Bristol Myers Squibb is a global biopharmaceutical leader dedicated to delivering innovative medicines across oncology, hematology, immunology, cardiovascular disease, and neuroscience. The company serves patients worldwide through a comprehensive portfolio of breakthrough therapies developed across multiple therapeutic areas.
In 2024, Bristol Myers Squibb reported annual revenue of $48.3 billion according to company earnings reports. At the end of 2024, the reports also reveal that BMS employed over 30,000 people, according to a company statement.
Although Bristol Myers Squibb does not publicly disclose precise investment amounts in AI, its commitment is evidenced by strategic partnerships. The company committed $40 billion over five years to initiatives including U.S.-based R&D and manufacturing, with portions allocated to AI and computational capabilities.
This analysis focuses on two AI use cases that directly support Bristol Myers Squibb’s business objectives:
Accelerating clinical trial operations and patient enrollment: Integrating learning and natural language processing into clinical workflows, thereby enabling real-time patient-trial matching within hospital systems
Optimizing workforce talent mobility and career development: Employing large language models analyzing employee skills to drive talent management based on transferable capabilities rather than formal credentials.
Accelerating Clinical Trial Operations and Patient Enrollment
Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS) is conducting dozens of concurrent Phase III clinical trials across multiple therapeutic areas. Industry-wide, Phase III trial costs range from $11.5 million to over $52.9 million per trial, according to a Straits Research study.
For companies of BMS’s scale managing a diverse portfolio of oncology, hematology, immunology, and cardiovascular programs, this complexity multiplies across the portfolio and manifests in two key operational challenges.
First, traditional patient enrollment process remained fundamentally fragmented and manual.
In describing the prior process in an interview with the Conference Forum, Gaelan Ritter, Head of Analytics Innovation and Digital Health at BMS, said that clinical professionals “would have to manually review the trial design and comb through patient records, whether digital on the EMR or paper records, to identify the patients that fit the trial.”
The temporal misalignment created a critical business problem. When patients were identified, the delay in communicating trial opportunities meant that treating physicians could not enroll them quickly enough before they progressed beyond optimal treatment windows.
According to Ritter, BMS’s traditional processes caused unacceptable delays for patients, and the company now aims to enroll patients within 2 weeks of patient identification.
The changes he describes represent a dramatic compression from industry norms, where median site startup times exceed nine months, according to a Jama Network Study on North American clinical trials.
Second, trial operations teams operated reactively rather than predictively.
Trial teams tracked metrics via fragmented legacy systems. According to an Accenture’s case study report, clinical trial operations at Bristol Myers Squibb were largely reactive. Trial teams lacked a unified, real-time view of their data and insights, relying instead on processes that made it difficult to anticipate issues early.
In response to these challenges, Bristol Myers Squibb partnered with Accenture to develop Workbench, a clinical trial accelerator that integrates real-time operational data and AI-driven insights to enable more proactive trial management.
But the platform’s performance depended critically on computational infrastructure capable of training large-scale AI models and processing massive clinical imaging datasets in real-time. As a result, BMS entered into a partnership with NVIDIA and its DGX SuperPOD in March 2024.
According to NVIDIA’s detailed customer story, this infrastructure provides GPUs and accelerated computing for:
Training machine learning models at scale on clinical datasets
Processing large datasets of clinical trial images (CT, MR scans, etc.)
The DGX SuperPOD enables BMS data science teams working globally in R&D to accelerate oncology research by developing foundational AI models trained on hundreds of thousands of clinical trial images. Leveraging NVIDIA MONAI and self-supervised learning approaches, these models have enhanced the speed and accuracy of image-based analysis, per NVIDIA.
According to Brian Wong, Director of Research Computing at Bristol Myers Squibb, speaking in the NVIDIA case study: “Leveraging DGX SuperPOD with Equinix’s seamless integrations with public cloud providers ensured cost-effective data movement while achieving 55% overall cost savings compared to the prior model. Our scientists can now easily adjust resources to meet workload demands, increasing nodes for large language model (LLM) training when needed and reallocating them to deep learning tasks as required.”
NVIDIA’s infrastructure enabled Workbench, a clinical trial accelerator that combines several core AI capabilities, according to Accenture’s detailed case study:
Generative AI and Large Language Models: The system translates regulatory and operational complexity into clear guidance tailored to the study context and user role.
