Bitarello BD, De Filippo C, Teixeira JC, Schmidt JM, Kleinert P, Meyer D, Andres AM. Signatures of long-term balancing selection in human genomes. Genome Biol Evol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evy054.
Piertney SB, Oliver MK. The evolutionary ecology of the major histocompatibility complex. Heredity. 2006;96(1):7–21.
Ebert D, Fields PD. Host–parasite co-evolution and its genomic signature. Nat Rev Genet. 2020;21(12):754–68.
Kaufman J. Unfinished business: evolution of the MHC and the adaptive immune system of jawed vertebrates. Annu Rev Immunol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052450.
Klein J. Natural history of the major histocompatibility complex. New York: Wiley; 1986.
Neefjes J, Jongsma MLM, Paul P, Bakke O. Towards a systems Understanding of MHC class I and MHC class II antigen presentation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11(12):823–36.
Braud VM, Allan DS, McMichael AJ. Functions of nonclassical MHC and non-MHC-encoded class I molecules. Curr Opin Immunol. 1999. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0952-7915(99)80018-1.
Alfonso C, Karlsson L. Nonclassical MHC class II molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.113.
Adams EJ, Luoma AM. The adaptable major histocompatibility complex (MHC) fold: structure and function of nonclassical and Mhc class I-like molecules. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31(1):529–61.
Saper MA, Bjorkman PJ, Wiley DC. Refined structure of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 at 2.6 Å resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(91)90567-P.
Brown JH, Jardetzky TS, Gorga JC, Stern LJ, Urban RG, Strominger JL, Wiley DC. Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA-DR1. Nature. 1993. https://doi.org/10.1038/364033a0.
Yuhki N, O’Brien SJ. Nature and origin of polymorphism in feline MHC class II DRA and DRB genes. J Immunol. 1997. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.158.6.2822.
Pierini F, Lenz TL. Divergent allele advantage at human MHC genes: signatures of past and ongoing selection. Mol Biol Evol. 2018;35(9):2145–58.
Takahata N, Nei M. Allelic genealogy under overdominant and frequency-dependent selection and polymorphism of major histocompatibility complex loci. Genetics. 1990. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/124.4.967.
Hughes AL, Nei M. Nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class II loci: evidence for overdominant selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.86.3.958.
Zinkernagel RM, Doherty PC. H 2 compatibility requirement for T cell mediated Lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H 2K or H 2D. J Exp Med. 1975. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.141.6.1427.
Clarke B, Kirby DRS. Maintenance of histocompatibility polymorphisms. Nature. 1966;211(5052):999–1000.
Nei M, Gu X, Sitnikova T. Evolution by the birth-and-death process in multigene families of the vertebrate immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(15):7799–806.
Klein J. Origin of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism: the trans-species hypothesis. Hum Immunol. 1987;19(3):155–62.
Těšický M, Vinkler M. Trans-Species polymorphism in immune genes: general pattern or MHC-Restricted phenomenon? J Immunol Res. 2015;2015(1):838035.
Aguilar A, Roemer G, Debenham S, Binns M, Garcelon D, Wayne RK. High MHC diversity maintained by balancing selection in an otherwise genetically monomorphic mammal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0306582101.
Castro-Prieto A, Wachter B, Sommer S. Cheetah paradigm revisited: MHC diversity in the world’s largest free-ranging population. Mol Biol Evol. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msq330.
Gutierrez-Espeleta GA, Hedrick PW, Kalinowski ST, Garrigan D, Boyce WM. Is the decline of desert bighorn sheep from infectious disease the result of low MHC variation? Heredity 2001, https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2540.2001.00853.x
Radwan J, Biedrzycka A, Babik W. Does reduced MHC diversity decrease viability of vertebrate populations? Biol Conserv. 2010;143(3):537–44.
Rao X, Hoof I, Fontaine Costa AICA, Van Baarle D, Keşmir C. HLA class I allele promiscuity revisited. Immunogenetics. 2011;63(11):691–701.
