Europe Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing Market Size
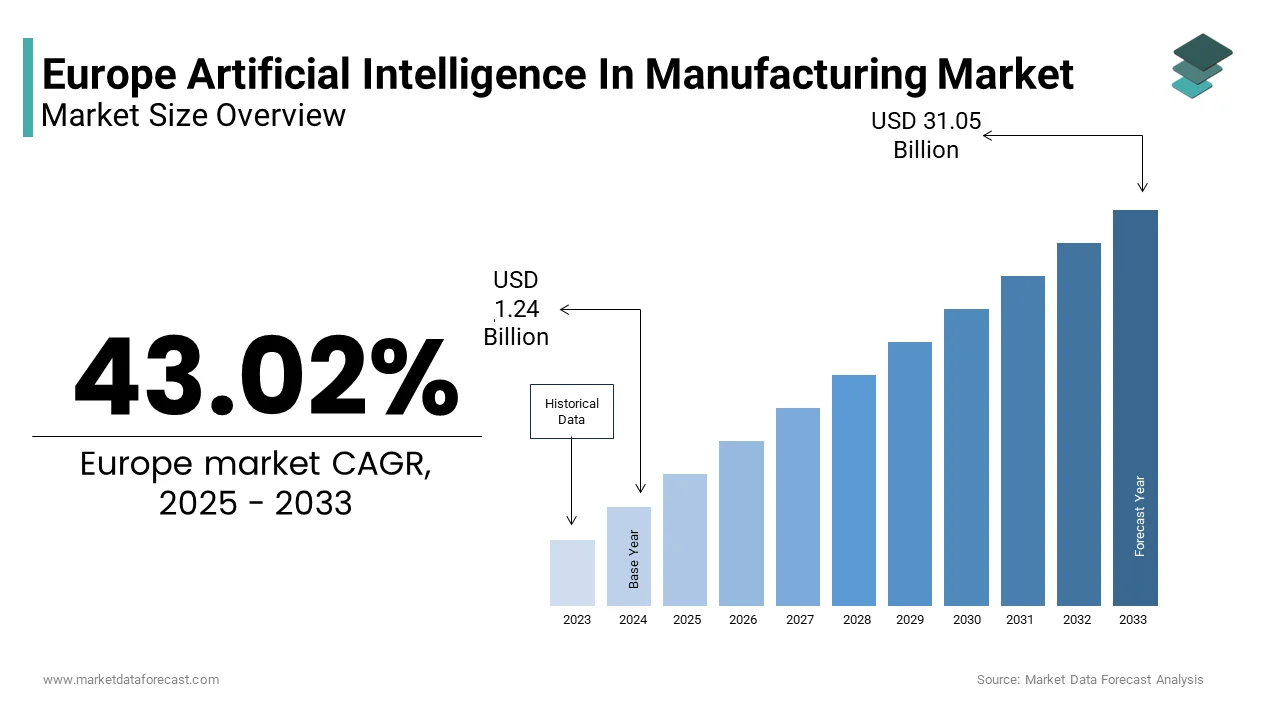
The Europe Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Manufacturing market size was valued at USD 1.24 billion in 2024 and is anticipated to reach USD 1.77 billion in 2025 and USD 31.05 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 43.02% during the forecast period from 2025 to 2033.
Current Introduction of the Europe Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing Market
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Manufacturing refers to the deployment of machine learning, computer vision, natural language processing, and predictive analytics to optimize production processes, enhance asset reliability, ensure quality control, and enable adaptive supply chains. Unlike generic automation, AI introduces cognitive capabilities that allow systems to learn from operational data and make real-time decisions without explicit programming. According to sources, the European Union encourages the widespread adoption of artificial intelligence in industrial sectors, huge manufacturing enterprises, through initiatives like the Industrial Digitalisation strategy under the Digital Europe Programme. Besides, as per research, the European Union promotes the integration of artificial intelligence technologies across manufacturing sectors, which supports general industry trends of seeking improvements in operational efficiency and energy consumption. The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) emphasizes the necessity of secure artificial intelligence deployment within operational technology networks as a critical element of the EU’s technological and strategic autonomy. The EU AI Act employs a risk-based framework, which has led manufacturers to prioritize the development of transparent, human-centric, and auditable AI systems. This convergence of industrial policy, technological readiness, and regulatory clarity positions artificial intelligence not as a peripheral innovation but as a core enabler of Europe’s resilient, sustainable, and sovereign manufacturing future.
