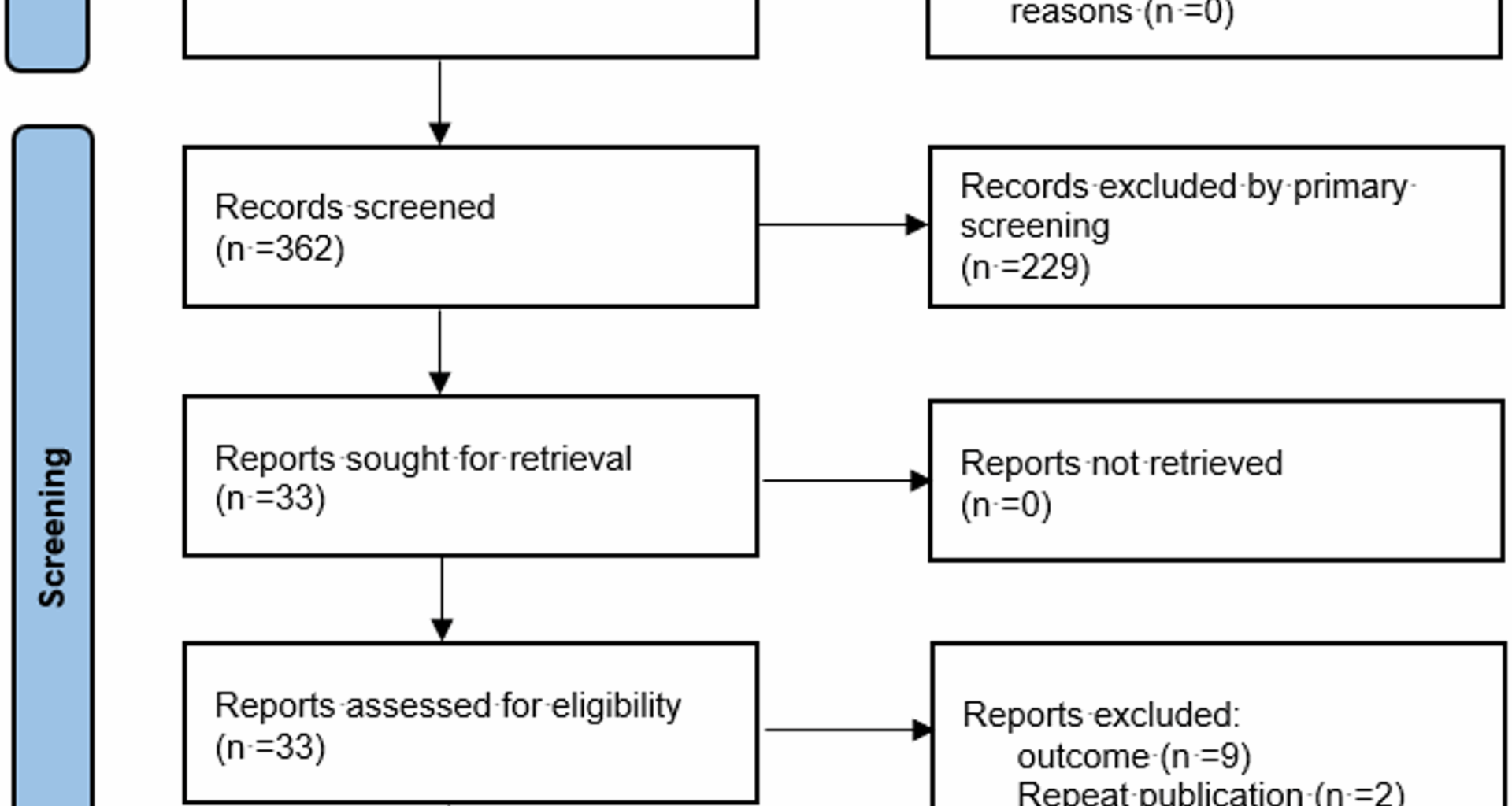
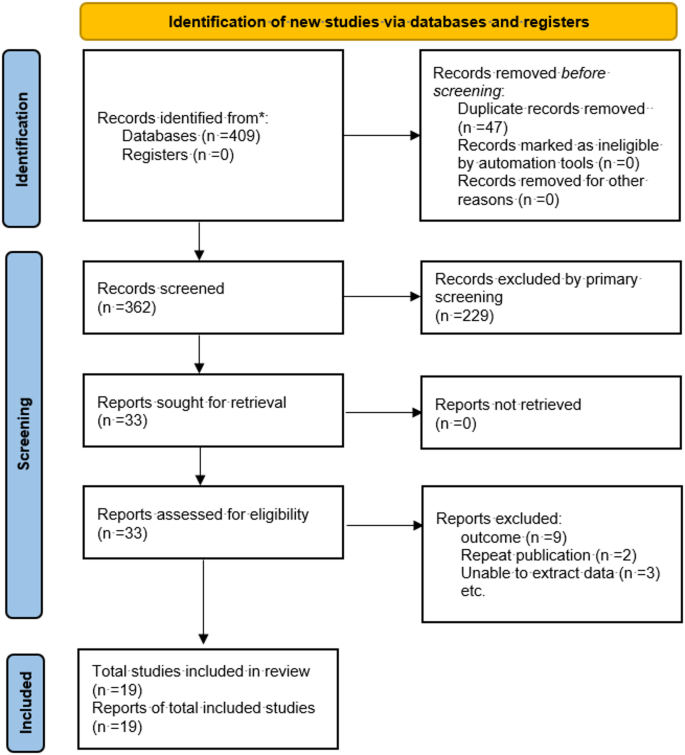
Literature screening process
A total of 409 articles were initially retrieved. After sequential screening, 19 studies were finally included [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25]. The literature screening process is shown in Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of the literature screening process
Basic characteristics and quality evaluation of the included studies
Of the 19 studies, a total of 188,172 participants were investigated, including 11 cohort studies [9, 11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18, 24, 25], 4 case-control studies [7, 10, 20, 22], and 4 cross-sectional studies [8, 19, 21, 23]. Among these, 9 studies were of high quality and 10 of moderate quality. The basic characteristics of the included studies are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Basic characteristics and quality assessment results of included studiesMeta-analysis resultsAttrition rate of PWH on ART
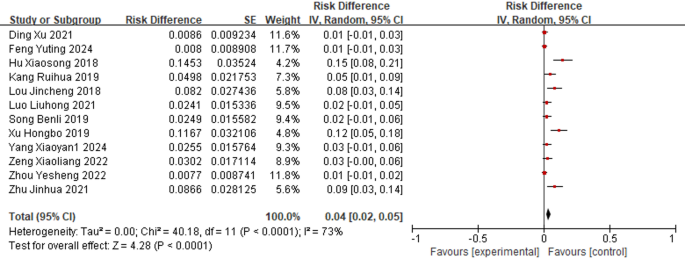
A heterogeneity test was performed on the 12 studies reporting the attrition rate. A high degree of heterogeneity was observed between studies (I² = 73%, P 2).
Overall attrition rate of PWH receiving ART in China (random-effects model)
Influencing factors for treatment attrition among PWH on ART
