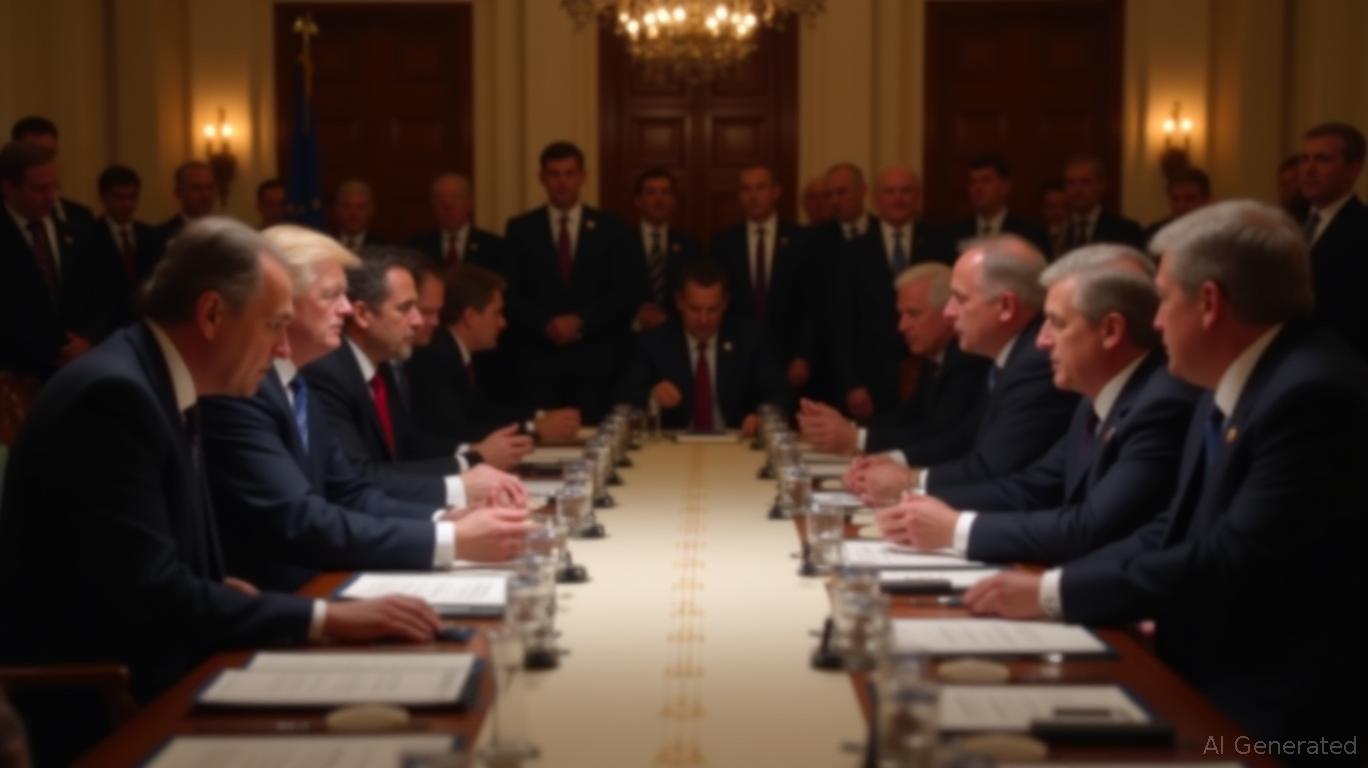
The United States and the European Union announced a landmark trade agreement on July 27, 2025, averting a potential trade war by establishing a 15% baseline tariff on most EU exports to the U.S. [1]. This compromise followed months of tense negotiations between President Donald Trump and European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen, who finalized the deal in Scotland. The agreement reduces the previously threatened 30%-50% tariffs to 15%, with the exception of steel and aluminum, which retain Trump’s existing 50% tariffs. The EU also pledged $750 billion in U.S. energy purchases and $600 billion in additional investments, marking a historic economic collaboration [2].
The deal includes mutual tariff adjustments to stabilize trade relations and address long-standing disputes. While the U.S. lowered tariffs on most goods, the EU agreed to maintain 0% tariffs on U.S. imports, creating a balanced framework for cross-border commerce [3]. President Trump emphasized the agreement’s scale, calling it “the biggest deal ever made” and highlighting its alignment with his “America First” agenda through infrastructure and technology sector growth [4]. The EU’s investment commitment, though unspecified by sector, is expected to bolster U.S. industries while ensuring European access to American markets.
Critics note unresolved tensions, such as EU subsidies for Airbus and U.S. agricultural tariffs, but the agreement prioritizes predictability over immediate resolution of all disputes. The 15% tariff structure, similar to Trump’s 2025 Japan deal, aims to balance U.S. manufacturing interests with European market access [5]. Analysts suggest the agreement could influence global markets by reducing uncertainty for businesses, though it may raise prices for EU-made automobiles and electronics in the U.S. [6]. The retention of high steel tariffs reflects ongoing U.S. concerns over trade deficits in critical industries [7].
The deal’s implications extend beyond tariffs, with analysts pointing to potential future collaboration in semiconductors and technology [8]. However, no explicit policies on digital assets or cryptocurrencies were outlined, leaving their market impact speculative. The agreement also avoids triggering the EU’s “Anti-Coercion Instrument,” a contingency tool for retaliating against economic coercion, which had been prepared earlier in July [9].
By prioritizing investment and tariff predictability over contentious sector-specific resolutions, the U.S.-EU pact signals a shift toward collaboration in a post-pandemic global economy. Its success will depend on the implementation of pledged investments and the ability to address remaining trade imbalances without reigniting tensions [10].
Sources:
[1] [Reuters](https://www.reuters.com/business/us-eu-strike-deal-with-15-tariff-avert-trade-war-2025-07-27/)
[2] [CBS](https://www.cbsnews.com/news/trump-european-union-trade-deal-reached-scotland/)
[3] [CNBC](https://www.cnbc.com/2025/07/27/trump-european-union-eu-trade-tariffs.html)
[4] [Yahoo Finance](https://finance.yahoo.com/news/live/trump-tariffs-live-updates-us-eu-agreement-announced-china-truce-extension-expected-200619379.html)
[5] [BBC](https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cx2xylk3d07o)
[6] [WKYC](https://www.wkyc.com/article/news/nation-world/us-eu-trade-deal-raise-costs-for-companies-consumers/507-686bfb59-a8c5-4f21-a19b-c17d15c8a855)
[7] [The New York Times](https://www.nytimes.com/live/2025/07/27/us/trump-news)
[8] [The Guardian](https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2025/jul/27/eu-delegation-poised-for-trump-trade-talks-in-scotland)
[9] [The New York Times](https://www.nytimes.com/live/2025/07/27/us/trump-news)
[10] [Reuters](https://www.reuters.com/business/view-reaction-us-eu-trade-deal-2025-07-27/)