Demand for vegan tuna in Japan is valued at USD 16.8 million in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 23.4 million by 2035 at a CAGR of 3.4%. The industry remains tightly linked to urban flexitarian consumption rather than mainstream household diets. Ready-to-eat toppings for rice bowls, onigiri fillings, sushi-style rolls, and salad proteins form the core product segments, with chilled and frozen formats dominating retail distribution.
Kanto and Kansai account for the highest sales density due to restaurant concentration and premium grocery penetration. Convenience stores and specialty health food chains contribute steady volume, while online platforms support trial-based demand. Domestic food innovators, plant protein specialists, and selected global alt-seafood brands shape the competitive field through private-label and co-manufactured offerings.
Quick Stats of the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan
Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan Value (2025): USD 16.8 million
Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan Forecast Value (2035): USD 23.4 million
Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035): 3.4%
Leading Source in Japan (2025): Wheat (24%)
Key Growth Regions in Japan: Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kinki, Chubu
Top Players in Japan: Good Catch Plant-Based Tuna, Sophies Kitchen Plant-Based Toona, Loma Linda TUNO, Vegan ZeaStar Tuna, Worthington Meatless Tuna
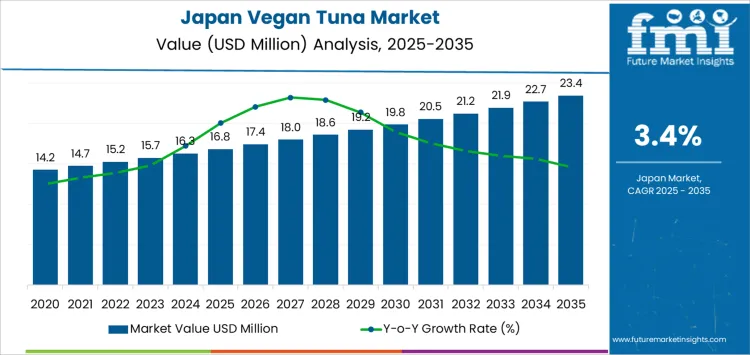
What is the Demand Forecast for Vegan Tuna in Japan through 2035?
After 2030, growth in the vegan tuna industry in Japan is driven less by ethical positioning and more by functional food substitution in prepared meals and institutional catering. Corporate cafeterias, school lunch programs, and airline catering introduce limited but recurring demand for allergen-controlled and shelf-stable alternatives. Flavor fidelity to traditional tuna remains the primary purchase trigger rather than sustainability branding.
Pricing sensitivity continues to constrain household pantry adoption, keeping most consumption within foodservice and premium retail. Regional demand spreads gradually beyond Tokyo and Osaka into Chubu and parts of Kyushu through tourism-linked dining. Competitive advantage increasingly depends on texture engineering, oil retention in rice-based dishes, and compatibility with soy sauce and vinegar profiles rather than brand-led storytelling.
The demand for vegan tuna in Japan is valued at USD 16.8 million in 2025 and reaches USD 19.2 million by 2030, reflecting a measured increase of USD 2.4 million over the first half of the forecast window. The rise from USD 14.2 million in 2020 to current levels has been shaped less by mass retail adoption and more by gradual expansion across urban food service, convenience meal producers, and specialty plant-based food outlets. The Japan vegan tuna industry is closely tied to ready-to-eat rice bowls, onigiri fillings, noodles, and sushi-style packaged meals where fish alternatives are tested in limited but repeat-use formats. Growth in this phase reflects menu extensions by food chains and controlled SKU expansion rather than volume-led supermarket penetration.
From 2030 to 2035, demand increases from USD 19.2 million to USD 23.4 million, adding USD 4.2 million in the second half of the period. The annual value additions strengthen modestly as consumption widens beyond novelty usage into routine inclusion within frozen foods, institutional catering, airline meals, and inbound tourism-driven food services. The expansion is also supported by rising seafood price volatility and supply constraints that encourage alternative protein substitution in processed meals. Product development focused on texture fidelity and umami replication strengthens repeat demand rather than trial consumption alone. By 2035, demand for vegan tuna in Japan remains niche relative to conventional seafood but becomes structurally embedded in processed food manufacturing rather than limited to lifestyle-driven consumption.
