Prasad R. Host dependency among haematophagous insects: a case study on flea-host association. Proc Indian Acad Sci (Anim Sci). 1987;96:349–60.
Bitam I, Dittmar K, Parola P, Whiting MMF, Raoult D. Fleas and flea-borne diseases. Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:e667–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2009.11.011.
Linardi PM. Fleas as useful tools for science. Diversity. 2023;15:1153. https://doi.org/10.3390/d15111153.
Boyer S, Gillespie TR, Miarinjara A. Xenopsylla cheopis (rat flea). Trends Parasitol. 2022;38:607–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pt.2022.03.006.
Buckland PC, Sadler JP. A biogeography of the human flea, Pulex irritans L. (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J Biogeogr. 1989;16:115. https://doi.org/10.2307/2845085.
Dittmar K, Mamat U, Whiting M, Goldmann T, Reinhard K, Guillen S. Techniques of DNA-studies on prehispanic ectoparasites (Pulex sp., Pulicidae, Siphonaptera) from animal mummies of the Chiribaya culture, southern Peru. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2003;98:53–8. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0074-02762003000900010.
Lareschi M, Venzal JM, Nava S, Mangold AJ, Portillo A, Palomar-Urbina AM, et al. The human flea Pulex irritans (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae) in northwestern Argentina, with an investigation of Bartonella and Rickettsia spp. Rev Mex Biodivers. 2018;89:375–81. https://doi.org/10.22201/ib.20078706e.2018.2.2392.
Belthoff JR, Bernhardt SA, Ball CL, Gregg M, Johnson DH, Ketterling R, et al. Burrowing owls, Pulex irritans, and plague. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2015;15:556–64. https://doi.org/10.1089/vbz.2015.1772.
Graham CB, Eisen RJ, Belthoff JR. Detecting burrowing owl bloodmeals in Pulex irritans (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J Med Entomol. 2016;53:446–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjv177.
McGee BK, Butler MJ, Pence DB, Alexander JL, Nissen JB, Ballard WB, et al. Possible vector dissemination by swift foxes following a plague epizootic in black-tailed prairie dogs in northwestern Texas. J Wildl Dis. 2006;42:415–20. https://doi.org/10.7589/0090-3558-42.2.415.
Oteo JA, Portillo A, Portero F, Zavala-Castro J, Venzal JM, Labruna MB. ‘Candidatus Rickettsia asemboensis’ and Wolbachia spp. in Ctenocephalides felis and Pulex irritans fleas removed from dogs in Ecuador. Parasit Vectors. 2014;7:455. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-014-0455-0.
Shu C, Jiang M, Yang M, Xu J, Zhao S, Yin X, et al. Flea surveillance on wild mammals in northern region of Xinjiang, northwestern China. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2020;11:12–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2019.11.004.
Munkhzul T, Murdoch JD, Reading RP. Ectoparasites on meso-carnivores in the desert-steppe of Mongolia. Mong J Biol Sci. 2018;16:65–74. https://doi.org/10.22353/mjbs.2018.16.06.
Blanc G, Baltazard M. Recherches sur le mode de transmission naturelle de la peste bubonique et septicemique. Archives de l’Institut Pasteur du Maroc, vol. Tome 3; 1945.
Karimi Y, Eftekhari M, Almeida CR. Sur l’écologie des puces impliquées dans l’épidemiologie de la peste et le rôle éventuel de certains insectes hématophages dans son processus au nord-est du Brésil. Bull La Société Pathol Exot. 1974;67:583–91.
Laudisoit A, Leirs H, Makundi RH, Van Dongen S, Davis S, Neerinckx S, et al. Plague and the human flea, Tanzania. Emerg Infect Dis. 2007;13:687–93. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid1305.061084.
Ratovonjato J, Rajerison M, Rahelinirina S, Boyer S. Yersinia pestis in Pulex irritans fleas during plague outbreak, Madagascar. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20:1414–5. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2008.130629.
Miarinjara A, Bland DM, Belthoff JR, Hinnebusch BJ. Poor vector competence of the human flea, Pulex irritans, to transmit Yersinia pestis. Parasit Vectors. 2021;14:317. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-021-04805-3.
Blanc G, Baltazard M. Recherches expérimentales sur la Peste. L’infection de la puce de l’homme: Pulex irritans L. Maroc-Médical J La Médecine La Pathol Comparée. 1941;213:81–2.
Burroughs A. Sylvatic plague studies. The vector efficiency of nine species of fleas compared with Xenopsylla cheopis. J Hyg (Lond). 1947;45:371–96.
Ledingham J. Reports on plague investigation in India. J Hyg (Lond). 1907;7:323–476. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.2.2480.91.
Prelezov P, Nizamov N. A case of multiple mixed invasion with ectoparasites in goats. Tradit Mod Vet Med. 2020;5:73–8. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3675960.
Christodoulopoulos G, Theodoropoulos G, Kominakis A, Theis JH. Biological, seasonal and environmental factors associated with Pulex irritans infestation of dairy goats in Greece. Vet Parasitol. 2006;137:137–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.12.012.