MARKET DRIVERS EU Industrial Strategy Mandates for Digital and Green Twin Transition
The European Commission’s twin transition agenda, simultaneously advancing digitalization and decarbonization, contributes to the growth of the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market. This has made AI adoption a strategic imperative for manufacturers seeking public funding and regulatory alignment. A majority of manufacturing projects recently approved under a major innovation funding initiative incorporated AI components focused on energy efficiency or maintenance strategies aimed at meeting emissions reduction targets. New regulatory requirements directly connect the deployment of AI-enabled process control, specifically for resource efficiency, to state aid eligibility for critical clean technology producers. Pilot programs across certain member states have demonstrated that using AI for yield optimization in energy-intensive plants can significantly reduce raw material waste. Substantial funding has been dedicated to establishing AI testing facilities specifically for manufacturing applications, with numerous operational innovation hubs now active across member states. This policy-driven integration ensures AI is no longer optional but a prerequisite for accessing capital, complying with sustainability mandates, and participating in EU-backed industrial ecosystems.
Escalating Labor Shortages in Skilled Industrial Workforce
Persistent shortages of qualified technicians and engineers across European manufacturing are accelerating AI adoption as a force multiplier for human expertise, which further propels the expansion of the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market. According to research, the European Union and specific member states like Germany face persistent labor and skills shortages in the manufacturing sector and related industries, driven by structural issues, demographic changes, and skills mismatches. This gap is particularly acute in maintenance and quality assurance, where experience-based judgment is critical. In addition, Companies in the manufacturing industry are increasingly deploying AI-powered visual inspection systems to enhance quality control and defect detection processes. Furthermore, Manufacturers are increasingly adopting AI-driven augmented reality and other digital technologies as training tools to help new technicians learn complex assembly and repair tasks. The European Commission’s Pact for Skills further incentivizes such deployments through co-funded reskilling initiatives that pair AI tools with human upskilling. This symbiotic approach transforms AI from a replacement technology into a cognitive support layer, enabling leaner teams to maintain productivity amid demographic decline.
MARKET RESTRAINTS Fragmented Data Infrastructure Across Legacy Production Systems
Many European manufacturers operate heterogeneous machinery fleets spanning multiple decades, which creates significant barriers to the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market. This is due to incompatible data protocols and absent real-time telemetry. Many production lines, particularly within Tier 2 and Tier 3 suppliers, face challenges with data availability and lack the sensor infrastructure necessary for advanced data analytics and machine learning applications. A significant portion of existing manufacturing equipment across various enterprises, including large ones, does not have standardized connectivity (such as OPC UA), requiring custom solutions like retrofitting or the use of edge gateways. The lack of standardized connectivity and resulting data fragmentation often leads to increased costs and implementation delays for AI and digital transformation projects in the manufacturing sector. National initiatives like Germany’s Plattform Industrie 4 0 have promoted interoperability standards, but adoption remains uneven, particularly in Southern and Eastern Europe. The inability to access and unify data uniformly prevents AI models from achieving the necessary scale for effective, organization-wide implementation, thereby restricting innovation to limited testing environments.
Stringent Interpretability Requirements Under the EU AI Act
The high-risk classification for most manufacturing AI within the EU’s regulatory framework introduces stringent requirements for human supervision and transparency, which hampers the growth of the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market. This poses significant hurdles for the use of complex architectures such as deep neural networks. European Union regulations, specifically the EU AI Act, mandate stringent transparency and interpretability requirements for high-risk AI systems in safety-critical industrial applications, ensuring human oversight can effectively monitor and interpret AI-generated outcomes. This requirement challenges the use of black box algorithms that offer high accuracy but limited explainability. The manufacturing industry faces significant challenges and caution in integrating AI technologies due to complexities in validating model logic, addressing ethical concerns, and ensuring regulatory compliance. Vendors are responding with hybrid approaches, such as symbolic AI layered atop neural networks, but these often sacrifice performance. The regulatory emphasis on algorithmic accountability thus creates a tension between predictive power and compliance, particularly in sectors like aerospace and medical devices, where certification bodies demand causal justifications for automated decisions. This legal framework, while protective, slows adoption compared to regions with more permissive AI governance.
