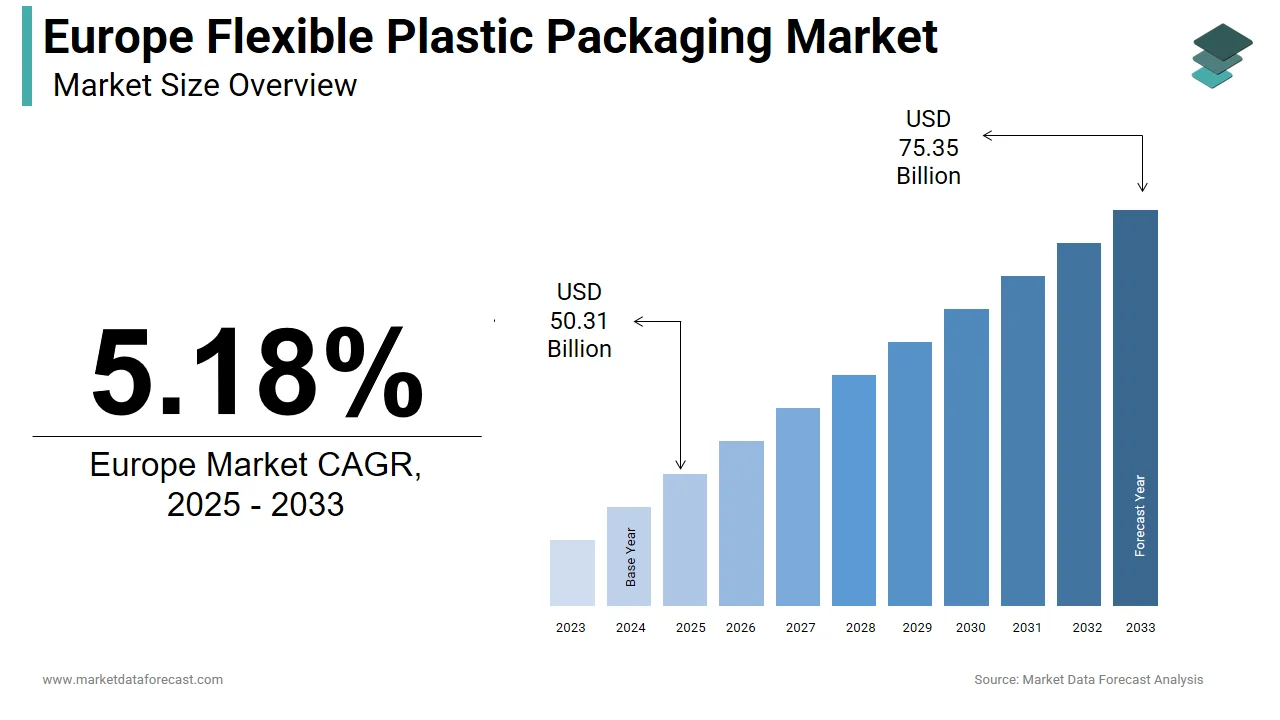
The Europe flexible plastic packaging market is transitioning toward a circular economy, projected to grow from $50.31 billion in 2025 to $75.35 billion by 2033, at a steady CAGR of 5.18%.
Market Snapshot (2025–2033)
Food & Beverage Dominance: This segment remains the primary market pillar, accounting for 55.7% of total demand as producers seek lightweight solutions to extend shelf life and reduce transport emissions.
Material Leadership: Polyethylene is the most widely used material (41.8% share), though the industry is rapidly shifting toward recyclable monomaterials to meet EU environmental mandates.
Regional Hubs: Germany is the top performer with a 22.9% market share. Italy is expected to record the highest growth (CAGR) due to its diverse manufacturing base and premium gourmet food exports.
UK E-commerce: The United Kingdom is seeing a surge in flexible packaging use driven by a highly developed e-commerce ecosystem and premium food export sectors.