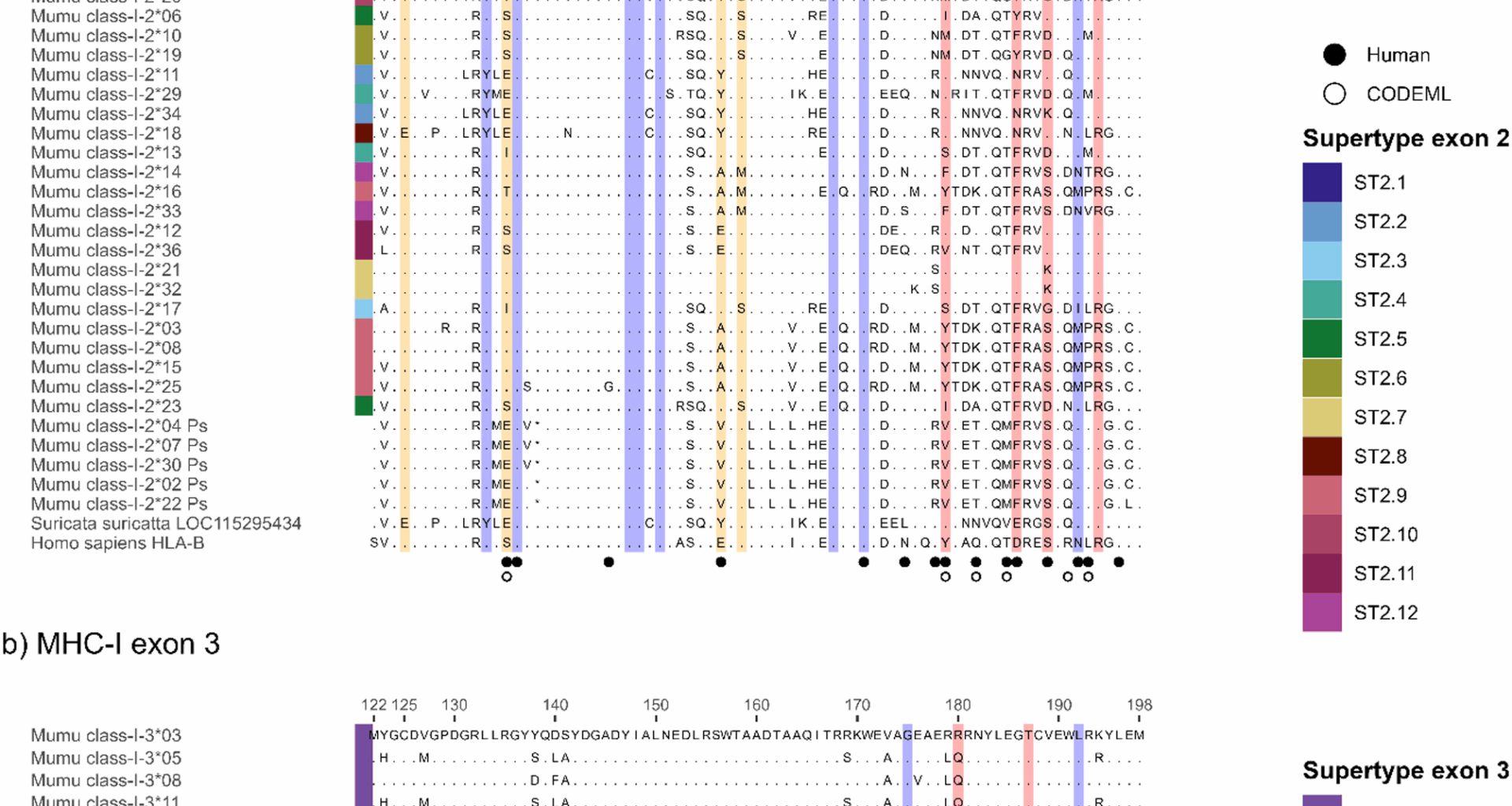
Reche PA, Reinherz EL. Definition of MHC supertypes through clustering of MHC peptide-binding repertoires. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, NJ) 2007, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-60327-118-9_11
Pedersen AB, Jones KE, Nunn CL, Altizer S. Infectious diseases and extinction risk in wild mammals. Conserv Biol. 2007;21(5):1269–79.