Vegan Tuna Industry in Japan Key Takeaways
Metric
Value
Industry Value (2025)
USD 16.8 million
Forecast Value (2035)
USD 23.4 million
Forecast CAGR (2025 to 2035)
3.4%
What Is Driving the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan?
The demand for vegan tuna in Japan has emerged from shifts in dietary ethics, seafood supply pressure, and changing consumer definitions of protein quality. Traditionally, tuna holds cultural and culinary importance through sushi, rice bowls, and convenience foods. Over time, overfishing concerns, seafood price instability, and food security debates created space for alternative seafood concepts.
Early demand for vegan tuna developed through specialty restaurants, plant based grocery sections, and health focused retailers in urban centers. Younger consumers and flexitarian households began to view plant based tuna not as a full replacement for seafood tradition but as a parallel option aligned with environmental and wellness priorities. Food service operators also adopted it as a way to diversify menus without supply risk tied to seasonal catch variation.
Future demand for vegan tuna in Japan will be shaped by expansion of plant based ready meals, corporate sustainability policies in food service, and export oriented development of Japanese style alternative seafood products. Convenience stores and meal kit providers will play a role in normalizing consumption beyond niche audiences. Growth will also be supported by tourist facing food outlets that seek inclusive menu formats for international dietary preferences.
Barriers include skepticism around taste authenticity, texture replication limits, and ingredient processing complexity. Supply chain scaling for plant based seafood analogs also remains capital intensive. Long term demand will depend on improvements in flavor engineering, cost parity with conventional tuna products, and broader acceptance of plant based seafood as a mainstream protein option within everyday Japanese eating habits.
What Is the Structural Breakdown of the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan by Source and Application?
The demand for vegan tuna in Japan is segmented by source and application. By source, usage includes wheat, soy based protein, seaweed, lentils, and yeast. By application, demand is distributed across other applications, salads, spreads, pies, and noodles. These segment divisions reflect how product texture, flavor carry, and protein yield influence formulation decisions across Japanese food manufacturing. Application demand is shaped by convenience food growth, foodservice volume stability, and retail readiness for plant based seafood analogs. Centralized procurement systems, strict allergen disclosure requirements, and consistent cold chain logistics define how source selection and application targeting are executed across Japan.
Why Does Wheat Dominate the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan by Source?
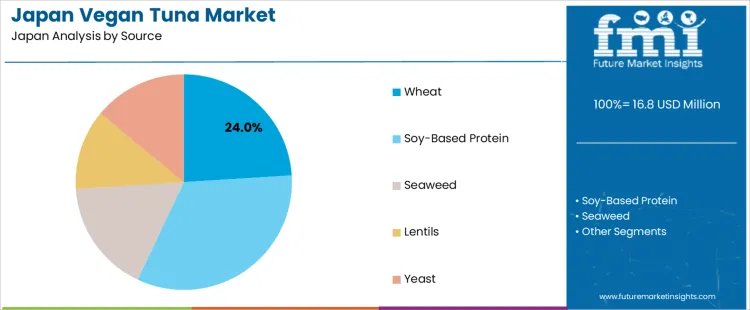
Wheat accounts for 24% of the demand for vegan tuna in Japan by source, reflecting strong alignment with domestic processed food infrastructure. Consumption intensity is driven by wheat gluten availability, neutral flavor carries, and cost stability across large scale protein texturization lines. Usage remains steady because wheat based analogs integrate easily into existing noodle, deli, and ready meal manufacturing. Procurement is contract driven through domestic milling and ingredient distributors. Price sensitivity remains moderate since texture yield and hydration performance outweigh raw input cost. Specification control centers on protein strength, allergen labeling, and moisture retention. Import dependence is limited, stability nationwide.
Wheat sourced vegan tuna contributes consistently to incremental demand in Japan due to predictable agricultural inputs and efficient domestic protein processing capacity. Repeat production runs remain high because wheat formulations perform reliably across extrusion, steaming, and retort cooking cycles. Buyers favor long term sourcing to stabilize batch hydration behavior and finished texture uniformity. Margin structure remains narrow under private label pricing discipline within convenience retail channels. Certification exposure is focused on allergen management, traceability, and food safety audits. Inventory risk remains low due to short ingredient lead times. Substitution pressure from soy and pea proteins persists, though wheat retains preference.