Strategic Industry Trends
Sustainability-Driven Innovation: Competition is no longer based on price but on material science. Companies are investing heavily in “Circular Design” to ensure packaging is fully recyclable or compostable.
Regulatory Foresight: Market leaders are proactively aligning with the EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR), which mandates increased recycled content and waste reduction.
Product Evolution: Films and Laminates remain the largest product category (48.4% share), with innovations focusing on high-barrier properties without using non-recyclable multi-material layers.
Key Industry Leaders
The European landscape is dominated by global packaging giants and specialized innovators, including Amcor, Berry Global, Mondi, Huhtamaki, Constantia Flexibles, and Sealed Air.
Europe Flexible Plastic Packaging Market Size
The Europe flexible plastic packaging market was valued at USD 47.83 billion in 2024, is estimated to reach USD 50.31 billion in 2025, and is projected to reach USD 75.35 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 5.18% from 2025 to 2033.
Flexible plastic packaging in Europe refers to non-rigid containers and wraps, such as pouches, films, sachets, and laminates that are engineered from polyethylene, polypropylene, polyester, and bio-based polymers to protect, preserve, and present food, pharmaceuticals, personal care, and industrial goods. Unlike rigid formats, these materials offer lightweight construction, material efficiency, and adaptability to modern filling and sealing technologies. According to Eurostat, the European Union generated more than 80 million metric tons of packaging waste in 2022, with flexible plastics constituting a significant yet increasingly scrutinized share due to recycling complexities. As per the European Food Safety Authority, a substantial share of processed foods sold in the EU depends on flexible barrier packaging to maintain shelf life and reduce spoilage, underscoring its functional indispensability. According to the German Plastics Industry Association, Germany remains one of Europe’s largest users of plastic films for packaging applications, consuming several million metric tons annually. As the EU advances its Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation targeting 65 percent packaging recycling by 2025, the flexible segment faces both pressure and opportunity to innovate toward circularity, which is balancing performance with environmental accountability in a highly regulated industrial landscape.
MARKET DRIVERS Proliferation of E-Commerce and On-the-Go Consumption Patterns
The structural shift toward digital retail and mobile lifestyles has intensified demand for lightweight, durable, and resealable flexible plastic packaging across Europe, which is majorly propelling the European flexible plastic packaging market growth. According to the European Commission’s Digital Economy and Society Index, online grocery sales in the EU reached €56 billion in 2024, marking a fourfold increase since 2020. This growth necessitates packaging that withstands multiple handling points, resists puncture during transit, and maintains product integrity without refrigeration. Single‑serve formats have also surged, particularly in urban centers where 68% of consumers aged 18–35 report purchasing meals or snacks for immediate consumption outside the home, as per a 2024 Eurobarometer survey. Flexible pouches for ready meals, coffee sticks, and personal‑care samples meet this need with minimal material use and reduced logistics weight. As per the Fraunhofer Institute for Environmental Safety and Energy Technology, replacing glass jars with stand‑up pouches can cut transport emissions by up to 70% per unit. Major food brands like Nestlé and Unilever have reformulated a significant share of their European snack lines into flexible formats since 2022 to align with this behavioral shift, driving consistent demand for high-barrier metallized and multilayer films that preserve freshness while supporting convenience.
Regulatory Push for Extended Shelf Life and Food Waste Reduction
Flexible plastic packaging plays a critical role in mitigating Europe’s food‑waste crisis, which is further contributing to the European flexible plastic packaging market. The EU’s Farm to Fork Strategy explicitly encourages packaging innovations that extend product shelf life, directly favouring advanced flexible solutions with oxygen and moisture barriers. As per Wageningen University’s Food & Biobased Research division, modified‑atmosphere packaging using co‑extruded PET and polyamide films has reduced spoilage in fresh meat by up to 40% in retail settings. Vacuum‑sealed flexible packs for cheese and cured meats have also enabled shelf‑life extension from 7 to over 30 days, significantly curbing household and supply‑chain waste. Retailers such as Carrefour and Tesco now mandate minimum shelf‑life requirements for perishables, indirectly increasing reliance on high‑performance flexible films. The European Commission estimates that effective packaging could prevent 10 million metric tons of food waste annually, reinforcing policy support for functional plastics even amid broader sustainability scrutiny. This dual mandate positions flexible plastics as a pragmatic, if contested, ally in Europe’s food system transformation.