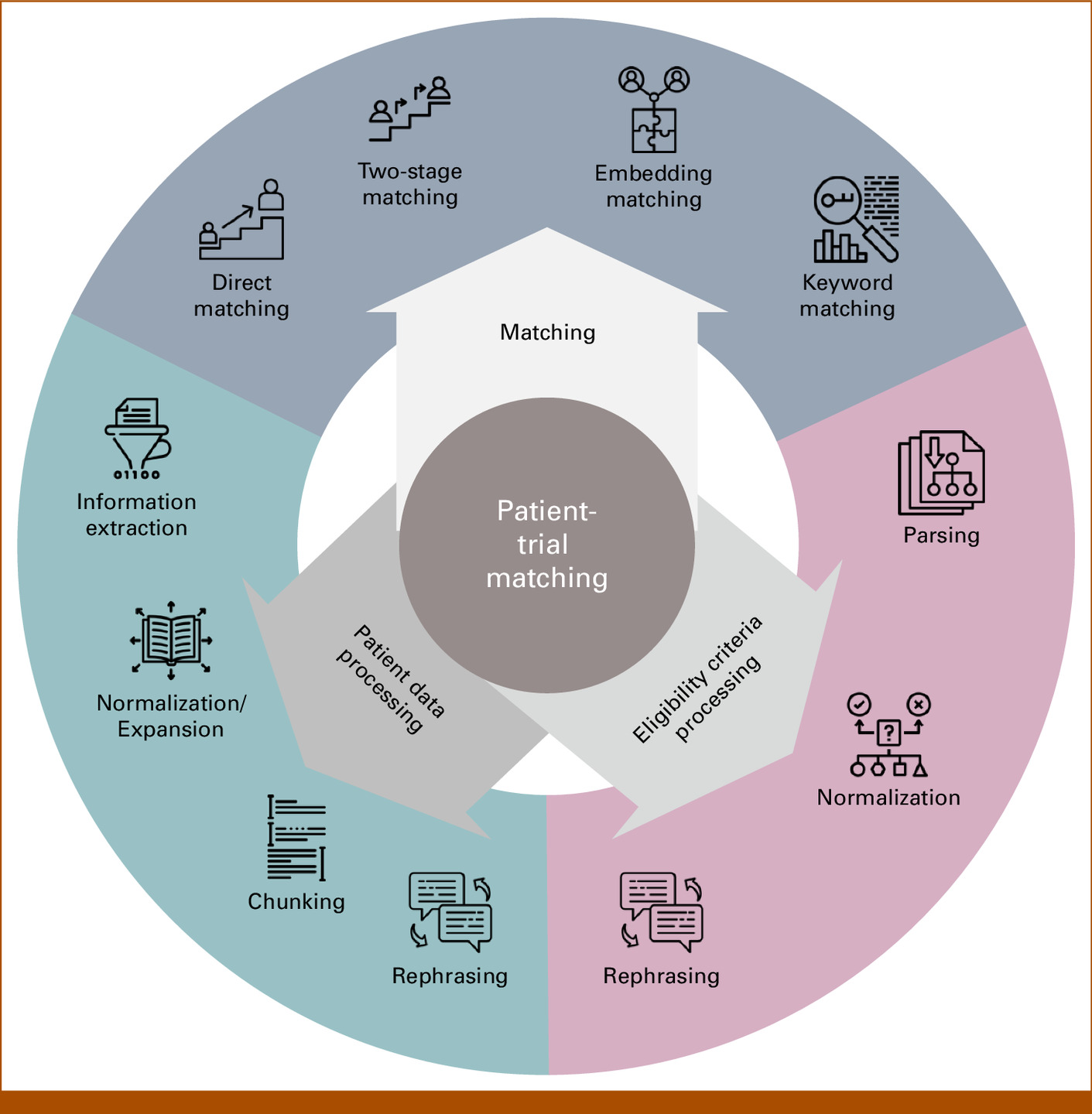
Real-World Data Integration and Trial Matching: According to Ritter, BMS leverages real-world data and predictive analytics, working with clinical systems companies to build trial-matching algorithms that run against EMR systems at patient sites. These algorithms analyze study design inclusion/exclusion criteria to flag patients in real-time when they qualify for trials.
Machine Learning for Data Conformance: According to ZS Associates’ case study, BMS implemented machine learning models trained on historical clinical studies that generate mapping and transformation recommendations using supervised and unsupervised methods. The solution was validated on test datasets of legacy studies and standardizes approximately 40 domains.
Predictive Analytics and Trial Design Optimization: According to BMS’s newsletter, Owkin’s analytical capabilities optimize endpoint definitions, patient subgroups, and treatment-effect estimation through covariate adjustment and external control arms. According to Venkat Sethuraman, SVP Global Biometrics at BMS, the company built a high-powered computing environment to simulate clinical trials without running any of them, leveraging existing datasets.
 Screenshot from American Society of Clinical Oncology research on large language models enhancing patient-trial matching workflows. (Source: ASCO)
Screenshot from American Society of Clinical Oncology research on large language models enhancing patient-trial matching workflows. (Source: ASCO)
Critically, Ritter described BMS’s target timeline transformation as identifying, then activating and enrolling patients in less than two weeks.
Ritter describes BMS’s solution as Workbench, which integrates trial matching algorithms directly into hospital EMR and CTMS workflows, automatically flagging eligible patients in real-time so treating physicians see trial opportunities without requiring separate training or platform. These are native integrations of trial awareness into existing clinical workflows. They eliminate manual chart review and dramatically reduce patient enrollment delays, enabling BMS to activate and enroll identified patients in less than two weeks.
According to Accenture’s case study, the platform also captures institutional knowledge from team experiences and shares it forward, enabling teams to learn from past trials, build trust in the system, and maintain consistency in execution across trial operations.