What Is Driving Other Applications to Lead the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan by Application?
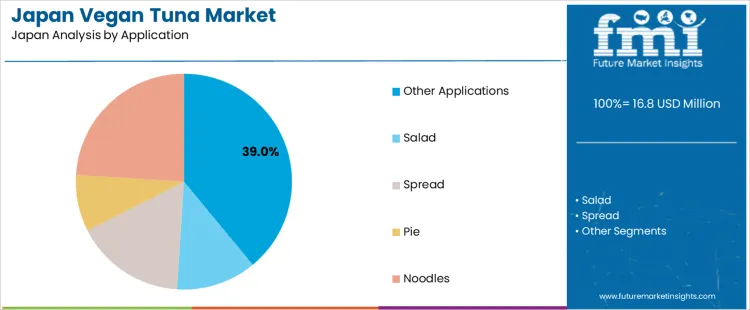
Other applications account for 39.0% of the demand for vegan tuna in Japan by application, covering ready meals, rice toppings, fillings, and institutional catering formats. Consumption intensity is driven by high volume bento production, convenience stores, airline catering, and corporate foodservice kitchens. Usage remains stable because these channels operate daily standardized menus with tight cost control. Procurement is centralized through foodservice distributors managing frozen and chilled inventory. Price sensitivity remains moderate as protein Analogs are balanced against portion cost targets. Specification control centers on flake size, water binding, and seasoning absorption. Import dependence varies by formulation but remains contracted programs.
Other applications drive recurring volume through menu rotation, seasonal promotions, and private label prepared food expansion across Japanese retailers. Repeat purchase frequency remains high because institutional customers require continuous replenishment on weekly delivery cycles. Buyers favor standardized ingredient specifications to reduce prep variability and staff training burdens. Margin structure remains tight due to competitive bidding between frozen food manufacturers. Certification exposure is shaped by school lunch standards, nursing care hygiene rules, and airline catering audits. Inventory risk is minimized through frozen logistics. Substitution pressure from plant based chicken and surimi style analogs persists, though tuna style formats retain demand nationwide.
What Is Shaping the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan Foodservice and Retail Protein Alternatives?
Demand for vegan tuna in Japan is shaped by seafood supply volatility, sustainability pressure, and changing urban consumption habits rather than by ideology alone. Tuna plays a central role in sushi, onigiri, and convenience meals, making its price and availability highly sensitive. Alternative products that replicate flake texture and umami profile are being tested by sushi chains, convenience stores, and prepared meal brands. Younger consumers in Tokyo, Osaka, and Yokohama show higher trial rates, driven by environmental awareness and health positioning. Demand is therefore developing as a functional seafood substitute within familiar formats.
How Is Seafood Supply Risk Influencing Acceptance of Tuna Alternatives?
Japan reliance on imported tuna and exposure to global fishing quotas, fuel costs, and geopolitical shipping risk are encouraging processors to evaluate alternative protein formats. Declining wild catch volumes and rising auction prices place pressure on mass sushi and ready-meal pricing. Vegan tuna offers cost stability and year-round supply independence when used in lower-priced menu items and private-label meals. It is being positioned as a buffering ingredient to protect margin rather than as a full seafood replacement. This supply-risk logic is a key structural driver of demand.
Why Are Convenience Stores and Foodservice Pilots Creating Early Commercial Traction?
Japan convenience store chains and quick-service restaurants play a central role in testing vegan tuna acceptance. Limited-time bento meals, rice balls, and salad toppings using tuna-style alternatives allow rapid consumer feedback without full menu conversion. Foodservice operators value the ease of cold storage, standardized portioning, and contamination control versus raw seafood. Urban office lunch demand supports these pilot volumes. This channel-led experimentation is creating real demand signals without requiring broad household adoption at an early stage.
How Do Cultural Food Expectations, Pricing, and Texture Limits Restrain Growth?