MARKET RESTRAINTS Stringent Recycling Infrastructure Limitations for Multilayer Films
Despite their functional benefits, multilayer flexible plastic packages often combining polyethylene, aluminum, and polyester face severe end‑of‑life challenges due to Europe’s underdeveloped sorting and reprocessing capabilities, which are impeding the regional market growth. According to Plastics Europe’s sustainability review, less than 6% of flexible plastic packaging was effectively recycled in the EU in 2023 because conventional mechanical recycling facilities cannot separate complex laminates. As per the European Commission’s 2023 audit of municipal waste systems, only 11 member states operate dedicated flexible‑film collection streams, with most curbside programs rejecting soft plastics due to contamination and machinery‑clogging risks. As a result, over 80% of post‑consumer flexible packaging ends up incinerated or landfilled, contradicting EU circular‑economy goals. The Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulations’ 2025 recyclability requirements now compel converters to redesign structures, yet viable mono‑material alternatives often compromise barrier performance. Companies adopting recyclable mono‑PE pouches report 15–20% higher oxygen‑transmission rates, increasing spoilage risk. This infrastructure gap imposes a critical technological and economic bottleneck and exposes brands to reputational and compliance risks under tightening Extended Producer Responsibility schemes.
Escalating Costs of Compliant and Sustainable Raw Materials
The transition toward circular and low‑carbon flexible packaging has significantly increased input costs for European converters, which is pressuring margins and slowing the adoption of eco‑friendly alternatives, and hampering the European flexible plastic packaging market growth. According to the European Bioplastics Association’s 2024 benchmark, bio‑based polyethylene derived from sugarcane costs 35–50% more than fossil‑based equivalents. As per the European Food Safety Authority, certified recycled polyethylene that meets EU food‑contact standards trades at a 28% premium due to limited supply and stringent decontamination requirements. The EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism, fully operational from 2026, will further raise resin prices by imposing levies on polymers with high embedded emissions. A 2024 study by the Institute for Energy and Environmental Research in Heidelberg estimated that compliant packaging films incorporating 30% recycled content and bio‑based layers increase production costs by 22–37%. Small and medium enterprises, which constitute 74% of Europe’s packaging converters according to Eurostat, struggle to absorb these premiums without passing costs to brand owners, many of whom resist price increases in inflation‑sensitive markets. Consequently, the economic viability of sustainable flexible packaging remains constrained, particularly for low-margin categories like dry groceries and household goods.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES Advancement of Mono Material and Recyclable Flexible Structures
Innovations in mono-material flexible packaging are unlocking new pathways to compliance with the EU’s 2030 circularity targets while preserving essential barrier functions, which is a promising opportunity in this regional market. Leading resin producers like LyondellBasell and Borealis have commercialized all polyethylene laminates that mimic the oxygen resistance of traditional polyester aluminum structures through nanocoating and additive technologies. These mono PE pouches are fully compatible with existing polyethylene recycling streams, which processed over 1.9 million metric tons in 2023 according to Plastics Europe. Brands such as Danone and Colgate Palmolive have already transitioned key product lines, yogurt tubes and toothpaste sachets respectively, to mono-material formats across Western Europe. The European Recycling Platform estimates that if 40% of flexible packaging adopts mono structures by 2027, collection and recycling rates could triple. Furthermore, the EU-funded Circular FPP project, coordinated by the Technical University of Denmark, demonstrated that advanced sorting using near infrared and AI algorithms can achieve 92% purity in post-consumer PE film recovery. These developments signal a structural shift from performance versus recyclability trade-offs toward integrated design solutions that satisfy both functional and regulatory imperatives.