Crooks KR, Burdett CL, Theobald DM, Rondinini C, Boitani L. Global patterns of fragmentation and connectivity of mammalian carnivore habitat. Philosophical Trans Royal Soc B: Biol Sci. 2011;366(1578):2642–51.
Ripple WJ, Estes JA, Beschta RL, Wilmers CC, Ritchie EG, Hebblewhite M, Berger J, Elmhagen B, Letnic M, Nelson MP. Status and ecological effects of the world’s largest carnivores. Science. 2014;343(6167):1241484.
Woodroffe R. Predators and people: using human densities to interpret declines of large carnivores. Anim Conserv. 2000;3(2):165–73.
Jeon Jong Y, Black Andrew N, Heenkenda Erangi J, Mularo Andrew J, Lamka Gina F, Janjua S, Brüniche-Olsen A, Bickham John W, Willoughby Janna R, DeWoody JA. Genomic diversity as a key conservation criterion: Proof-of-concept from mammalian whole-genome resequencing data. Evol Appl. 2024;17(9):e70000.
Yuhki N, Beck T, Stephens R, Neelam B, O’Brien SJ. Comparative genomic structure of human, dog, and Cat MHC: HLA, DLA, and FLA. J Hered. 2007;98(5):390–9.
Graumann MB, DeRose SA, Ostrander EA, Storb R. Polymorphism analysis of four canine MHC class I genes. Tissue Antigens. 1998;51(4):374–81.
Holmes JC, Scholl EH, Dickey AN, Hess PR. High-resolution characterization of the structural features and genetic variation of six feline leukocyte antigen class I loci via single molecule, real-time (SMRT) sequencing. Immunogenetics. 2021;73(5):381–93.
Zhu Y, Sun D, Ge Y, Yu B, Chen Y, Wan Q. Isolation and characterization of class I MHC genes in the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Chin Sci Bull. 2013;58(18):2140–7.
Marsden CD, Mable BK, Woodroffe R, Rasmussen GSA, Cleaveland S, McNutt JW, Emmanuel M, Thomas R, Kennedy LJ. Highly endangered African wild dogs (Lycaon pictus) lack variation at the major histocompatibility complex. J Hered. 2009;100(suppl1):S54–65.
Kennedy LJ, Randall DA, Knobel D, Brown JJ, Fooks AR, Argaw K, Shiferaw F, Ollier WER, Sillero-Zubiri C, Macdonald DW, et al. Major histocompatibility complex diversity in the endangered Ethiopian Wolf (Canis simensis). Tissue Antigens. 2011;77(2):118–25.
Hedrick PW, Lee RN, Garrigan D. Major histocompatibility complex variation in red wolves: evidence for common ancestry with Coyotes and balancing selection. Mol Ecol. 2002;11(10):1905–13.
Luo S-J, Kim J-H, Johnson WE, Walt Jvd, Martenson J, Yuhki N, Miquelle DG, Uphyrkina O, Goodrich JM, Quigley HB, et al. Phylogeography and genetic ancestry of Tigers (Panthera tigris). PLoS Biol. 2004;2(12):e442.
Pokorny I, Sharma R, Goyal SP, Mishra S, Tiedemann R. MHC class I and MHC class II DRB gene variability in wild and captive Bengal Tigers (Panthera Tigris Tigris). Immunogenetics. 2010;62:667–79.
Castillo S, Srithayakumar V, Meunier V, Kyle CJ. Characterization of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) DRB exon 2 and DRA exon 3 fragments in a primary terrestrial rabies vector (Procyon lotor). PLoS ONE. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012066.
Hammond JA, Guethlein LA, Norman PJ, Parham P. Natural selection on marine carnivores elaborated a diverse family of classical MHC class I genes exhibiting haplotypic gene content variation and allelic polymorphism. Immunogenetics. 2012;64(12):915–33.