Demand for vegan tuna in Japan is restrained by deep cultural expectations around freshness, mouthfeel, and marine flavor authenticity. Many consumers judge tuna primarily on texture fiber and natural fat release, which plant-based versions still struggle to replicate fully. Pricing remains higher than entry-grade real tuna used in mass retail. In addition, ingredient labeling scrutiny and allergen management complicate foodservice rollout. These factors slow mainstream conversion and confine near-term demand to experimental menu formats and selected retail categories.
What is the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan by Region?
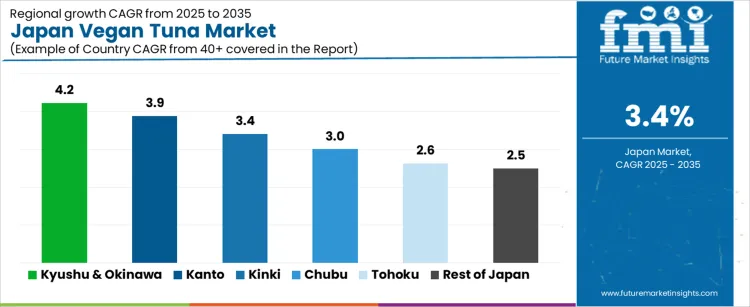
Region
CAGR (%)
Kyushu & Okinawa
4.2%
Kanto
3.9%
Kinki
3.4%
Chubu
3.0%
Tohoku
2.6%
Rest of Japan
2.5%
The demand for vegan tuna in Japan is rising steadily across regions, with Kyushu and Okinawa leading at a 4.2% CAGR. Growth in this region is supported by strong tourism driven foodservice demand, adoption by hotel and restaurant operators, and rising interest in plant based seafood alternatives. Kanto follows at 3.9%, driven by dense urban retail networks, rapid product innovation in convenience foods, and higher exposure to global food trends.
Kinki records 3.4% growth, reflecting stable demand from ready meal producers and specialty food retailers. Chubu at 3.0% shows moderate uptake linked to regional food manufacturing and private label expansion. Tohoku and the Rest of Japan, at 2.6% and 2.5%, reflect slower growth shaped by traditional seafood consumption preferences, lower penetration of alternative proteins, and limited shelf space allocation in local retail formats.
How Is Coastal Food Innovation in Kyushu and Okinawa Shaping Vegan Tuna Demand?
Demand for vegan tuna in Kyushu and Okinawa is advancing at a CAGR of 4.2% through 2035, supported by strong tourism activity, rising flexitarian diets, and seafood alternative adoption across resort foodservice and urban retail. Fukuoka and Okinawa restaurant clusters are expanding plant based menu options targeting international visitors and younger consumers. Unlike Tohoku, growth here is shaped by hospitality driven food experimentation rather than household retail alone. Vegan tuna is gaining placement in sushi alternatives, salad toppings, and ready meals supplied through hotels and specialty dining brands.
Tourism driven foodservice anchors primary demand
Sushi alternatives support menu level adoption
Urban health retail strengthens packaged product sales
Resort supply chains influence procurement volumes
What Is Driving Vegan Tuna Consumption Across Retail and Convenience Channels in Kanto?
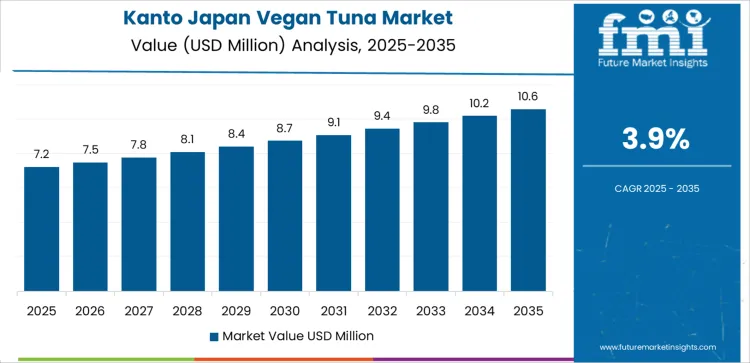
Demand for vegan tuna in Kanto is expanding at a CAGR of 3.9% through 2035, led by dense supermarket networks, convenience food expansion, and rising plant based ready meal penetration across Tokyo and surrounding prefectures. This region differs from Kyushu and Okinawa through stronger influence of mass retail rather than hospitality led consumption. Vegan tuna is increasingly used in onigiri fillings, sandwich spreads, sushi trays, and chilled deli items positioned for office workers. Large food processors and private label brands dominate packaging and distribution across metro retail corridors.
