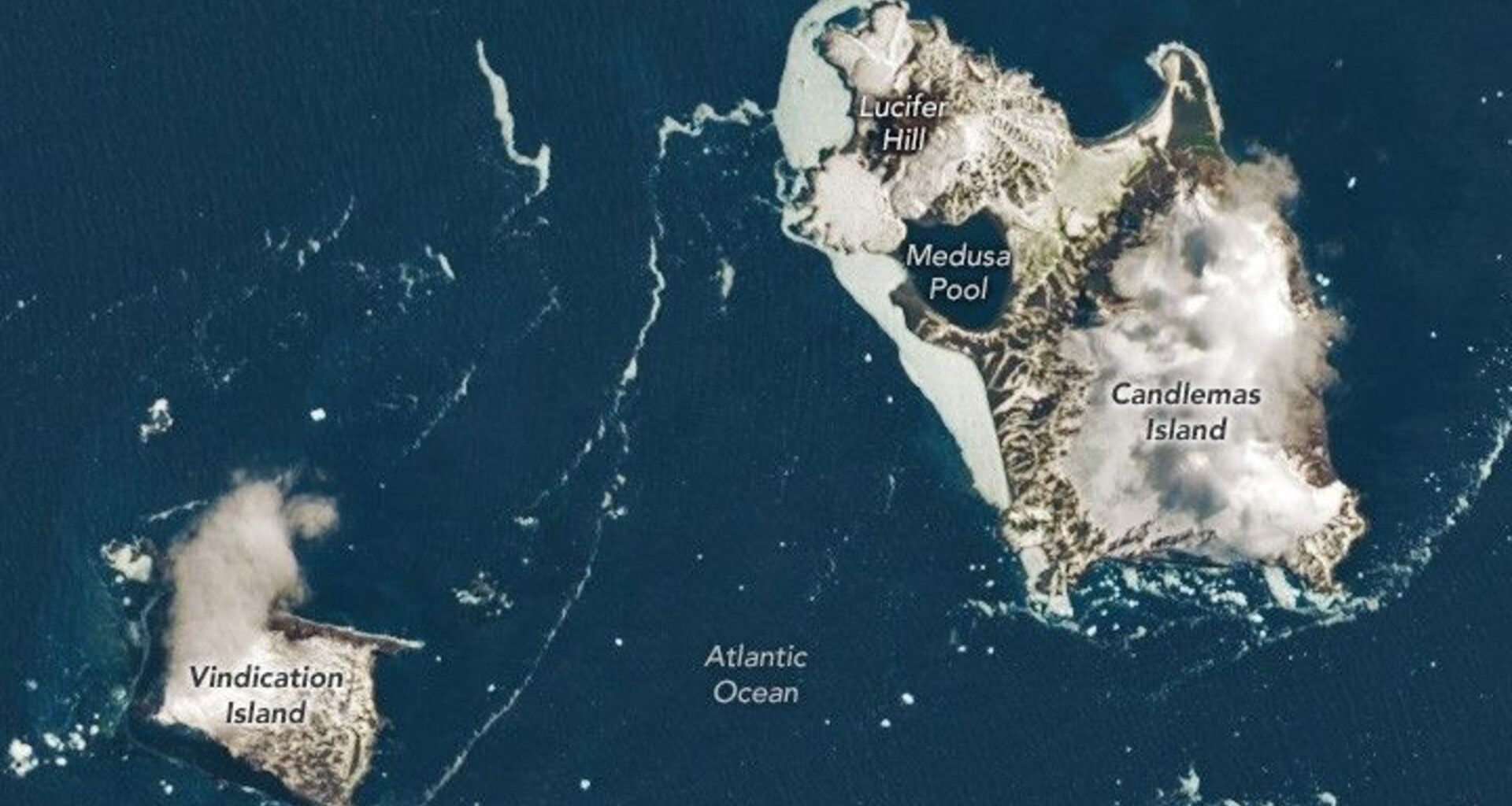
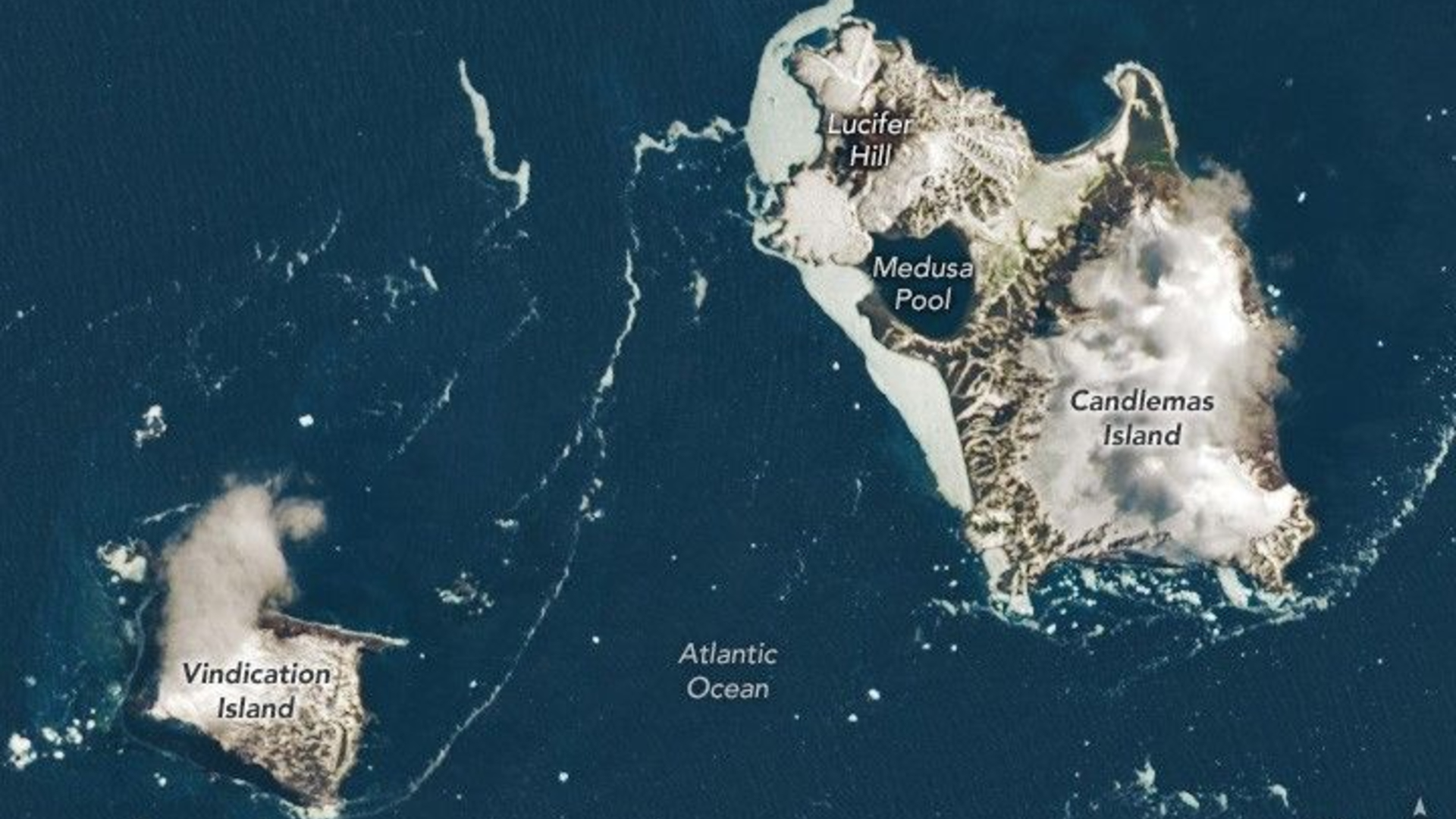
Far from shipping lanes, cities, and even most scientific outposts lie the South Sandwich Islands, one of the most remote island chains on Earth. Stretching in a slender arc through the stormy South Atlantic Ocean, these islands sit more than 994 miles (1,600 kilometers) from both South America and Antarctica. In this satellite image, puffs of low-level cloud drift across Vindication and Candlemas Islands, two of the South Sandwich Islands, mingling with rugged volcanic terrain and icy shorelines. The image was captured by the Operational Land Imager-2 (OLI-2) instrument aboard the Earth-observing satellite Landsat 9, a collaboration between NASA and the U.S. Geological Survey.
Such scenes are uncommon in satellite records from this region, where clouds often obscure the surface.
What is it?
Since Captain James Cook first reported two closely spaced islands in 1775 — later named Candlemas and Vindication — the region has remained largely inaccessible. Persistent cloud cover, harsh seas, and extreme weather make direct observation rare. As a result, satellites have become the primary way scientists study these islands, monitoring volcanic activity, glaciation, erosion, and atmospheric behavior in one of Earth’s least disturbed environments.
You may like
Thanks to fewer clouds, the satellite was able to observe some of Candlemas Island’s features, including Lucifer Hill and Medusa Pool.
Where is it?
The image was taken above Candlemas and Vindication Islands in the South Atlantic Ocean.
These two islands are hard to access, and experts rely on satellite technology to study them. (Image credit: NASA Earth Observatory image by Wanmei Liang, using Landsat data from the U.S. Geological Survey.)Why is it amazing?
Using satellite images like this one, scientists can understand how volcanic islands evolve in extreme climates. Candlemas Island itself began as two separate islands that merged centuries ago. Its southeastern portion is an older, heavily eroded stratovolcano now mantled in ice, while its northwestern side hosts younger lava flows radiating from cinder cones like Lucifer Hill. Historical accounts describe eruptions and steam clouds as recently as the 20th century, suggesting that volcanic heat and glacial ice have long coexisted here in tension.
The image also highlights the dominant role of erosion. Vindication Island shows no evidence of recent volcanism. Instead, steep cliffs and reduced land area testify to the power of waves, freezing temperatures and storms, forces that slowly dismantle volcanic edifices once tectonic energy subsides.
The clouds themselves are also part of the story. The South Sandwich Islands are famous for producing striking wave clouds, created when strong winds are forced upward by steep terrain. These atmospheric patterns, occasionally visible from space, provide insight into air flow and stability in remote oceanic environments, data useful for both weather and climate studies.
Want to learn more?
You can learn more about Earth-observing satellites and climate change.