Cant MA, Nichols HJ, Thompson FJ, Vitikainen E. Banded mongooses: Demography, life history, and social behavior. In: Cooperative breeding in vertebrates: Studies of ecology, evolution and behavior. Edited by Koenig WD, Dickinson JL. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107338357.019. Cambridge UK: Cambridge University Press; 2016: 318–337.
Hodge SJ, Bell MBV, Cant MA. Reproductive competition and the evolution of extreme birth synchrony in a cooperative mammal. Biol Lett. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsbl.2010.0555.
Marshall HH, Johnstone RA, Thompson FJ, Nichols HJ, Wells D, Hoffman JI, Kalema-Zikusoka G, Sanderson JL, Vitikainen EIK, Blount JD, et al. A veil of ignorance can promote fairness in a mammal society. Nat Commun. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23910-6.
Wells DA, Cant MA, Hoffman JI, Nichols HJ. Inbreeding depresses altruism in a cooperative society. Ecol Lett. 2020;23(10):1460–7.
Wells DA, Cant MA, Nichols HJ, Hoffman JI. A high-quality pedigree and genetic markers both reveal inbreeding depression for quality but not survival in a cooperative mammal. Mol Ecol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.14570.
Khera M, Arbuckle K, Hoffman JI, Sanderson JL, Cant MA, Nichols HJ. Cooperatively breeding banded mongooses do not avoid inbreeding through familiarity-based kin recognition. Behav Ecol Sociobiol. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00265-021-03076-3.
Nichols HJ, Cant MA, Sanderson JL. Adjustment of costly extra-group paternity according to inbreeding risk in a cooperative mammal. Behav Ecol. 2015;26(6):1486–94.
Sanderson JL, Wang J, Vitikainen EIK, Cant MA, Nichols HJ. Banded mongooses avoid inbreeding when mating with members of the same Natal group. Mol Ecol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1111/mec.13253.
Alexander KA, Laver PN, Williams MC, Sanderson CE, Kanipe C, Palmer MV. Pathology of the emerging Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex Pathogen, Mycobacterium mungi, in the banded mongoose (Mungos mungo). Vet Pathol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985817741730.
Alexander KA, Sanderson CE, Larsen MH, Robbe-Austerman S, Williams MC, Palmer MV. Emerging tuberculosis pathogen hijacks social communication behavior in the group-living banded mongoose (Mungos mungo). mBio 2016, https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00281-16
Alexander KA, Sanderson CE, Laver PN. Novel Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex spp. In group-living African mammals. Tuberculosis, leprosy and mycobacterial diseases of man and animals: the many hosts of mycobacteria. Wallingford UK: CABI; 2015. pp. 386–401. https://doi.org/10.1079/9781780643960.0386.
Brüns AC, Tanner M, Williams MC, Botha L, O’Brien A, Fosgate GT, van Helden PD, Clarke J, Michel AL. Diagnosis and implications of Mycobacterium Bovis infection in banded mongooses (Mungos mungo) in the Kruger National Park, South Africa. J Wildl Dis. 2017. https://doi.org/10.7589/2015-11-318.
Jordan NR, Mwanguhya F, Kyabulima S, Rüedi P, Cant MA. Scent marking within and between groups of wild banded mongooses. J Zool. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7998.2009.00646.x.
ASAB Ethical Committee, ABS Animal Care Committee. Guidelines for the treatment of animals in behavioural research and teaching. Anim Behav. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0003-3472(21)00389-4.
Yuhki N, O’Brien SJ. DNA variation of the mammalian major histocompatibility complex reflects genomic diversity and population history. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.2.836.
Katoh K, Standley DM. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010.
Untergasser A, Cutcutache I, Koressaar T, Ye J, Faircloth BC, Remm M, Rozen SG. Primer3-new capabilities and interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks596.
Faircloth BC, Glenn TC. Not all sequence tags are created equal: designing and validating sequence identification tags robust to indels. PLoS ONE. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042543.
Sebastian A, Herdegen M, Migalska M, Radwan J. Amplisas: A web server for multilocus genotyping using next-generation amplicon sequencing data. Mol Ecol Resour. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12453.