Integration of Digital Watermarks for Enhanced Sorting and Traceability
Emerging digital identification technologies are poised to revolutionize the recyclability of flexible plastic packaging across Europe’s fragmented waste management landscape, which is another lucrative opportunity in this European flexible plastic packaging market. The HolyGrail 2.0 initiative, led by AIM Europe and involving over 180 companies, including Procter & Gamble and Amcor, embeds invisible digital watermarks detectable by high-speed optical sorters. In 2024, a full-scale pilot at the Veolia facility in Lommel, Belgium, achieved 95% accurate sorting of flexible film types using this technology, enabling separation of food-grade from non-food streams. As per AIM Europe, digital watermarks could boost flexible packaging recycling rates to over 30% by 2030 if deployed at scale. The European Commission has endorsed the approach under its Digital Product Passport framework, requiring traceability data for all packaging by 2034. This not only improves material recovery but also enables lifecycle transparency, which allows brands to verify recycled content claims and consumers to access disposal instructions via smartphone scans. With Germany and the Netherlands already mandating digital tagging trials in municipal waste contracts, the technology represents a systemic enabler for circularity, transforming flexible plastics from a recycling liability into a traceable, recoverable resource.
MARKET CHALLENGES Technical Trade-Offs Between Sustainability and Product Protection
The drive to eliminate problematic materials like polyvinyl chloride and metallized layers has forced difficult compromises in barrier performance, particularly for oxygen and moisture-sensitive goods, which is a major challenge to this regional market. Mono-material polyethylene structures, while recyclable, exhibit oxygen transmission rates up to 50 times higher than traditional polyester-aluminum laminates according to testing by the Fraunhofer Institute for Process Engineering and Packaging. This limitation restricts their use in premium coffee, nuts, and pharmaceutical blister packs where a shelf life below 12 months is commercially unviable. Attempts to compensate with bio-based barrier coatings often fail under high humidity conditions common in Southern Europe, leading to premature spoilage. A 2024 field study by the University of Bologna found that mono PE coffee pouches lost 22% of aroma compounds within 30 days under Mediterranean storage conditions, compared to 5% for metallized alternatives. Consequently, converters face a functional dilemma: comply with recyclability mandates at the risk of product failure, or retain high-performance laminates and incur eco-modulated fees under Extended Producer Responsibility schemes. This technical tension slows the pace of sustainable transition, especially in categories where consumer safety and regulatory compliance are non-negotiable.
Fragmented Policy Implementation Across EU Member States
Despite harmonized EU directives, divergent national transpositions of packaging regulations create operational complexity and compliance uncertainty for flexible packaging producers, which further challenges the regional market expansion. While France mandates 100% reusable or recyclable packaging by 2025 under its Anti-Waste Law, Poland has delayed implementation of Extended Producer Responsibility fees for flexible films until 2026, according to national environmental ministry decrees. Germany’s Central Agency Packaging Register requires digital registration of every packaging variant, whereas Spain relies on voluntary industry collectives like Ecoembes. This patchwork increases administrative burdens; a multinational brand must manage over 15 distinct compliance regimes for a single product line across Europe as per the European Brands Association. Furthermore, definitions of “recyclable” vary, as Italy accepts mono-material films with up to 5% additives, while the Netherlands rejects any non-pure polymer stream. These inconsistencies hinder investment in standardized sustainable solutions and fragment recycling infrastructure development. The European Court of Auditors noted in its 2024 report that regulatory asymmetry reduces cross-border packaging circularity by an estimated 18%, undermining the single market’s efficiency and delaying the sector’s collective transition toward circular design principles.