Supermarket private labels drive recurring product turnover
Convenience meals support high frequency consumption
Office lunch formats expand daily demand exposure
National processors control bulk production volumes
Why Is Regional Manufacturing Supporting Moderate Vegan Tuna Growth in Kinki?
Vegan tuna demand in Kinki is advancing at a CAGR of 3.4% through 2035, supported by regional food brands, soy processing facilities, and plant based seafood innovation in Osaka and Kyoto. Kinki contrasts with Kanto through greater reliance on local brand portfolios rather than national retail consolidation. Vegan tuna is used in bento meals, frozen entrees, pasta sauces, and mixed protein Alternatives supplied to school catering and workplace cafeterias. Growth remains tied to steady institutional food demand rather than rapid consumer driven trial cycles.
Regional brands sustain steady product demand
Bento and cafeteria meals support institutional uptake
Frozen food formats stabilize volume movement
Local soy processors shape supply availability
How Is Manufacturing and Retail Balance Influencing Vegan Tuna Adoption in Chubu?
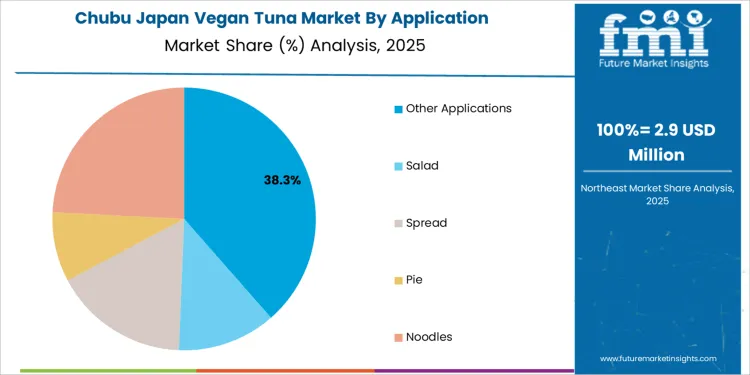
Demand for vegan tuna in Chubu is progressing at a CAGR of 3.0% through 2035, supported by balanced growth in food processing, automotive workforce catering, and suburban retail penetration around Nagoya. Unlike Kinki, this region shows stronger ties between industrial employment centers and plant based food demand. Vegan tuna is increasingly supplied into factory canteens, frozen meal kits, supermarket deli counters, and protein blended products for health oriented consumers. Procurement remains volume driven with emphasis on cost control and portion standardization.
Factory catering drives recurring meal inclusion
Frozen meal kits support controlled portion demand
Suburban retail supports gradual household adoption
Cost focused sourcing guides supplier selection
What Is Sustaining Gradual Vegan Tuna Uptake in Tohoku Household Food Markets?
Vegan tuna demand in Tohoku is increasing at a CAGR of 2.6% through 2035, supported by gradual shift toward plant based diets, public health food programs, and limited foodservice experimentation. This region differs from Kanto and Kyushu and Okinawa through lower restaurant density and slower premium food adoption. Vegan tuna is mainly used in home cooking kits, shelf stable canned alternatives, school lunch supplements, and community meal services. Budget sensitivity and limited product diversity continue to restrain faster consumption expansion.
Household cooking drives primary product usage
School meal programs support basic demand base
Shelf stable formats suit rural distribution needs
Budget sensitivity limits rapid premium product uptake
How Do Low Density Foodservice Networks Shape Vegan Tuna Demand in the Rest of Japan?
Demand for vegan tuna in the Rest of Japan is advancing at a CAGR of 2.5% through 2035, shaped by small town foodservice operators, institutional catering, and limited specialty retail. This region contrasts with Kanto and Chubu through slower product rotation and minimal exposure to trend led food innovation. Vegan tuna is primarily used in hospital meals, corporate lunches, community cafeterias, and value ready meal packs. Procurement patterns remain conservative and closely linked to distributor led menu standardization and annual supply contracts.
