed scaffolds using collagen, hyaluronic acid and tricalcium phosphate for bone regeneration. These materials must meet exacting sterility, mechanical and degradation profiles, driving demand for high-purity medical-grade formulations. With a large and growing number of CE-marked 3D printed medical devices now active in the EU, this clinical integration establishes a premium and rapidly growing channel for advanced 3D printing materials.
MARKET CHALLENGES Supply Chain Vulnerability for Critical Raw Materials
The dependence of Europe on third countries for essential raw materials used in 3D printing powders and filaments poses a strategic challenge to material security and the European 3D printing materials market. According to the European Commission, Europe relies heavily on imports of key alloying elements such as cobalt, niobium and rare earths. The Critical Raw Materials Act identified titanium sponge and high-purity aluminium as strategic vulnerabilities, with domestic refining capacity covering only a limited share of demand. Market disruptions have previously driven sharp increases in titanium alloy powder prices. Furthermore, the lack of integrated refining and atomization infrastructure means even domestically sourced scrap often requires processing abroad, which adds logistical and geopolitical risk. The European Institute of Innovation and Technology warned that without greater vertical integration, Europe could face material shortages, delaying aerospace, medical and energy projects reliant on additive manufacturing. This systemic exposure undermines the continent’s ambition for technological sovereignty in advanced production.
Technical Barriers in Multi-Material and Functional Graded Printing
The inability to reliably process multi-material and functionally graded components limits the performance envelope of 3D printed parts and constrains material innovation, which is further challenging the expansion of the regional market. As per the Technical University of Munich, only a small share of industrial 3D printers in Europe support true multi-material deposition due to incompatibilities in melting points, thermal expansion and interfacial adhesion. Attempts to print polymer–metal hybrids often result in delamination or residual stress cracks with high failure rates in validation trials conducted by the Swiss Federal Laboratories for Materials Science in 2023. Similarly, functionally graded materials require precise control of powder mixing and laser parameters that current commercial systems cannot consistently deliver. According to the European Space Agency, project setbacks are due to inconsistent dielectric properties in printed polymer–ceramic composites. Material suppliers struggle to develop compatible material pairs because standardised interfacial testing methods do not exist. Until hardware, software, and material science co-evolve to enable seamless multi-material integration, the full potential of additive manufacturing for complex functional systems will remain unrealised in the European context.
REPORT COVERAGE
REPORT METRIC
DETAILS
Market Size Available
2024 to 2033
Base Year
2024
Forecast Period
2025 to 2033
CAGR
23.74%
Segments Covered
By Type, Form, Technology, Application, End User Industry, and Region
Various Analyses Covered
Global, Regional, & Country Level Analysis; Segment-Level Analysis; DROC, PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis; Competitive Landscape; Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities
Regions Covered
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, and the Czech Republic
Market Leaders Profiled
Formlabs (U.S.), EOS (Germany), ENVISIONTEC US LLC (U.S.), American Elements (U.S.), Höganäs AB (Sweden), UltiMaker (Netherlands), Carbon, Inc. (U.S.), KRAIBURG TPE GmbH & Co. KG (Germany), Covestro AG (Germany), Markforged, Inc. (U.S.), Stratasys (U.S.), ExOne (U.S.), Arkema (France), 3D Systems, Inc. (U.S.), Evonik Industries AG (Germany), Materialise (Belgium), BASF SE (Germany), Sandvik AB (Sweden), and Solvay (Belgium)
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS By Technology Insights
The fused deposition modelling segment held 37.7% of the European 3D printing materials market in 2024. The dominance of the fused deposition modelling segment in the European market is driven by cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and broad compatibility with engineering thermoplastics. In Germany, many small and medium enterprises use FDM printers for functional prototyping and tooling. The technology’s open material ecosystem allows users to source filaments from dozens of certified European suppliers, reducing vendor lock-in. Automotive suppliers like Bosch and Continental leverage FDM with flame-retardant and chemically resistant filaments to produce jigs and end-of-arm tooling that withstand factory floor conditions. Furthermore, leading aerospace programs have validated Stratasys’s Antero 840 FDM material for satellite applications, which is citing its outgassing resistance and electrostatic dissipation. The combination of industrial robustness, material versatility, ty and low operational barriers ensures FDM remains the backbone of polymer material consumption across Europe.