REPORT COVERAGE
REPORT METRIC
DETAILS
Market Size Available
2024 to 2033
Base Year
2024
Forecast Period
2025 to 2033
Segments Covered
By Material, Product Type, End-use Industry, and Country.
Various Analyses Covered
Global, Regional, and Country-Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, Challenges; PESTLE Analysis; Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview of Investment Opportunities
Countries Covered
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and the Rest of Europe.
Market Leaders Profiled
Amcor, Berry Global, Sealed Air, Aluflexpack AG, Bak Ambalaj Sanayi, Constantia Flexibles, Clondalkin Group, Danaflex Group, Printpack, Inc., ProAmpac Intermediate, Inc., Huhtamaki, Mondi, Sonoco Products Company, Coveris, Transcontinental Inc., and Others.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS By Material Insights
The polyethylene segment occupied 41.8% of the European flexible plastic packaging market share in 2024. The leading position of the polyethylene segment in this regional market is driven by its versatility, cost efficiency, and compatibility with circular‑economy initiatives. Polyethylene’s leadership is anchored in its suitability for primary and secondary packaging across food and e‑commerce applications. According to Eurostat, plastics remain the most widely used material in EU food packaging, with PE dominating flexible formats due to its moisture barrier, sealability, and softness. Europe’s online grocery sector, valued at tens of billions of euros annually as per the European Commission, relies heavily on PE mailers and insulated pouches to maintain product integrity during last‑mile delivery. In Germany, parcel‑delivery associations report substantial PE film usage per shipment due to protective‑wrapping requirements. PE’s compatibility with established recycling systems further strengthens its regulatory acceptance. As per the Dutch Plastics Pact, post‑consumer PE film collection rates are among the highest in Europe, which is reinforcing brand preference for PE in sustainability‑driven markets. Polyethylene is expected to maintain its dominant position over the forecast period as recycling infrastructure expands and demand for lightweight packaging intensifies.
The polypropylene segment is the fastest-growing material segment in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market and is expected to exhibit a promising CAGR of 6.14% over the forecast period. Biaxially oriented polypropylene films have gained strong traction in high‑clarity, high‑gloss applications such as chocolate wrappers, biscuit packs, and tea bags due to their stiffness, printability, and moisture resistance. According to Eurostat, Europe’s confectionery and bakery sectors continue to expand, supporting demand for high‑performance flexible packaging materials. Major food manufacturers across Europe have increasingly adopted BOPP films to improve packaging efficiency and reduce material weight. BOPP’s compatibility with solvent‑free lamination also reduces volatile‑organic‑compound emissions, aligning with EU industrial‑air‑quality directives. Additionally, advancements in plasma‑deposited oxide coatings allow BOPP to replace aluminum foil in certain dry‑food applications while maintaining barrier performance. Polypropylene is expected to grow rapidly over the forecast period as brands pursue recyclable mono‑material structures and lower‑carbon packaging alternatives.
By Product Type Insights
The films and laminates segment constituted the largest product category in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market in 2024, representing 48.4% of the European market share in 2024. Their ubiquity stems from foundational use across food, pharma, and industrial sectors. Roll stock films and laminates are essential inputs for vertical and horizontal form‑fill‑seal machines that dominate modern packaging operations. According to Eurostat, the EU food manufacturing sector operates thousands of automated packaging lines, many of which rely on co‑extruded PE/PA or PE/PET laminates for tensile strength, heat‑seal integrity, and clarity. In Germany, the food industry is one of the largest users of flexible films due to its extensive processing infrastructure. The shift toward modified‑atmosphere packaging further drives demand for multilayer films with engineered gas‑barrier properties. As per Wageningen University research, modified‑atmosphere systems significantly extend shelf life by regulating oxygen and carbon‑dioxide exchange, directly supporting EU food‑waste‑reduction objectives. Their seamless integration into high‑speed packaging lines ensures continued dominance despite sustainability pressures. Films and laminates are expected to maintain strong growth over the forecast period as shelf‑life extension and automation remain central to EU food‑processing strategies.