Institutional catering anchors baseline demand
Hospital and corporate meals support steady usage
Limited specialty retail restricts trial driven growth
Distributor contracts determine product availability
What Is Driving the Demand for Vegan Tuna in Japan and Which Brands Shape Retail and Foodservice Access
The demand for vegan tuna in Japan is shaped by flexitarian diet adoption, seafood sustainability concerns, and experimentation with alternative proteins in convenience meals and casual dining. Domestic food groups such as Otsuka Foods and Maruha Nichiro have expanded plant based seafood style products through established chilled and frozen distribution networks serving supermarkets and bento suppliers.
Fuji Oil supports formulation development through plant protein texturization used by private label operators. Good Catch Plant Based Tuna participates through imported ready to use formats supplied to natural food retailers and selected café chains in major urban centers. Sophies Kitchen Plant Based Toona serves niche consumer segments through specialty retailers focused on imported vegan products and allergen free diets.
Loma Linda TUNO and Worthington Meatless Tuna participate through distributor led access tied to health food stores and institutional foodservice channels serving schools and wellness facilities. Vegan ZeaStar Tuna supports limited foodservice trials in sushi style applications used by plant focused restaurants in Tokyo and Osaka. Procurement in Japan is guided by texture fidelity to skipjack tuna, neutral flavor profile for soy sauce and mayonnaise pairing, allergen labeling, and frozen stability.
Buyer preference favors suppliers that can demonstrate culinary compatibility with rice bowls, onigiri fillings, and pasta toppings while meeting domestic food additive and labeling standards. Demand visibility tracks younger consumer trial rates, inbound tourism dining trends, and private label experimentation by major grocery chains.
Key Players in the Vegan Tuna Industry in Japan
Good Catch Plant-Based Tuna
Sophies Kitchen Plant-Based Toona
Loma Linda TUNO
Vegan ZeaStar Tuna
Worthington Meatless Tuna
Scope of the report
Items
Values
Quantitative Units (2025)
USD million
Source
Wheat, Soy-Based Protein, Seaweed, Lentils, Yeast
Application
Other Applications, Salad, Spread, Pie, Noodles
Distribution Channel
Convenience Stores, Supermarkets, Specialty Food Stores, Online Retail
End Use
Foodservice, Retail Ready Meals, Institutional Catering, Home Cooking Kits
Regions Covered
Kyushu & Okinawa, Kanto, Kansai, Chubu, Tohoku, Rest of Japan
Key Companies Profiled
Good Catch Plant-Based Tuna, Sophies Kitchen Plant-Based Toona, Loma Linda TUNO, Vegan ZeaStar Tuna, Worthington Meatless Tuna
Additional Attributes
Dollar by sales by region, source, application, and distribution channel; growth projections through 2035; penetration in convenience and specialty retail; adoption in foodservice and institutional meals; chilled and frozen format distribution; texture fidelity to conventional tuna; functional protein substitution; cold chain logistics and allergen compliance; brand and private label participation; pilot menu integration and repeat usage; import dependence for select plant protein bases; pricing sensitivity and premium positioning; culinary compatibility with rice bowls, onigiri, and salads
Vegan Tuna Industry in Japan Segmentation
Source:
Wheat
Soy-Based Protein
Seaweed
Lentils
Yeast
Application:
Other Applications
Salad
Spread
Pie
Noodles
Distribution Channel:
Convenience Stores
Supermarkets
Specialty Food Stores
Online Retail
Region
Kyushu & Okinawa
Kanto
Kansai
Chubu
Tohoku
Rest of Japan
The demand for vegan tuna in Japan is estimated to be valued at USD 16.8 million in 2025.
The market size for the vegan tuna in Japan is projected to reach USD 23.4 million by 2035.
The demand for vegan tuna in Japan is expected to grow at a 3.4% CAGR between 2025 and 2035.
The key product types in vegan tuna in Japan are wheat, soy-based protein, seaweed, lentils and yeast.
In terms of application, other applications segment is expected to command 39.0% share in the vegan tuna in Japan in 2025.