The powder bed fusion (PBF) segment is predicted to register the fastest CAGR of 22.8% over the forecast period in the European market. The escalating demand for high-performance metal and polymer components in aerospace, healthcare, and energy sectors is one of the key factors propelling the growth of the powder bed fusion segment in the European market. Airbus increased its annual consumption of titanium and aluminium PBF powders in 2023 to produce structural brackets and heat exchangers as stat ed in its sustainability and innovation report. In healthcare, European hospitals now use PBF-printed PEEK and titanium spinal implants with patient-specific geometries. European defence authorities advanced certification efforts for nickel-based superalloys used in jet engines. Additionally, innovations in multi-laser systems from companies like SLM Solutions and EOS enable higher build rates, dramatically improving economic viability. These industrial and regulatory enablers position PBF as the primary gateway for advanced material adoption in mission-critical applications.
By End User Industry Insights
The aerospace and defence segment led the market by holding 33.8% of the regional market share in 2024. The growth of the aerospace and defence segment in the European market is attributed to the industry’s uncompromising requirements for weight reduction, part consolidation, and performance under extreme conditions, which are needs uniquely met by additive manufacturing. Airbus reported that its A320neo family now integrates a large number of metal 3D printed components per aircraft, which are primarily from titanium, aluminium, scandium and Inconel 718 powders and contributo te fuel burn reduction. Rolls-Royce confirmed in 2023 that its UltraFan engine includes a major 3D printed aerospace component, which is a titanium front bearing housing manufactured via laser powder bed fusion. The European Space Agency’s Prometheus rocket engine project utilises GRCop42 copper alloy printed via PBF, which is achieving significant cost reduction and improved cooling efficiency. National defence programs in France, Germany and Sweden also deploy 3D printed radar housings and UAV components using radar-absorbing composites. The convergence of performance imperatives, regulatory acceptance and strategic autonomy makes aerospace and defence the most material-intensive and technologically advanced adopter in Europe.
The healthcare segment is the fastest growing end user segment in the Europe 3D printing materials market and is anticipated to grow at a CAGR of 25.5% over the forecast period, owing to the clinical adoption of patient-specific implants, surgical guides and bioresorbable scaffolds that require certified biocompatible materials. In 2023, French hospitals performed thousands of craniofacial reconstructions using 3D printed PEEK and bioactive glass implants meeting relevant quality and biocompatibility standards. The UK’s National Health Service established regional 3D printing hubs producing high volumes of dental aligners and orthopaedic models annually from medical-grade resins and thermoplastics. Furthermore, the European Union’s Horizon Europe program funded a consortium to develop tricalcium phosphate and collagen-based inks for bone regeneration, with human trials planned. Regulatory pathways have also matured with a large number of CE-marked 3D printed medical devices active in the EU, as confirmed by EUDAMED. This clinical integration, on regulatory clarity, and public funding create an accelerating trajectory for advanced medical materials across Europe.
REGIONAL ANALYSIS Germany Market Analysis
Germany emerged as the largest national market for 3D printing materials in Europe by accounting for 28.5% of the regional market share in 2024. The dominating position of Germany in the European market is attributed to its world-class industrial base, particularly in automotive, aerospace and machinery, where additive manufacturing is embedded in serial production. BMW Group operates a large fleet of metal and polymer 3D printers across its German plants using certified aluminium, titanium and high-temperature polymers for end-use parts, as confirmed in its production reports. The Fraunhofer network runs multiple additive manufacturing research centres that collaborate with many companies annually to qualify new materials and processes. Germany also hosts leading material producers such as Evonik and BASF, which supply high-performance polyamides and polyether ketones to global supply chains. Public investment is robust, with the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs supporting material certification and circular recycling. This ecosystem of industrial demand, technological excellence and policy support makes Germany the leading engine of Europe’s 3D printing materials innovation.