The pouches and sachets segment is the fastest-growing product type in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market and is anticipated to record a prominent CAGR during the forecast period. Urbanization and changing consumption habits have fuelled demand for convenient, lightweight, and resealable pouch formats across food, personal care, and detergents. According to Eurobarometer consumer surveys, a majority of EU households regularly purchase single‑serve or portion‑controlled packaged goods, reflecting a shift toward an on‑the‑go lifestyle. Stand‑up pouches for plant‑based beverages and protein shakes have seen rapid adoption, supported by wellness and fitness trends. These formats reduce material use by up to 60% compared to rigid bottles while offering superior branding surfaces. The average weight of a 1‑liter liquid pouch is significantly lower than that of a PET bottle, reducing transport emissions an increasingly important factor under EU Green Public Procurement criteria. Pouches and sachets are expected to grow rapidly over the forecast period as sustainability, convenience, and lightweighting continue to shape packaging choices across Europe.
By End‑use Industry Insights
The food and beverage segment occupied 55.7% of the European market share in 2024. The dominance of the F&B segment in this regional market is driven by stringent hygiene, shelf‑life, and logistics requirements. Flexible packaging is indispensable for extending the shelf life of perishable foods under EU food‑safety regulations. According to the European Food Safety Authority, vacuum and modified‑atmosphere packaging are essential for maintaining freshness and preventing microbial growth in meat, poultry, and seafood. In 2024, the EU processed tens of millions of metric tons of meat, each requiring substantial volumes of flexible packaging, as documented by Eurostat’s agricultural processing data. Cheese relies heavily on multilayer and aluminum‑laminated films to prevent mold and fat oxidation. As per Wageningen University’s food‑logistics research, flexible packaging plays a critical role in preventing food waste across the supply chain, supporting the EU’s Farm to Fork Strategy. The food and beverage sector is expected to retain its dominance over the forecast period as safety, shelf‑life optimization, and cold‑chain efficiency remain top priorities.
The E‑commerce segment is the fastest-growing end‑use segment for flexible plastic packaging in Europe and is likely to register a CAGR of 8.8% over the forecast period. The explosive rise of online grocery and direct‑to‑consumer models has accelerated demand for lightweight, puncture‑resistant, and insulated flexible packaging. According to the European Commission’s Digital Economy and Society Index, online grocery sales in the EU continue to grow rapidly, driven by convenience and urban consumer behaviour. Each online grocery order requires flexible films for primary wrapping and thermal protection, especially for chilled and frozen goods. Research from the University of Groningen highlights the importance of flexible materials in maintaining cold‑chain integrity during last‑mile delivery. Beyond food, direct‑to‑consumer brands in beauty, supplements, and pet care increasingly use recyclable PE mailer pouches to reduce shipping weight and dimensional space. Eurostat reports that a large share of EU urban consumers shop online weekly, reinforcing the need for durable, printable, and compact flexible mailers. E‑commerce packaging demand is expected to grow strongly over the forecast period as digital retail penetration deepens across Europe.
COUNTRY-LEVEL ANALYSIS Germany Flexible Plastic Packaging Market Analysis
Germany accounted for 22.9% of the Europe flexible plastic packaging market share in 2024. The dominance of Germany in the European market is attributed to its strong industrial base, advanced packaging machinery ecosystem, and strict regulatory oversight. These structural advantages continue to shape national consumption patterns. Germany’s food industry remains one of the largest in Europe, generating significant demand for flexible films across processed foods, bakery items, and confectionery. The country also hosts major packaging manufacturers that invest heavily in recyclable mono‑material technologies aligned with EU circularity goals. Germany’s Central Agencyfor Packaging Register enforces rigorous Extended Producer Responsibility requirements, accelerating the shift toward certified recyclable structures. National recycling systems continue to expand collection and sorting capacity for flexible plastics, reinforcing Germany’s leadership in circular packaging. With its combination of industrial capability and regulatory momentum, Germany is expected to remain the region’s most influential market.