Meta-analysis was performed for influencing factors that were reported in at least 2 studies, yielding a total of 14 factors. The results showed that older age (> 50 years), male gender, being single or living alone, alcohol consumption, infection via intravenous drug use, initial treatment regimens containing protease inhibitors (PI), baseline CD4⁺ T lymphocyte count > 350/µL, occurrence of adverse drug reactions, inconvenience in obtaining medications, low family support, passive receipt of treatment, interval from diagnosis to ART initiation > 1 year, and ART initiation year in 2016 or later were all significantly associated with attrition in PWH (P 2).
Table 2 Meta-analysis results for influencing factors of ART attrition in PWHDescriptive analysis
Nine additional influencing factors—including occupation (farmer), migrant work, monthly income, HBV infection before ART, tuberculosis infection before ART, HIV viral load, missed doses in the last month of treatment, initial regimen including zidovudine, and WHO clinical stage 3/4—were also reported to be associated with treatment attrition. Because these factors were each reported in only a single study, their combined effect sizes could not be pooled, and hence they were analyzed descriptively.
Publication bias assessment
For factors reported in 10 or more studies, publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots. Begg’s test (Z = 1.01, P = 0.312) and Egger’s test (t = 1.67, P = 0.130) suggested that there was little possibility of publication bias among the included studies.