France Market Analysis
France captured the second-largest share of the European market in 2024. The growth of France in the European market is attributed to its aerospace and nuclear sectors, where 3D printing materials enable strategic autonomy and performance leadership. Airbus’s Saint Nazaire facility printed titanium structural components in 2023 for the A350 program using powders sourced from domestic supplier Aubert & Duval. The French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission developed a proprietary stainless-steel alloy for nuclear reactor parts designed to withstand radiation embrittlement and qualified for serial use. In healthcare, France leads in craniofacial reconstruction with numerous university hospitals using 3D printed PEEK and bioceramic implants. Public support is substantial, with the France 2030 investment plan dedicating significant funding to advanced manufacturing, including material development for additive processes. This fusion of high-tech industry, national security priorities and state backing cements France’s pivotal role in the European materials landscape.
Italy Market Analysis
Italy is projected to account for a prominent share of the European 3D printing materials market over the forecast period, owing to its advanced design and manufacturing culture, particularly in luxury automotive, biomedical devices and industrial machinery. Lamborghini’s Sant’Agata plant uses carbon fibre reinforced thermoplastics to 3D print lightweight ducts and brackets for its hybrid supercars, achieving notable weight savings. Italy is also a European leader in dental 3D printing, with clinics using biocompatible resins and zirconia powders for crowns and aligners. Material innovation thrives through partnerships such as the one between the Polytechnic University of Milan and CRP Technologie, which developed Windform XT 2 0 a glass fibre-filled polymer certified for aerospace use. The Italian government’s National Recovery and Resilience Plan allocated funding in 2023 to support additive manufacturing in SMEs, including material qualification grants. This blend of artisanal precision, industrial application and policy stimulus sustains Italy’s strong material consumption trajectory.
United Kingdom Market Analysis
The United Kingdom is estimated to showcase a prominent CAGR in the European 3D printing materials market during the forecast period. Despite post-Brexit challenges, the UK maintains leadership in high-value applications, particularly in aerospace and regenerative medicine. Rolls-Royce’s Derby facility printed nickel alloy turbine blades in 2023 using its proprietary powder bed fusion process, reducing material waste compared to machining. In healthcare, the Royal College of Surgeons endorsed 3D printed surgical models in a majority of major hospitals, with material use growing rapidly as per its 2024 clinical adoption survey. The UK also pioneers biofabrication with companies like 3D LifePrint producing patient-specific vascular scaffolds from collagen and hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Public funding remains active with UK Research and Innovation awarding grants in 2023 to projects focused on sustainable and medical-grade 3D printing materials. The UK’s strength lies not in volume but in high-margin innovation, making it a critical node for advanced material development in Europe.
Sweden Market Analysis
Sweden is expected to exhibit a healthy CAGR in the European 3D printing materials market during the forecast period. Sweden excels in sustainable and high-performance material solutions aligned with its green industrial strategy. Sandvik Additive Manufacturing produces atomised titanium and nickel powders using hydropower-sourced electricity and has documented low-carbon operations in sustainability audits. Volvo Construction Equipment uses recycled steel powders to 3D print hydraulic manifolds, achieving faster lead times and advancing circularity. Sweden also leads in standards development, with the Royal Institute of Technology contributing to the European Committee for Standardisation’s work on material qualification for safety-critical parts. The Swedish Energy Agency funded multiple material innovation projects in 2023, focused on bio-based polymers and low-energy processing. This commitment to sustainability, technological rigour and circularity positions Sweden as a quality-driven leader despite its modest market size.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Some of the notable key players in the European printing materials market are
Formlabs (U.S.) EOS (Germany) ENVISIONTEC US LLC (U.S.) American Elements (U.S.) Höganäs AB (Sweden) UltiMaker (Netherlands) Carbon, Inc. (U.S.) KRAIBURG TPE GmbH & Co. KG (Germany) Covestro AG (Germany) Markforged, Inc. (U.S.) Stratasys (U.S.) ExOne (U.S.) Arkema (France) 3D Systems, Inc. (U.S.) Evonik Industries AG (Germany) Materialise (Belgium) BASF SE (Germany) Sandvik AB (Sweden) Solvay (Belgium) TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PLAYERS
Key players in the European 3D printing materials market pursue several strategic imperatives to sustain leadership and drive adoption. They invest heavily in application-specific material development, collaborating directly with end users in aerospace, automotive and healthcare to qualify formulations for serial production. Companies prioritise sustainability by launching recyclable bio bio-based, and circular material systems aligned with EU regulations. Strategic partnerships with printer OEMs ensure seamless hardware material integration and co-certification. Expansion of production capacity for high-purity polymers and metal powders addresses supply chain reliability concerns. Additionally, firms establish application labs and validation centres across Europe to accelerate customer onboarding and regulatory compliance, thereby embedding their materials deeply into industrial workflows.