MARKET OPPORTUNITIES Integration of AI in Circular Manufacturing and Remanufacturing Workflows
The region’s command in circular economy policy is creating novel AI applications for reverse logistics, component recovery, and material traceability in remanufacturing, and thereby is expected to fuel the growth of the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market. Under the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation, manufacturers must ensure product reparability and material recovery, tasks increasingly managed by AI vision and robotic sorting systems. The implementation of automated disassembly systems has improved the precision with which reusable components are identified from electric vehicle systems. Artificial intelligence facilitates more effective quality grading of returned textiles, leading to higher rates of material recovery. Digital product passports are expected to utilize intelligent data processing to evaluate the history and remaining lifespan of electronic devices. The growing number of EU member states funding circular economy clusters highlights AI’s role as the enabling infrastructure for sustainable manufacturing, allowing for the systematic conversion of waste into valuable, verified resources and introducing new business paradigms centered on product-as-a-service and product reuse. AI-Driven Reshoring of Strategic Production Through Adaptive Automation
Geopolitical instability and supply chain vulnerabilities are prompting European governments to incentivize the reshoring of pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and clean tech, with AI serving as a key enabler of flexible, small-batch domestic manufacturing. This provides new prospects for the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market. According to sources, the integration of AI in advanced manufacturing facilitates faster production line reconfigurations compared to traditional methods, enhancing the economic viability of local manufacturing for specialized, low-volume, high-value goods. The Chips Act and Critical Raw Materials Act both allocate funding for AI-integrated pilot lines. As per research, the semiconductor industry is increasingly leveraging advanced automation techniques, including AI and machine learning, to automate and calibrate manufacturing equipment, particularly in new packaging and testing facilities, to manage complex designs and enhance efficiency. Besides, as per various studies, AI technology supports the ongoing industry shift towards “batch size one” (mass customization) production, which can significantly lower the minimum order requirements for highly customized products, such as medical devices, enabling more efficient local and regional sourcing. This convergence of strategic autonomy, adaptive automation, and public investment positions AI not merely as an efficiency tool but as a foundational technology for Europe’s industrial sovereignty.
MARKET CHALLENGES Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities in AI-Enhanced Operational Technology Networks
The integration of AI into industrial control systems expands the attack surface for cyber threats targeting data integrity and model behavior, which raises safety and production continuity risks, and negatively impacts the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market expansion. According to multiple sources, Ransomware remains a dominant and highly impactful threat within the manufacturing sector, frequently leading to significant operational disruptions and data encryption, with attacks becoming more sophisticated and financially motivated. Adversarial attacks, where subtle input perturbations cause misclassification, pose particular danger in vision-based quality control, with ENISA documenting cases where modified lighting conditions caused AI inspectors to approve defective aerospace components. The manufacturing sector is lagging in the implementation of advanced, AI-specific security measures (e.g., model integrity monitoring), even as the NIS2 Directive imposes stricter general cybersecurity risk management and governance requirements on critical entities. Legacy OT environments often lack segmentation, allowing compromised AI endpoints to propagate malware across production networks. Manufacturers face a delicate balance between pursuing innovative solutions and building robust, secure systems when there are no standardized AI security frameworks tailored to industrial needs; this stalls the wider deployment of AI despite potential operational advantages.
Lack of Harmonized AI Validation and Certification Protocols Across Member States
The absence of unified technical standards for validating manufacturing AI systems creates uncertainty in compliance and cross-border deployment, despite the EU AI Act’s overarching framework, which is among the major challenges to the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market growth. The European Committee for Standardization (CEN) and CENELEC are actively developing numerous harmonized standards to support the EU AI Act, a process that extends beyond early 2025 with ongoing drafting and public enquiry phases for various essential standards, which are highly anticipated to clarify compliance pathways for industry. National bodies are developing country-specific certification schemes, leading to divergent testing requirements. The European Confederation of Trade Unions (ETUC) actively participates in the development of AI standardization, consistently highlighting the need for greater transparency and robust safeguards to ensure that AI systems in the workplace are trustworthy and compliant with safety directives, while also ensuring effective participation of worker representatives in the conformity assessment process. This fragmentation increases time to market. A predictive maintenance solution approved in the Netherlands may require full re-validation to operate in Italy. The European Commission’s AI Testing and Experimentation Facilities aim to address this, but coverage remains limited to automotive and electronics. The absence of harmonized measurement standards for AI safety and performance means producers face inconsistent oversight, leading to higher expenses and hindering the pan-European scaling of industrial AI solutions.
