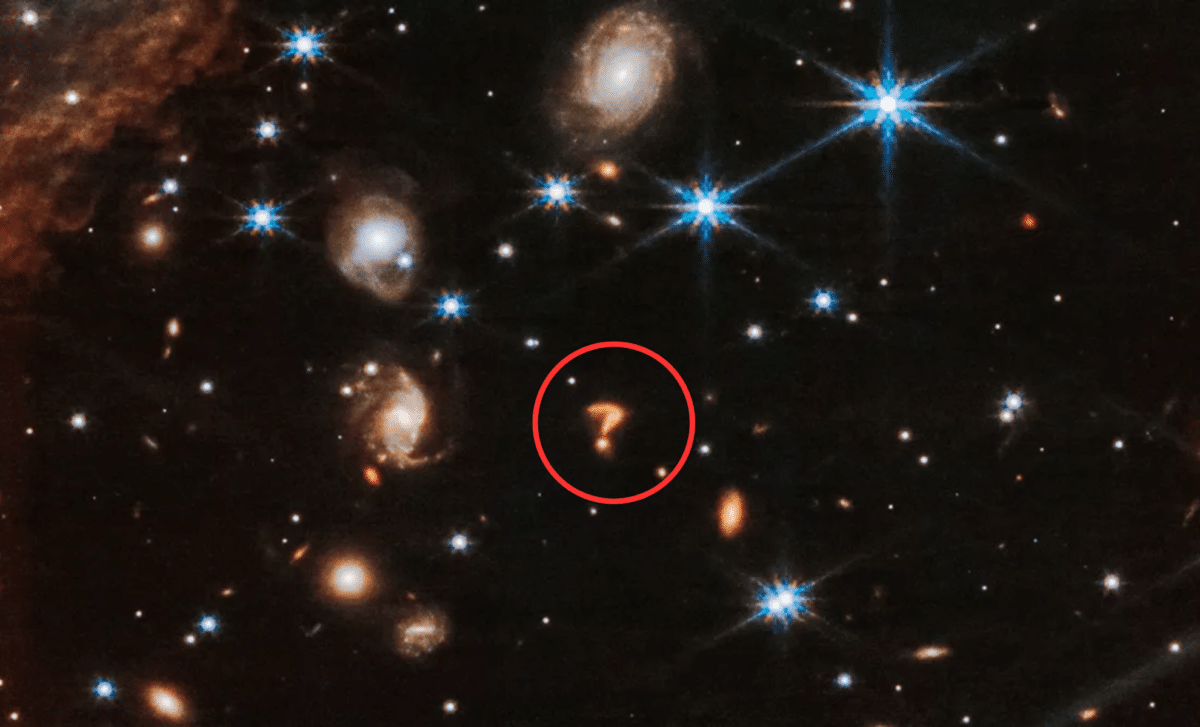
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has captured images of a distant galaxy that is forming a peculiar cosmic structure resembling a question mark. This observation, revealed in a study published by NASA, showcases not only the power of JWST but also the fascinating processes that occur as galaxies collide and evolve. These “cosmic question marks” are not just visual anomalies; they offer profound insight into the mechanisms of galaxy formation and the dynamic forces at play in our universe. By studying these structures, astronomers hope to uncover more about the formation of galaxies, stars, and the larger cosmic forces that shape our universe.
The Cosmic Question Mark: A Visual Phenomenon
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope captured an awe-inspiring image of a distant galaxy that, due to cosmic interactions, took on the appearance of a giant question mark. This peculiar formation is not an isolated incident. It highlights how powerful cosmic forces like galaxy mergers can distort galaxies into strange shapes. The observed object is believed to be the result of two galaxies merging, a process that is common throughout the universe as galaxies evolve. The merger of these galaxies creates gravitational distortions that lead to unique and sometimes unexpected visual formations.
 The cosmic question mark.
The cosmic question mark.
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA / Image Processing Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Anton M. Koekemoer (STScI)
This particular observation, which was not initially the primary focus of the image, has captivated astronomers and the public alike. While the focus was on a pair of stars forming in the center of the image, it was the distant galaxy’s unusual shape, created by the collision of two galaxies, that stole the show.
“This looks like the kind of thing that you get fairly frequently — as galaxies grow and evolve over cosmic time — which is that they sometimes collide with their near neighbors,” explained Matt Caplan, assistant professor of physics at Illinois State University. “And when that happens, they can get distorted into all kinds of different shapes — including a question mark, apparently.”
The Role of Galaxy Mergers in Cosmic Evolution
Galaxy mergers are essential events in the cosmic evolution of galaxies, contributing to their growth and transformation over billions of years. These mergers are common occurrences as galaxies move through space and interact with nearby galaxies. The formation of a “cosmic question mark” is a perfect example of how these mergers can cause galaxies to merge into odd shapes. As galaxies collide, their stars and gas clouds are not uniform, and they often get stretched and warped into various shapes by the immense gravitational forces at play.