The platform brought the following business results for BMS:
Greater Data Integration Accuracy: Reducing the rate of false positives from 98-99% to 30%, a ~40% reduction in five years per Ritter
Clinical Data Conformance Efficiency: Reduced clinical data conformance to regulations/guidelines time by 85%, enabled a three-fold increase in conformed studies published annually, and delivered $3 million cost avoidance across three years, according to the ZS Associates’ case study
Patient Enrollment Timeline Compression: BMS now targets patient enrollment in less than two weeks.
Optimizing Workforce Talent Mobility and Career Development
Bristol Myers Squibb, like many large pharmaceutical organizations, faced a significant internal workforce challenge that was impacting organizational agility and employee retention.
According to Melissa Keiser, BMS HR leader, in an Eightfold case study, BMS faced two critical challenges: leaders complained that hiring was not happening quickly enough and that people with the right skills and qualifications weren’t being hired. Additionally, employee surveys revealed that “people were frustrated with navigating career development internally”.
The Pharma Executive reports in their study headlines that recruiting and retaining talent is the biggest challenge facing the pharmaceutical industry. SHRM data extracted by Alex Benjamin, Vice President of Talent Acquisition at OnPoint Consulting, shows that time-to-fill for healthcare and pharmaceutical positions averages 49 days — significantly longer than the 36-day average across all industries.
According to Ben Wein, Director of Workforce Skills Enablement at BMS, in a conversation with the TechWolf Podcast, earlier HR leaders and the CPO were already exploring a skills-based approach. Then in 2022–2023, a mission-critical talent shortage in BMS’s cell therapy organization became the concrete business case and pilot context for their skills-based initiative.
Wein articulates how the company chose talent acquisition as the starting point for its skills-based journey. BMS leadership eventually saw the need for a talent intelligence platform. It piloted an internal talent marketplace to address critical talent shortages, improve time-to-fill, and increase internal mobility, using skills data to inform recruiting and workforce decisions.
According to BMS’s company statement on AI-driven career tools, the company recognized that employees were requesting more opportunities to navigate career development, explore new roles, and access upskilling opportunities — but the present infrastructure to match these requests to actual opportunities did not exist at scale.
As a result, BMS partnered with Eightfold AI to develop MyGrowth, an AI-powered talent marketplace that matches employees to internal opportunities based on skills rather than traditional credentials. According to Eightfold’s case study of BMS and BMS’s own company reports, the platform combines several core AI capabilities:
Personalized Career and Development Planning: MyGrowth personalizes career and development plans by analyzing profiles and career interests, matching employees with open roles, projects, and learning and development course recommendations for the skills needed in the modern workplace.
Skills Analysis and Profile Building: The platform analyzes work experience and skills to build enhanced profiles that help managers identify suitable candidates for specific roles. BMS emphasizes that the platform empowers employees to shape their career paths by pairing their skills with open projects, new roles, or training opportunities.
Skills-Based Matching for Internal Opportunities: MyGrowth enables recruiters to match relevant skills to openings, rather than looking only for lateral or up-the-ladder moves for potential employees. The platform evolved recruiting practices to be broader and more skills-focused, looking beyond degrees.
Internal Talent Mobility: BMS integrated skills into their talent practices to foster more mobility and skill acquisition through short-term assignments, such as projects and tours of duty.
 Screenshot demonstrating natural language processing applications in human resources for extracting and analyzing employee skills from profiles and work history. (Source: Maddevs)
Screenshot demonstrating natural language processing applications in human resources for extracting and analyzing employee skills from profiles and work history. (Source: Maddevs)
Critically, according to Melissa Keiser, BMS Executive Director of Global Skills and Career Development Strategy, the paradigm shift came in the form of standardizing terms around skills that previously been colloquial and opaque:
“The feedback coming from our employees leveraging the platform and from leaders using the platform to post projects and opportunities, and how it shifted the dialogue.
It provided a different conversation than before because now you have a language around skills that gives you [answers to] ‘How do I navigate this discussion?’ when in the past it’s been very foggy and gray.”
– Melissa Keiser, Executive Director of Global Skills and Career Development Strategy at Bristol Myers Squibb
So far, BMS’s MyGrowth has already produced measurable business impacts, per EightFold’s case study:
Organizational Change Management Impact: By aligning skills visibility with opportunity visibility, BMS leaders personally attested to the public press that the platform “shifted” organizational behavior toward skills-based decision-making across recruiting, talent management, and career development practices.
Adoption Velocity and Employee Engagement: MyGrowth generated 1,000 employee profiles in the first two days of launch, with over 20% adoption on early access. The platform achieved 75% employee engagement in career development activities, substantially exceeding typical participation rates in organizational development programs.
Hiring Time Reduction and Internal Candidate Quality: During MyGrowth’s 16-week pilot phase, BMS saw reduced hiring times through skills-based matching and sourced better candidates faster than traditional methods. A 19% reduction in time-to-fill was achieved for open positions, enabling faster resource allocation to priority projects, per Eightfold’s Pathfinder Awards.
Internal Mobility and Role Filling: BMS increased internal mobility by 31% through filling open roles with internal talent, preserving institutional knowledge, and avoiding external hiring costs, per Eightfold’s Pathfinder Awards.