Zhang Z, Schwartz S, Wagner L, Miller W. A greedy algorithm for aligning DNA sequences. J Comput Biol. 2000;7(1–2):203–14.
Kaufman J, Salomonsen J, Flajnik M. Evolutionary conservation of MHC class I and class II molecules – different yet the same. Semin Immunol. 1994;6(6):411–24.
Reche PA, Reinherz EL. Sequence variability analysis of human class I and class II MHC molecules: functional and structural correlates of amino acid polymorphisms. J Mol Biol. 2003. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(03)00750-2.
Huang K, Zhang P, Dunn DW, Wang T, Mi R, Li B. Assigning alleles to different loci in amplifications of duplicated loci. Mol Ecol Resour. 2019;19:1240–53.
IUCN: The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2024-1. 2024, https://www.iucnredlist.org
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sanchez-DelBarrio JC, Guirao-Rico S, Librado P, Ramos-Onsins SE, Sanchez-Gracia A. DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol Biol Evol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx248.
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K. MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096.
Winternitz J, Chakarov N, Rinaud T, Ottensmann M, Krüger O. High functional allelic diversity and copy number in both MHC classes in the common buzzard. BMC Ecol Evol. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-023-02135-9.
Martin DP, Murrell B, Golden M, Khoosal A, Muhire B. RDP4: detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. 2015. https://doi.org/10.1093/ve/vev003.
Martin D, Rybicki E. RDP: detection of recombination amongst aligned sequences. Bioinformatics. 2000. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/16.6.562.
Padidam M, Sawyer S, Fauquet CM. Possible emergence of new geminiviruses by frequent recombination. Virology. 1999;265(2):218–25.
Salminen MO, Carr JK, Burke DS, McCutchan FE. Identification of breakpoints in intergenotypic recombinants of HIV type 1 by bootscanning. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1995. https://doi.org/10.1089/aid.1995.11.1423.
Gibbs MJ, Armstrong JS, Gibbs AJ. Sister-scanning: A Monte Carlo procedure for assessing signals in rebombinant sequences. Bioinformatics. 2000. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/16.7.573.
Smith JM. Analyzing the mosaic structure of genes. J Mol Evol. 1992. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182389.
Posada D, Crandall KA. Evaluation of methods for detecting recombination from DNA sequences: computer simulations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.241370698.
Boni MF, Posada D, Feldman MW. An exact nonparametric method for inferring mosaic structure in sequence triplets. Genetics. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.106.068874.
Martin DP, Murrell B, Khoosal A, Muhire B. Detecting and analyzing genetic recombination using RDP4. In: Bioinformatics Methods in Molecular Biology. Edited by Kieth J, vol. 1525. New York, NY: Humana Press; 2017.
Murrell B, Moola S, Mabona A, Weighill T, Sheward D, Kosakovsky Pond SL, Scheffler K. FUBAR: A fast, unconstrained bayesian approximation for inferring selection. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst030.
Murrell B, Wertheim JO, Moola S, Weighill T, Scheffler K, Kosakovsky Pond SL. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLoS Genet. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002764.
Weaver S, Shank SD, Spielman SJ, Li M, Muse SV, Kosakovsky Pond SL. Datamonkey 2.0: A modern web application for characterizing selective and other evolutionary processes. Mol Biol Evol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx335.
Gao F, Chen C, Arab DA, Du Z, He Y, Ho SYW. EasyCodeML: A visual tool for analysis of selection using codeml. Ecol Evol. 2019;9(7):3891–8.
Yang Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24(8):1586–91.
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma KI, Miyata T. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf436.
Trifinopoulos J, Nguyen LT, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ. W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKW256.
Kalyaanamoorthy S, Minh BQ, Wong TKF, Von Haeseler A, Jermiin LS. ModelFinder: fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat Methods. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.4285.
Nguyen LT, Schmidt HA, Von Haeseler A, Minh BQ. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32(1):268–74.
Hoang DT, Chernomor O, Von Haeseler A, Minh BQ, Vinh LS. UFBoot2: improving the ultrafast bootstrap approximation. Mol Biol Evol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx281.