REPORT COVERAGE
REPORT METRIC
DETAILS
Market Size Available
2024 to 2033
Base Year
2024
Forecast Period
2025 to 2033
CAGR
43.02%
Segments Covered
By Offering, Application, Technology, Industry, and Country
Various Analyses Covered
Regional & Country Level Analysis, Segment-Level Analysis, DROC, PESTLE Analysis, Porter’s Five Forces Analysis, Competitive Landscape, Analyst Overview on Investment Opportunities
Countries Covered
UK, France, Spain, Germany, Italy, Russia, Sweden, Denmark, Switzerland, Netherlands, Turkey, Czech Republic, and the Rest of Europe
Market Leaders Profiled
NVIDIA Corporation, Cisco Systems, Inc., Microsoft Corporation, IBM Corporation, Intel Corporation, Oracle Corporation, Google LLC, Micron Technology, Inc., Siemens AG, General Electric (GE) Co.
SEGMENTAL ANALYSIS By Offering Insights
The software segment held the leading share of 58.5% of the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market in 2024. The leading position of the software segment is driven by its role as the cognitive layer that transforms raw sensor data into actionable intelligence. Unlike hardware, which provides infrastructure, software enables dynamic applications such as anomaly detection, yield prediction, and adaptive scheduling across diverse production environments. According to research, the adoption of AI in EU enterprises is increasing, with businesses commonly integrating software solutions into their existing IT infrastructure to manage and automate production and administrative processes. The EU, through initiatives like the Digital Europe Programme, actively supports the creation and operation of AI Testing and Experimentation Facilities (TEFs) across member states to accelerate the adoption of AI technologies, particularly among SMEs. Besides, the European DIGITAL SME Alliance highlights that software-based digitisation options often provide a quicker and more financially accessible path to value and modernisation for SMEs compared to significant hardware investments or retrofits. The rise of no-code AI tools from vendors like Dataiku and Hasty further democratizes access, allowing plant engineers to build vision models without data science expertise. This combination of interoperability, speed, and scalability ensures software remains the cornerstone of AI value creation in European manufacturing.
The services segment is predicted to witness the highest CAGR of 24.3% from 2025 to 2033 due to the acute shortage of in-house AI talent and the complexity of aligning AI initiatives with EU regulatory and operational requirements. European manufacturing firms are increasingly engaging with external consultants and partners to help with the complex process of artificial intelligence model development, validation, and integration, indicating a trend toward specialized external support for data science initiatives, as per research. The EU AI Act’s high-risk classification mandates human oversight, data governance, and continuous monitoring, tasks that require specialized advisory services. According to sources, there is a growing trend of manufacturers collaborating with third-party artificial intelligence implementation partners, as businesses seek external expertise for integrating new AI technologies into their operations. In addition, Digital Innovation Hubs, supported by programs like the Digital Europe Programme, are actively providing various AI readiness and digital maturity assessments to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to foster digital transformation across the EU. Managed services for AI model retraining, cybersecurity hardening, and regulatory compliance audits are also gaining traction, particularly in Germany and France. The demand for end-to-end service orchestration, beyond mere technology, is driving AI’s rapid expansion from experimental pilots to mission-critical operations.
By Application Insights
The predictive maintenance and machinery inspection segment dominated the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market by accounting for a 32.1% share in 2024. The dominance of the predictive maintenance and machinery inspection segment is credited to the direct impact on asset uptime, maintenance cost reduction, and safety compliance, critical priorities in capital-intensive industries like automotive and chemicals. According to multiple sources, the adoption of AI-driven predictive maintenance in European factories is increasing, and it is widely reported to enhance operational efficiency and reduce the incidence of unplanned equipment downtime. The European Commission encourages the deployment of AI solutions in industrial settings, with initiatives aimed at fostering innovation and the application of digital technologies like vibration and thermal analytics for improved manufacturing processes. Apart from these, as per research, the industrial sector is seeing a rise in new machinery equipped with advanced diagnostics and condition monitoring capabilities, with a growing emphasis on standardization and data interoperability through frameworks like the ISO 13374 standard series. The pressure from EU Green Deal mandates, which require plants to optimize equipment performance for energy efficiency, has elevated predictive maintenance. It is now seen less as a simple reliability tool and more as a key strategy for ensuring sustainability and operational resilience, making it the most prevalent and established AI use case.