France Flexible Plastic Packaging Market Analysis
France held a promising share of the Europe flexible plastic packaging market in 2024. The growth of France in the European market is driven by strong policy intervention, brand‑led sustainability commitments, and a mature food and beverage sector. The country’s Anti‑Waste for a Circular Economy Law continues to accelerate the transition toward recyclable and reusable packaging formats. Major French brands have publicly committed to full recyclability targets, prompting rapid conversion to mono‑material structures. France is also a leader in digital watermarking and advanced sorting trials, supported by national waste‑management agencies and major FMCG companies. The country’s large dairy, cheese, and wine industries rely on high‑barrier flexible packaging for domestic and export markets, reinforcing baseline demand. With growing household participation in soft‑plastic collection pilots and continued regulatory pressure, France is positioned to remain a frontrunner in circular packaging innovation.
United Kingdom Flexible Plastic Packaging Market Analysis
The United Kingdom occupied a prominent share of the Europe flexible plastic packaging market in 2024. The strong e‑commerce ecosystem and premium food export sector are fuelling the market growth in the UK. The UK maintains one of Europe’s highest online grocery penetration rates, driving demand for insulated pouches, protective films, and tamper‑evident formats. Premium food exports such as whisky, biscuits, and specialty seafood rely on high‑clarity laminates with advanced barrier and authentication features. The UK’s Plastic Packaging Tax has accelerated the adoption of recycled‑content materials, prompting investments in food‑grade recycled PE production. Post‑Brexit regulatory autonomy allows the UK to maintain alignment with EU food‑contact rules while introducing its own compliance mechanisms. With its blend of digital retail growth and sustainability‑driven reformulation, the UK is expected to remain a dynamic and innovation‑oriented market.
Italy Flexible Plastic Packaging Market Analysis
Italy is anticipated to record a prominent CAGR in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market during the forecast period due to its strong gourmet food exports and diverse manufacturing base. The country’s pasta, olive oil, coffee, and cured‑meat industries rely on specialized barrier films to maintain product quality and meet export standards. Italy also has a large network of artisanal food producers that use custom‑printed flexible packaging to differentiate products in local and tourist markets. The luxury fashion sector contributes additional demand through garment and accessory packaging, with increasing interest in bio‑based and compostable materials. National investment programs continue to support packaging innovation, including pilots for advanced recycling technologies. With its combination of traditional food heritage and design‑driven consumer culture, Italy is expected to maintain steady demand for high‑quality flexible packaging.
Spain Flexible Plastic Packaging Market Analysis
Spain is anticipated to account for a noteworthy share of the Europe flexible plastic packaging market over the forecast period, owing to its strong agricultural export sector and rising domestic consumption. Spain is one of Europe’s largest exporters of fresh fruits and vegetables, requiring breathable and protective flexible films for long‑distance transport. The country’s expanding e‑commerce sector continues to drive demand for insulated and lightweight packaging formats. National circular‑economy initiatives are increasing regional collection and recycling capacity for flexible plastics. Spain’s tourism sector also contributes to demand for single‑serve and convenience packaging across hospitality and foodservice channels. With its combination of export‑driven logistics and growing domestic retail activity, Spain is positioned for continued growth within Southern Europe.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
Competition in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market is characterized by rapid technological adaptation, sustainability-driven differentiation, and deep integration with brand owner sustainability goals. Leading players compete not on price but on material science expertise, regulatory foresight, and circular design capabilities. The market features a mix of global giants and regional specialists with innovation concentrated in mono-material structures, bio-based resins, and digital identification technologies. Regulatory pressure from the Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation and national EPR schemes has raised barriers to entry, favoring incumbents with established compliance systems and recycling partnerships. At the same time, brand owners increasingly demand end-to-end accountability, pushing converters to offer take-back programs, lifecycle assessments, and certified recycled content. This environment rewards agility, collaboration, and long term investment in circular infrastructure over short term cost advantages, creating a highly dynamic and technically sophisticated competitive landscape across the region.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The leading companies operating in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market include:
Amcor Berry Global Sealed Air Aluflexpack AG Bak Ambalaj Sanayi Constantia Flexibles Clondalkin Group Danaflex Group Printpack, Inc. ProAmpac Intermediate, Inc. Huhtamaki Mondi Sonoco Products Company Coveris Transcontinental Inc. TOP PLAYERS IN THE MARKET Amcor is a global leader in flexible packaging with a formidable presence across Europe, serving food, pharmaceutical, and personal care sectors through high-barrier, lightweight, and recyclable solutions. The company actively advances circular economy goals by developing mono-material structures and participating in cross-industry initiatives like CEFLEX. In 2024, Amcor launched a fully recyclable PE-based lidding film for dairy applications in partnership with a major German dairy cooperative, replacing traditional aluminum laminates. It also expanded its pilot program for digital watermarks under the HolyGrail 2.0 initiative across France and the Netherlands. These actions reinforce Amcor’s commitment to regulatory compliance, sustainability, and technical innovation while strengthening its position as a solutions partner for Europe’s leading brands. Headquartered in Austria, Constantia Flexibles is a key European player specializing in premium flexible packaging for food, healthcare, and pet care with a strong emphasis on barrier performance and recyclability. The company operates over 20 production sites across the continent and exports to more than 100 countries globally. In early 2024, Constantia introduced its “EcoLid” portfolio, aluminum-free, mono PP lidding films for ready meals, designed to meet the EU’s stringent recyclability criteria. It also invested 65 million euros in a new production line in Poland dedicated to solvent-free lamination, reducing volatile organic compound emissions. These strategic moves align with evolving EU environmental standards and enhance the company’s ability to deliver high-performance sustainable packaging at scale. Huhtamaki, a Finland-based multinational, plays a pivotal role in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market through its focus on food on the go, fiber and plastic packaging integration, and circular systems. The company supplies flexible films and pouches to quick service restaurants, coffee chains, and e-commerce brands across the region. In 2024, Huhtamaki accelerated its “Blueloop” initiative by launching a new range of recyclable PE pouches for dry foods in collaboration with French and Spanish retailers. It also established a dedicated R&D center in Germany to develop advanced barrier coatings using bio-based materials. These efforts underscore Huhtamaki’s strategy to combine functionality with circularity, ensuring relevance in a market increasingly defined by sustainability mandates and consumer accountability. TOP STRATEGIES USED BY THE KEY MARKET PARTICIPANTS
Key players in the Europe flexible plastic packaging market prioritize the development of mono-material and recyclable structures to comply with EU packaging regulations and Extended Producer Responsibility schemes. They invest heavily in research and development to create high-barrier films using bio-based or recycled content without compromising performance. Strategic participation in industry consortia such as CEFLEX and HolyGrail 2.0 enables collaborative advancement of sorting and recycling infrastructure. Companies also deepen partnerships with brand owners to co-design sustainable packaging solutions tailored to specific product needs. Additionally, they enhance digital capabilities by integrating traceability features like QR codes and digital watermarks to support the upcoming Digital Product Passport requirements and improve consumer engagement.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe flexible plastic packaging market has been segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Material
Polyethylene (PE) Polypropylene (PP) Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Others
By Product Type
Bags Pouches & Sachets Films & Laminates Tapes & Labels Tubes Others
By End-use Industry
Food & Beverage Healthcare Home Care Personal Care Agriculture E-commerce Others
By Country
United Kingdom France Spain Germany Italy Russia Sweden Denmark Switzerland Netherlands Rest of Europe