Nei M, Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986;3(5):418–26.
Sandberg M, Eriksson L, Jonsson J, Sjöström M, Wold S. New chemical descriptors relevant for the design of biologically active peptides. A multivariate characterization of 87 amino acids. J Med Chem. 1998. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm9700575.
Osorio D, Rondón-Villarreal P, Torres R. Peptides: A package for data mining of antimicrobial peptides. R J. 2015. https://doi.org/10.32614/rj-2015-001.
Jombart T. Adegenet: A R package for the multivariate analysis of genetic markers. Bioinformatics. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btn129.
Gamer M, Lemon J, Fellows I, Singh P. Irr: various coefficients of interrater reliability and agreement. R package version 0.84.1. In.; 2019.
Wei T, Simko V. R package ‘corrplot’: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix. In, https://github.com/taiyun/corrplot, Version 0.95 edn; 2024.
Yuhki N, Mullikin JC, Beck T, Stephens R, O’Brien SJ. Sequences, annotation and single nucleotide polymorphism of the major histocompatibility complex in the domestic Cat. PLoS ONE. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002674.
Okano M, Miyamae J, Suzuki S, Nishiya K, Katakura F, Kulski JK, Moritomo T, Shiina T. Identification of novel alleles and structural haplotypes of major histocompatibility complex class I and DRB genes in domestic Cat (Felis Catus) by a newly developed NGS-based genotyping method. Front Genet. 2020;11:750.
Drake GJC, Kennedy LJ, Auty HK, Ryvar R, Ollier WER, Kitchener AC, Freeman AR, Radford AD. The use of reference strand-mediated conformational analysis for the study of cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) feline leucocyte antigen class II DRB polymorphisms. Mol Ecol. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.02027.x.
Burnett RC, Geraghty DE. Structure and expression of a divergent canine class I gene. J Immunol. 1995. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.155.9.4278.
Zhu Y, Sun DD, Ge YF, Yu B, Chen YY, Wan QH. Isolation and characterization of class I MHC genes in the giant panda (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Chin Sci Bull. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5582-4.
D’Souza MP, Adams E, Altman JD, Birnbaum ME, Boggiano C, Casorati G, Chien YH, Conley A, Eckle SBG, Früh K, et al. Casting a wider net: immunosurveillance by nonclassical MHC molecules. PLoS Pathog. 2019;15(2):e1007567.
Upham NS, Esselstyn JA, Jetz W. Inferring the mammal tree: Species-level sets of phylogenies for questions in ecology, evolution, and conservation. PLoS Biol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000494.
Revell LJ. Phytools: an R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol Evol. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2041-210X.2011.00169.x.
Yu G, Smith DK, Zhu H, Guan Y, Lam TTY. Ggtree: an r package for visualization and annotation of phylogenetic trees with their covariates and other associated data. Methods Ecol Evol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12628.
R Core Team. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. In., https://www.R-project.org/: R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria; 2025.
Bürkner PC. Brms: an R package for bayesian multilevel models using Stan. J Stat Softw. 2017. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v080.i01.
Revell LJ. Phytools 2.0: an updated R ecosystem for phylogenetic comparative methods (and other things). PeerJ. 2024. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.16505.
Lüdecke D. Ggeffects: tidy data frames of marginal effects from regression models. J Open Source Softw. 2018. https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.00772.
Aphalo P. gginnards: Explore the Innards of ‘ggplot2’ Objects. R package version 0.2.0. 2024, https://cran.r-project.org/package=gginnards
Slowikowski K. ggrepel: Automatically Position Non-Overlapping Text Labels with ‘ggplot2’. In., https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.ggrepel, R package version 0.9.6 edn; 2024.
Campitelli E: ggnewscale: Multiple Fill and Colour Scales in ‘ggplot2’. In., https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.ggnewscale, R package version 0.5.2 edn; 2025.
Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis. Second Edition. Springer; 2016.
Singh PB. The present status of the ‘carrier hypothesis’ for chemosensory recognition of genetic individuality. Genetica. 1998. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026475118901.