The quality control segment is anticipated to witness the fastest CAGR of 26.8% during the forecast period, owing to rising customer expectations, circular economy mandates, and the need for zero defect production in high-value sectors. According to sources, AI-powered visual inspection systems are increasingly being adopted across electronics and automotive manufacturing plants, significantly enhancing defect detection capabilities beyond human capacity and improving overall production quality. The EU’s Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation requires accurate material and defect tracking for product reparability, making AI vision essential for compliance. The advanced semiconductor industry, including new 300-millimeter wafer fabrication plants in Europe, widely integrates deep learning and advanced metrology tools to analyze nanoscale anomalies in real-time and optimize manufacturing processes. Additionally, food and pharmaceutical manufacturers are adopting hyperspectral imaging AI to ensure batch consistency and contamination detection. The convergence of regulatory traceability, premium quality demands, and automation of subjective human judgment establishes quality control as the highest momentum AI application across European industrial sectors.
By Industry Insights
The automotive segment was the largest in the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market and captured a 28.5% share in 2024. The supremacy of the automotive segment is attributed to its complex supply chains, high automation levels, and pressure to electrify production. According to sources, the European Automobile Manufacturers Association (ACEA) notes a general trend towards the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in EU vehicle assembly plants to optimize manufacturing processes, which includes applications like robotic path efficiency, battery quality control, and predictive maintenance to reduce downtime. The shift to electric vehicles has intensified quality demands: each EV battery pack contains thousands of cells requiring visual and electrical validation, a task only feasible through AI at scale. As per research, the German Association of the Automotive Industry (VDA) highlights the growing application of AI in German battery production facilities to enhance quality control and optimize processes, leading to improved efficiency and a reduction in production waste. Besides, the Chips Act and Net Zero Industry Act prioritize automotive as a strategic sector, unlocking public funding for AI-integrated pilot lines. The automotive industry uses AI to secure its dominance in the European industrial AI landscape, as just-in-time manufacturing’s tight tolerances and intense global competition make artificial intelligence a critical operational necessity rather than a simple innovative tool.
The semiconductor & electronics segment is likely to experience the fastest CAGR of 29.1% from 2025 to 2033. The swift growth of the semiconductor & electronics segment is fueled by Europe’s strategic push for chip sovereignty, the extreme precision required in nanofabrication, and the capital intensity of wafer production. New semiconductor manufacturing facilities are increasingly integrating artificial intelligence to monitor production processes. Advanced systems utilize machine learning for the immediate identification of defects and the correction of deviations in manufacturing. AI capabilities are employed to forecast production outcomes and anticipate potential losses in output. The high value of individual production components has led to an emphasis on early-stage fault detection. Automated systems analyze a wide range of variables during the fabrication process to improve the precision of quality assessments. Regional funding initiatives for the microelectronics sector may include requirements for the inclusion of intelligent technologies in facility design. The convergence of geopolitical urgency, technical necessity, and unprecedented public investment positions semiconductor manufacturing as the highest growth vector for industrial AI in Europe.
COUNTRY ANALYSIS Germany Artificial Intelligence In Manufacturing Market Analysis
Germany was the top performer in the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market by accounting for a 22.5% share in 2024. The dominance of the German market is driven by its world-leading machinery and automotive sectors, robust Industrie 4 0 ecosystem, and strong public private R and D collaboration. German large manufacturers are increasingly integrating AI into their operations, particularly for applications like predictive maintenance and quality control, a trend that is strongly supported by various government-funded AI initiatives and innovation clusters under the national AI strategy. The Plattform Industrie 4 0 has standardized data interfaces like Asset Administration Shell, enabling seamless AI integration across heterogeneous equipment. Additionally, German research institutes, including those within the Fraunhofer Society and the federal AI competence centers, are actively engaged in pioneering industrial AI research and contributing to patent filings, with notable research trends focusing on areas such as edge inference and explainable models for critical applications. Major corporations operate AI factories that serve as testbeds for sovereign, EU-compliant solutions. Germany’s combination of engineering excellence, regulatory foresight, and industrial density makes it the undisputed engine of AI adoption in European manufacturing.