COMPETITION OVERVIEW
Competition in the European 3D printing materials market is defined by a dynamic interplay between global chemical giants, specialised European innovators and agile startups targeting niche applications. Unlike commodity markets, pricing is secondary to performance certification and regulatory compliance, with players competing on material properties reproducibility and application validation. BA, SF Solvay, and Evonik dominate the high-end polymer segment through decades of chemical engineering expertise, while companies like Sandvik and Heraeus lead in metal powders. The market is increasingly shaped by vertical integration as material producers partner with OEMs to co-develop end-use parts. Differentiation hinges on the ability to meet aerospace medical and automotive standards while offering sustainable and traceable supply chains. Entry barriers remain high due to capital intensity, certification timelines, and technical complexity, ty ensuring that competitors favour established players with deep R and D infrastructure and regulatory acumen.
TOP PLAYERS IN THE MARKET BASF 3D Printing Solutions, a division of BASF SE, is a global pioneer in advanced polymer materials for additive manufacturing with a strong footprint across Europe. The company contributes to the global market by developing high-performance filamentous resins, powders such as Ultrasint polyamides and Photocure photopolymers engineered for industrial durability. Recently, BASF expanded its material validation program with major aerospace and automotive OEMs in Germany and France to certify its Ultrasint GF3000 for serial production. It also launched a circular economy initiative in the Netherlands, enabling customers to return used powder for reprocessing into certified feedstock. These actions reinforce BASF’s leadership in sustainable high-grade materials and deepen integration with Europe’s industrial additive manufacturing ecosystem. Solvay Speciality Polymers is a key European innovator in high-temperature and chemically resistant 3D printing materials serving the aerospace, healthcare and energy sectors worldwide. The company is renowned for its KetaSpire PEEK and AvaSpire PAEK formulations, which meet stringent regulatory standards, including FAA and ISO 10993. In 202,3, Solvay partnered with Airbus and Siemens Energy to qualify its KetaSpire KT 880 CF10 composite for jet engine and turbine components. It also established a dedicated additive manufacturing lab in Brussels to accelerate custom development and material testing. These strategic moves enhance Solvay’s ability to deliver mission-critical materials while supporting Europe’s push for technological sovereignty in advanced manufacturing. Evonik Industries is a leading German speciality chemicals company with a focused portfolio of high-performance polymer powders and bio resins for additive manufacturing. Globally, Evonik supplies its Vestosint polyamide 12 and VESTAMID powders to major 3D printer manufacturers and industrial users across the automotive and medical sectors. To strengthen its European position, Evonik inaugurated a new high-purity PA12 production line in Marl, GermaGermany 223, doubling its capacity for additive grade materials. It also collaborated with the University Hospital of Heidelberg to develop resorbable bone scaffolds using its medical-grade PCL powder. These initiatives underscore Evonik’s dual commitment to industrial scale and cutting-edge biomedical innovation in the 3D printing materials domain. MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the European 3D printing materials market has been segmented and sub-segmented based on categories.
By Type
Plastic Metal Ceramic Others
By Form
By Technology
Stereolithography Fuse Deposition Modelling (FDM) Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) Electron Beam Melting (EBM) Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) Others
By Application
Spare Parts Dental Products Prosthetics Jewellery Glasses and Eyewear Tooling Model Making Functional Prototypes Others
By End User Industry
Automotive Aerospace & Défense Medical and Healthcare Consumer Goods Building & Construction Others
By Country
UK France Spain Germany Italy Russia Sweden Denmark Switzerland Netherlands Turkey Czech Republic Rest of Europe