Maccari G, Robinson J, Bontrop RE, Otting N, de Groot NG, Ho CS, Ballingall KT, Marsh SGE, Hammond JA. IPD-MHC: nomenclature requirements for the non-human major histocompatibility complex in the next-generation sequencing era. Immunogenetics. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-018-1072-4.
Kelley J, Walter L, Trowsdale J. Comparative genomics of major histocompatibility complexes. Immunogenetics. 2005;56:683–95.
Winternitz JC, Wares JP. Duplication and population dynamics shape historic patterns of selection and genetic variation at the major histocompatibility complex in rodents. Ecol Evol. 2013;3(6):1552–68.
Sommer S. The importance of immune gene variability (MHC) in evolutionary ecology and conservation. Front Zool. 2005;2:1–18.
Ujvari B, Belov K. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) markers in conservation biology. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(8):5168–86.
Coker OM, Osaiyuw OH, Fatoki AO. Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) diversity and its implications in human and wildlife health and conservation. Genet Biodivers J. 2023;7(2):1–11.
Nichols HJ, Jordan NR, Jamie GA, Cant MA, Hoffman JI. Fine-scale Spatiotemporal patterns of genetic variation reflect budding dispersal coupled with strong Natal philopatry in a cooperatively breeding mammal. Mol Ecol. 2012;21(21):5348–62.
Schubert N, Nichols HJ, Mwanguhya F, Businge R, Kyambulima S, Mwesige K, Hoffman JI, Cant MA, Winternitz JC. Sex-dependent influence of major histocompatibility complex diversity on fitness in a social mammal. BioRxiv. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.18.629201.
Gonzalez-Galarza Faviel F, McCabe A, Santos Eduardo J, Md, Jones J, Takeshita L, Ortega-Rivera Nestor D, Cid-Pavon Glenda MD, Ramsbottom K, Ghattaoraya G, Alfirevic A, et al. Allele frequency net database (AFND) 2020 update: gold-standard data classification, open access genotype data and new query tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;48(D1):D783–8.
Schaschl H, Herzog T, Oberreiter V, Kutanan W, Jakobsson M, Larena M. HLA diversity and signatures of selection in the Maniq, a nomadic hunter-gatherer population in Southern Thailand. Immunogenetics. 2025;77(1):23.
Denyer AL, Massey JP, Davison LJ, Ollier WER, Catchpole B, Kennedy LJ. Dog leucocyte antigen (DLA) class II haplotypes and risk of canine diabetes mellitus in specific dog breeds. Canine Med Genet. 2020;7(1):15.
Nielsen JF, English S, Goodall-Copestake WP, Wang J, Walling CA, Bateman AW, Flower TP, Sutcliffe RL, Samson J, Thavarajah NK, et al. Inbreeding and inbreeding depression of early life traits in a cooperative mammal. Mol Ecol. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2012.05565.x.
Mueller-Klein N, Risely A, Wilhelm K, Riegel V, Manser M, Clutton-Brock T, Santos P, Melville D, Sommer S. Twenty-year co-evolutionary arms race between meerkat MHC and tuberculosis. PREPRINT (Version 1) Available Res Square. 2024. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4685784/v1.
Cutrera AP, Lacey EA. Major histocompatibility complex variation in Talas tuco-tucos: the influence of demography on selection. J Mammal. 2006;87(4):706–16.
Anderson RM, May RM. Population biology of infectious diseases: part I. Nature. 1979;280(5721):361–7.
Altizer S, Nunn CL, Thrall PH, Gittleman JL, Antonovics J, Cunningham AA, Dobson AP, Ezenwa V, Jones KE, Pedersen AB et al. Social organization and parasite risk in mammals: Integrating theory and empirical studies. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics 2003, 34(Volume 34, 2003):517–547.
Côté IM, Poulin R. Parasitism and group size in social animals: a meta-analysis. Behav Ecol. 1995;6(2):159–65.
Hambuch TM, Lacey EA. Enhanced selection for Mhc diversity in social tuco-tucos. Evolution. 2002;56(4):841–5.