France Artificial Intelligence In Manufacturing Market Analysis
France was the second-largest player in the Europe artificial manufacturing market and captured a 16.6% share in 2024. The growth of the French market is propelled by its national AI strategy, strategic focus on clean tech and aerospace, and significant public investment in sovereign AI infrastructure. According to sources, public investment in France, primarily through Bpifrance under the France 2030 plan, increasingly supports the integration of artificial intelligence in key manufacturing sectors, including applications such as advanced battery production and aerospace assembly processes. The national AI research institute, MIAI, collaborates with Schneider Electric and Safran to develop energy-efficient AI models tailored to industrial edge devices. Additionally, the French government offers various initiatives, such as the AI Booster and calls for projects under France 2030, to encourage a broader adoption of AI technologies among small and mid-sized industrial enterprises. France’s emphasis on technological autonomy ensures AI solutions adhere to EU data governance norms. This fusion of state direction, sectoral specialization, and SME enablement solidifies France’s role as a high-intensity AI manufacturing hub.
United Kingdom Artificial Intelligence In Manufacturing Market Analysis
The United Kingdom maintains a significant position in the Europe artificial intelligence market due to its advanced engineering base, world-class AI research institutions, and agile regulatory approach post Brexit. Innovate UK, through its BridgeAI programme and the UKRI Technology Missions Fund, is investing significantly in artificial intelligence projects to boost productivity across various high-growth industries, encouraging the development and adoption of AI solutions to address skills gaps and accelerate innovation. The funding supports a range of applications, including those within transport, construction, and other sectors. The UK’s AI Regulation White Paper promotes a pro-innovation, context-specific framework that allows faster deployment of experimental AI in non-safety-critical processes compared to EU counterparts. Companies use AI to optimize jet engine blade coatings and drug batch consistency, achieving yield improvements. Additionally, AI adoption among large UK businesses showed an increasing trend into 2024, though specific adoption rates in manufacturing lagged behind other sectors like services. Despite reduced EU program access, the UK leverages its academic excellence, through institutions like the Alan Turing Institute, and private capital to sustain AI momentum. This unique blend of scientific rigor and commercial agility ensures continued leadership in specialized, high-value manufacturing domains.
Italy Artificial Intelligence In Manufacturing Market Analysis
Italy grew steadily in the European AI manufacturing market owing to its dense network of small and medium enterprises in fashion, machinery, and food processing, now embracing AI for competitiveness. Manufacturing small and medium-sized enterprises have begun integrating artificial intelligence into their operations, aided by national digital transition funding. The textile industry utilizes artificial intelligence vision systems to identify flaws in materials during the production process. Food producers are implementing acoustic artificial intelligence to monitor the quality and structural integrity of products during the maturation phase. Machine tool manufacturers have incorporated self-calibrating systems to decrease the time required for equipment setup. Government tax incentives for industrial modernization have encouraged technology adoption among firms that have typically maintained traditional practices. Italy’s strength lies not in scale but in vertical specialization, where AI preserves artisanal quality while enabling industrial efficiency, creating a distinctive model of human-centric automation.
Netherlands Artificial Intelligence In Manufacturing Market Analysis
The Netherlands is likely to grow in the Europe artificial intelligence market from 2025 to 2033 due to its advanced semiconductor infrastructure, logistics leadership, and open innovation culture. A significant number of advanced manufacturing companies are utilizing artificial intelligence to manage precision processes and enhance supply chain stability. The country hosts Europe’s most advanced AI testbed for chip equipment, where companies validate reinforcement learning models for nanometer-scale alignment under EU Chips Act funding. Additionally, Industrial areas within major ports have incorporated AI-powered systems for energy management in various facilities, leading to a reduction in carbon emissions through real-time balancing of power and steam resources. The Dutch AI Coalition, comprising universities, corporates, and government, prioritizes “responsible AI” with strong emphasis on data sovereignty and human oversight. This alignment with EU ethical standards, combined with world-class infrastructure in high-tech systems, positions the Netherlands as a critical node in Europe’s AI-enabled advanced manufacturing network.