Rahbari S, Nabian S, Nourolahi F, Arabkhazaeli F, Ebrahimzadeh E. Flea infestation in farm animals and its health implication. Iran J Parasitol. 2008;3:43–7.
Miarinjara A, Raveloson AO, Mugel SG, An N, Andriamiadanarivo A, Rajerison ME, et al. Socio-ecological risk factors associated with human flea infestations of rural household in plague-endemic areas of Madagascar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024;18:e0012036.
Lu C, Adamkiewicz G, Attfield KR, Kapp M, Spengler JD, Tao L, et al. Household pesticide contamination from indoor pest control applications in urban low-income public housing dwellings: a community-based participatory research. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47:2018–25. https://doi.org/10.1021/es303912n.
Smith A. The susceptibility to dieldrin of Pulex irritans and Pediculus humanus corporis in the Pare area of north-east Tanganyika. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;21:240–1.
Seidy S, Tavassoli M, Malekifard F. Pyrethroids resistance in Pulex irritans and Ctenocephalides canis in west and northwest Iran. Vet Res Forum. 2022;13:529–35. https://doi.org/10.30466/vrf.2021.534642.3215.
Ghavami MB, Haghi FP, Alibabaei Z, Enayati AA, Vatandoost H. First report of target site insensitivity to pyrethroids in human flea, Pulex irritans (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2018;146:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2018.03.004.
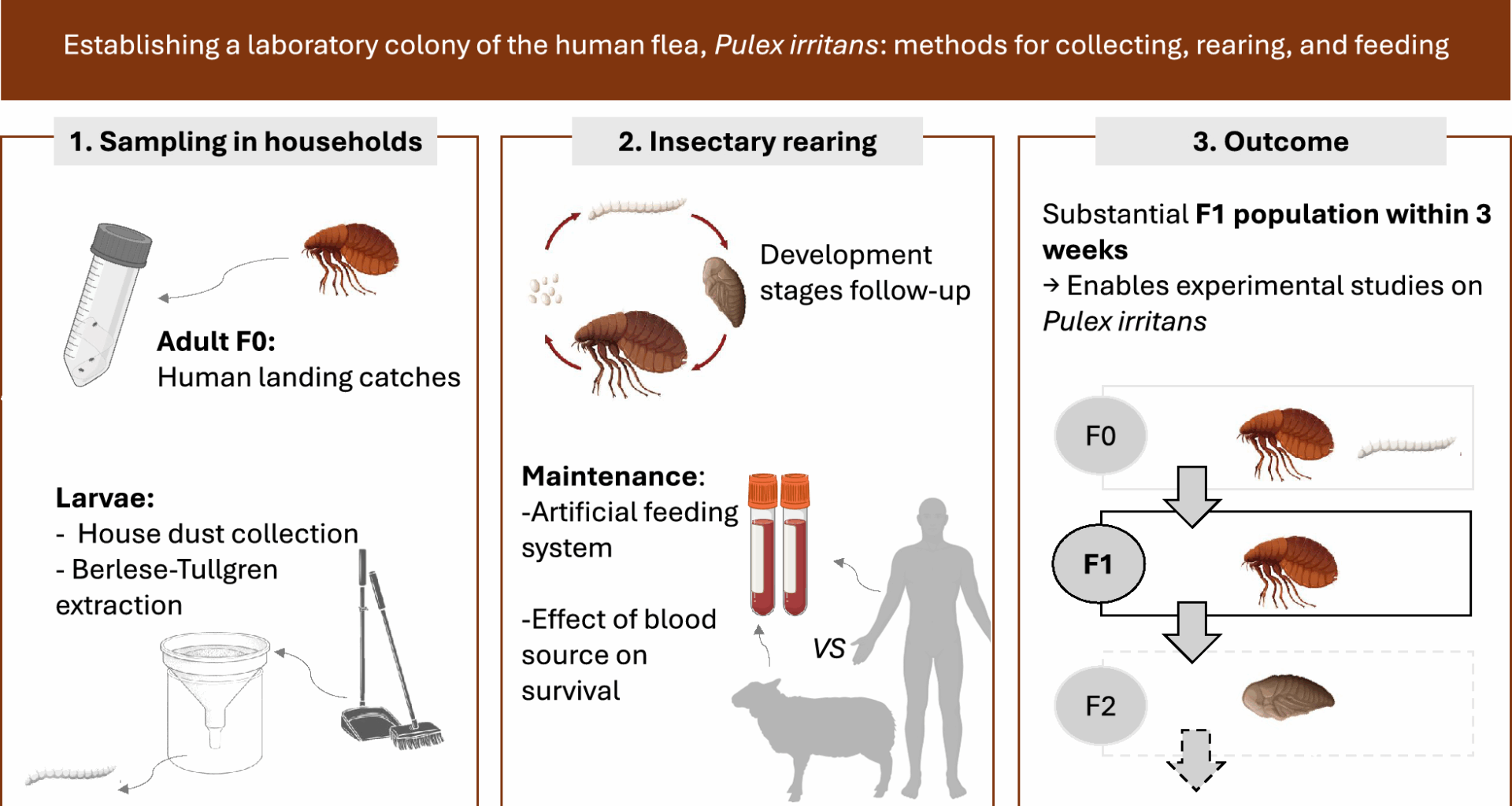
Hudson BW, Prince FM. Culture methods for the fleas Pulex irritans (L.) and Pulex simulans (Baker). Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19:1129–33.