Minias P, Whittingham LA, Dunn PO. Coloniality and migration are related to selection on MHC genes in birds. Evolution. 2017;71(2):432–41.
Cant MA. Social control of reproduction in banded mongooses. Anim Behav. 2000. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbe.1999.1279.
Nichols HJ, Amos W, Cant MA, Bell MBV, Hodge SJ. Top males gain high reproductive success by guarding more successful females in a cooperatively breeding mongoose. Anim Behav. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2010.06.025.
Birch G, Nichols HJ, Mwanguhya F, Thompson FJ, Cant MA, Blount JD. Lifetime trajectories of male mating effort under reproductive conflict in a cooperatively breeding mammal. Proceedings B 2024, 291(2031):20241499–20241499.
Mitchell J, Vitikainen EIK, Wells DA, Cant MA, Nichols HJ. Heterozygosity but not inbreeding coefficient predicts parasite burdens in the banded mongoose. J Zool. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/jzo.12424.
Winternitz JC, Abbate JL. The genes of attraction: Mating behavior, immunogenetic variation, and parasite resistance. In: Animal Behavior and Parasitism. Edited by Ezenwa V, Altizer SM, Hall R. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780192895561.003.0011: Oxford University Press; 2022.
Winternitz J, Abbate JL, Huchard E, Havlíček J, Garamszegi LZ. Patterns of MHC-dependent mate selection in humans and nonhuman primates: a meta‐analysis. Mol Ecol. 2017;26(2):668–88.
Kamiya T, O’Dwyer K, Westerdahl H, Senior A, Nakagawa S. A quantitative review of MHC-based mating preference: the role of diversity and dissimilarity. Mol Ecol. 2014;23(21):5151–63.
Abduriyim S, Nishita Y, Kosintsev PA, Raichev E, Väinölä R, Kryukov AP, Abramov AV, Kaneko Y, Masuda R. Evolution of MHC class I genes in Eurasian badgers, genus Meles (Carnivora, Mustelidae). Heredity. 2019;122(2):205–18.
Zhang C, Anderson A, DeLisi C. Structural principles that govern the peptide-binding motifs of class I MHC molecules. J Mol Biol. 1998. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.1982.
Kuduk K, Babik W, Bojarska K, Śliwińska EB, Kindberg J, Taberlet P, Swenson JE, Radwan J. Evolution of major histocompatibility complex class I and class II genes in the brown bear. BMC Evol Biol. 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-12-197.
Abduriyim S, Zou DH, Zhao H. Origin and evolution of the major histocompatibility complex class I region in eutherian mammals. Ecol Evol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5373.
Takahashi K, Rooney AP, Nei M. Origins and divergence times of mammalian class II MHC gene clusters. J Hered. 2000;91(3):198–204.
Rammensee HG, Bachmann J, Stevanović S. MHC ligands and peptide motifs. Springer Science & Business Media; 2013.
Satta Y, O’Huigin C, Takahata N, Klein J. Intensity of natural selection at the major histocompatibility complex loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.15.7184.
Babik W, Durka W, Radwan J. Sequence diversity of the MHC DRB gene in the Eurasian beaver (Castor fiber). Mol Ecol. 2005. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02751.x.
Castro-Prieto A, Wachter B, Melzheimer J, Thalwitzer S, Sommer S. Diversity and evolutionary patterns of immune genes in free-ranging Namibian leopards (Panthera Pardus Pardus). J Hered. 2011;102(6):653–65.
Yuhki N, Heidecker GF, O’Brien SJ. Characterization of MHC cDNA clones in the domestic cat. Diversity and evolution of class I genes. J Immunol. 1989. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.142.10.3676.
Yuhki N, O’Brien SJ. Exchanges of short polymorphic DNA segments predating speciation in feline major histocompatibility complex class I genes. J Mol Evol. 1994. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178246.
Okamura K, Dijkstra JM, Tsukamoto K, Grimholt U, Wiegertjes GF, Kondow A, Yamaguchi H, Hashimoto K. Discovery of an ancient MHC category with both class I and class II features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2021;118(51):e2108104118.