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE ANALYSIS
The Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market is characterized by intense collaboration between industrial automation giants, enterprise software vendors, and specialized AI startups, all operating under the EU’s stringent regulatory framework. Competition centers not on algorithmic novelty alone but on the ability to embed AI securely within operational technology stacks while satisfying requirements for transparency, human oversight, and data sovereignty. Incumbents like Siemens and ABB leverage decades of domain expertise and hardware integration to deliver edge native AI, while SAP and Microsoft focus on cloud-based cognitive enterprise layers. Startups gain traction through vertical-specific solutions—such as AI for semiconductor metrology or steel yield prediction—but often require partnerships to achieve scale. The absence of harmonized AI validation standards creates both opportunity and risk, as companies race to align with evolving interpretations from national regulators. Ultimately, success hinges on balancing innovation with compliance in a region where trust, safety, and sustainability are non-negotiable pillars of industrial intelligence.
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
The most dominant players that are in the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market are
NVIDIA Corporation Cisco Systems, Inc. SAP SE ABB Ltd Microsoft Corporation IBM Corporation Intel Corporation Oracle Corporation Google LLC Micron Technology, Inc. Siemens AG General Electric (GE) Co. Top Players In The Market Siemens AG is a global industrial technology leader with deep integration of artificial intelligence across its digital factory and automation portfolios in Europe. The company’s AI solutions power predictive maintenance, quality inspection, and energy optimization in automotive, machinery, and electronics manufacturing through its Industrial AI suite and MindSphere platform. It also launched an AI factory in Berlin dedicated to developing sovereign, EU-compliant AI models for industrial use. Siemens is solidifying its role as a trusted enabler of cognitive manufacturing in Europe, North America, and Asia by integrating explainable AI into its automation hardware and ensuring compliance with the high-risk provisions of the EU AI Act. SAP SE plays a pivotal role in the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market through its AI-infused enterprise resource planning and supply chain platforms that connect production, procurement, and logistics data into intelligent decision systems. Its Joule generative AI assistant, integrated into SAP S 4HANA Cloud, enables manufacturers to forecast equipment failures, optimize inventory, and simulate production disruptions using real-time shop floor and supplier data. The company also established an AI validation lab in Walldorf to certify model transparency under the EU AI Act. These initiatives reinforce SAP’s ability to deliver end-to-end, regulation-ready AI solutions that serve both European industrial champions and multinational enterprises worldwide. ABB Ltd delivers advanced artificial intelligence capabilities embedded within its robotics, process automation, and electrification systems across European heavy industry, including steel, chemicals, and automotive sectors. The company’s ABB Ability platform integrates machine learning models for predictive quality control, arc welding optimization, and energy consumption forecasting in real time. It also co-developed an AI safety monitor with TÜV Rheinland that validates robotic behavior against ISO 10218 standards using real-time sensor fusion. ABB is extending its influence across global mining, power, and transport infrastructure projects by focusing on edge AI that operates effectively within the constraints of operational technology and adheres to EU machinery safety directives, ensuring its solutions are technically robust and legally compliant. Top Strategies Used By The Key Market Participants
Key players in the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market focus on developing EU AI Act-compliant explainable models, embedding generative AI into engineering and operations workflows, establishing sovereign AI development facilities within Europe, forming public-private partnerships for circular economy and green manufacturing use cases, and certifying edge AI systems with notified bodies for machinery and cybersecurity safety standards.
MARKET SEGMENTATION
This research report on the Europe artificial intelligence in manufacturing market is segmented and sub-segmented into the following categories.
By Offering
Software Hardware Services
By Application
Predictive maintenance & Machinery Inspection Inventory Optimization Quality Control Cybersecurity Industrial robots Field Services Production Planning Others
By Technology
Machine Learning Computer Vision Natural Language Processing Context-aware Computing
By Industry
Automotive Food & Beverage Pharmaceutical Heavy Metals & Machine Manufacturing Semiconductor & Electronics Others
By Country
UK France Spain Germany Italy Russia Sweden Denmark Switzerland Netherlands Turkey Czech Republic Rest of Europe