Roe AD, Demidovich M, Dedes J. Origins and history of laboratory insect stocks in a multispecies insect production facility, with the proposal of standardized nomenclature and designation of formal standard names. J Insect Sci. 2018;18:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/jisesa/iey037.
Bacot AW. LXIX. A study of the bionomics of the common rat fleas and other species associated with human habitations, with special reference to the influence of temperature and humidity at various periods of the life history of the insect. J Hyg (Lond). 1914;13:447–654.
Cole MM, VanNatta DL, Ellerbe W, Washington F. Rearing the Oriental rat flea. J Econ Entomol. 1972;65:1495–6.
Gilbert IH. Laboratory rearing of cockroaches, bed-bugs, human lice and fleas. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;31:561–3.
Ratovonjato J, Duchemin JB, Chanteau S. Méthode optimisée d’élevage de pulicidés (Xenopsylla cheopis et Synopsyllus fonquerniei). Arch Inst Pasteur Madagascar. 2000;66:75–7.
Smith CN, Eddy GW. Techniques for rearing and handling body lice, Oriental rat fleas, and cat fleas. Bull World Health Organ. 1954;10:127–37.
Andrianaivoarimanana V, Piola P, Wagner DM, Rakotomanana F, Maheriniaina V, Andrianalimanana S, et al. Trends of human plague, Madagascar, 1998–2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25:220–8. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2502.171974.
Matharu AK, Ouma P, Njoroge MM, Amugune BL, Hyuga A, Mutebi F, et al. Identification of tungiasis infection hotspots with a low-cost, high-throughput method for extracting Tunga penetrans (Siphonaptera) off-host stages from soil samples–an observational study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024;18:e0011601. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0011601.
Hudson BW, Prince FM. A method for large-scale rearing of the cat flea, Ctenocephalides felis felis (Bouché). Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19:1126–9.
Harimalala M, Ramihangihajason TR, Rakotobe Harimanana R, Girod R, Duchemin JB. Illustrated morphological keys for fleas (Siphonaptera) in Madagascar. J Med Entomol. 2021;58:1701–16. https://doi.org/10.1093/jme/tjab023.
RStudio: integrated development environnement for R. RStudio Inc 2018.
Lawrence W, Foil LD. The effects of diet upon pupal development and cocoon formation by the cat flea (Siphonaptera: Pulicidae). J Vector Ecol. 2002;27:39–43.
Yasumatsu K. Rearing of flea larvae on various diets. J Fac Agric Kyushu Univ. 1949;9:121–6. https://doi.org/10.5109/22616.
Metzger ME, Rust MK. Laboratory techniques for rearing the fleas (Siphonaptera: Ceratophyllidae and Pulicidae) of California ground squirrels (Rodentia: Sciuridae) using a novel nest box. J Med Entomol. 2001;38:465–70. https://doi.org/10.1603/0022-2585-38.3.465.
Shelly M, Biswas S, Lal S, Reddy M. Preliminary study on rodent flea larval feed. J Biol Innov. 2013;8330:43–50.
Yakhchali M, Bahramnejad K. IJVST a survey of Pulex irritans (Linnaeus 1758, Siphonaptera: Pulicidae ) infestation in sheep and residential areas in Kurdistan Province, Iran. Iran J Vet Sci Technol. 2015;7:40–7. https://doi.org/10.22067/veterinary.v7i1.37203.
Krasnov BR. Ecology of haematophagy. In: Krasnov BR, editor. Functional and evolutionary ecology of fleas. Cambridge University Press; 2008. p. 154–81. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511542688.011.
Geetha Devi S, Prasad RS. Phagostimulants in artificial feeding systems of rat fleas Xenopsylla cheopis and X. astia. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad Part B Biol Sci. 1985;51:566–73.
Kernif T, Stafford K, Coles GC, Bitam I, Papa K, Chiaroni J, et al. Responses of artificially reared cat fleas Ctenocephalides felis felis (Bouché, 1835) to different mammalian bloods. Med Vet Entomol. 2015;29:171–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/mve.12100.
Vantaux A, Moiroux N, Dabiré KR, Cohuet A, Lefèvre T. Multiple hosts, multiple impacts: the role of vertebrate host diversity in shaping mosquito life history and pathogen transmission. Peer Community J. 2023;3:e72. https://doi.org/10.24072/pcjournal.288.
Bland DM, Jarrett CO, Bosio CF, Hinnebusch BJ. Infectious blood source alters early foregut infection and regurgitative transmission of Yersinia pestis by rodent fleas. PLoS Pathog. 2018;14:e1006859. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006859.
Hinnebusch BJ, Bland DM, Bosio CF, Jarrett CO. Comparative ability of Oropsylla montana and Xenopsylla cheopis fleas to transmit Yersinia pestis by two different mechanisms. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0005276.