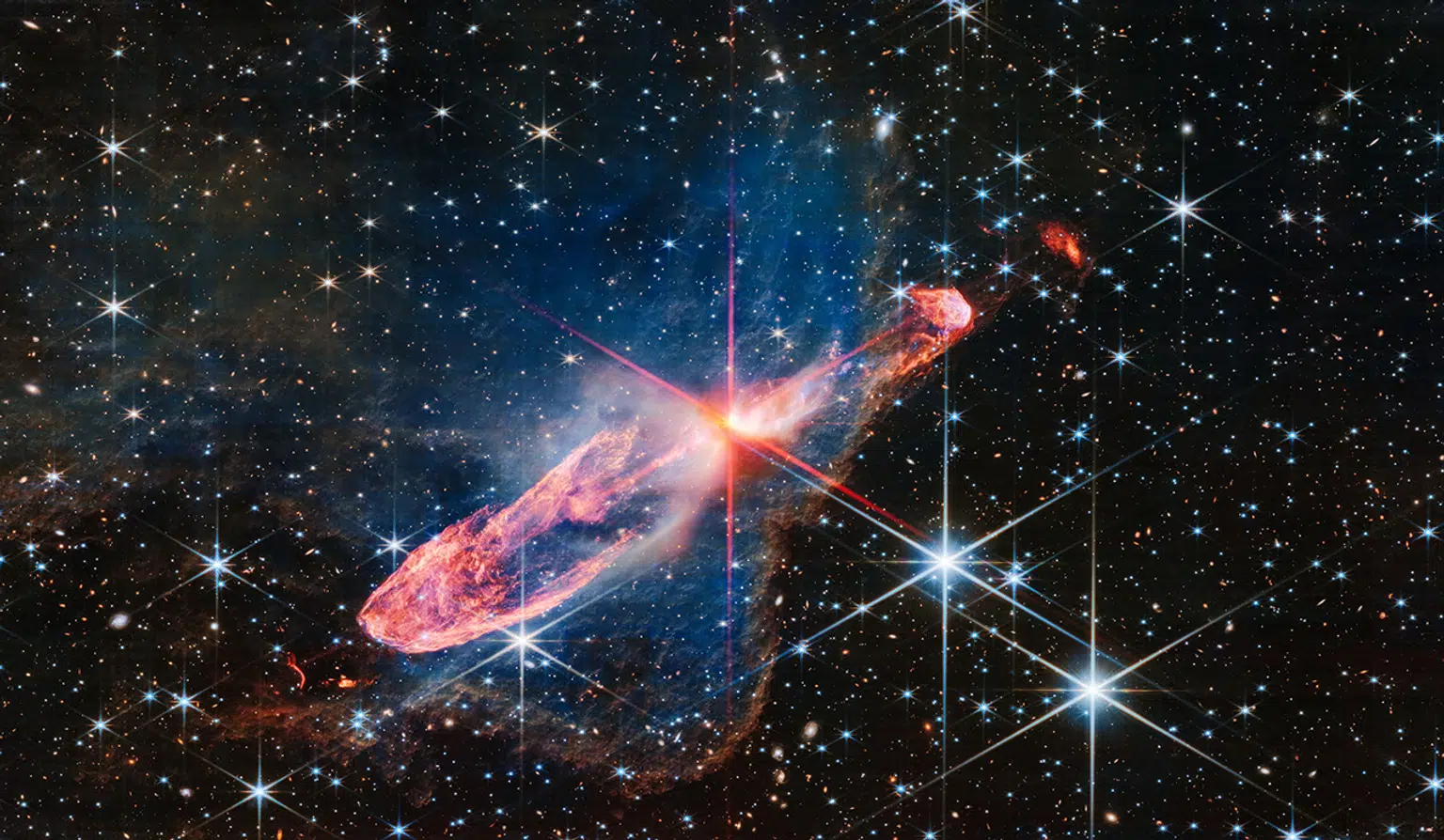 A complex of Herbig-Haro objects
A complex of Herbig-Haro objects
Image: NASA, ESA, CSA; Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI), Anton Koekemoer (STScI)
Understanding these mergers is key for astronomers, as they play a pivotal role in the ongoing growth of galaxies. This particular formation could help scientists better understand how galaxies evolve and what forces contribute to their formation. The NASA team highlights the importance of objects like Herbig-Haro 46/47, which is only a few thousand years old.
“Herbig-Haro 46/47 is an important object to study because it is relatively young — only a few thousand years old. Stars take millions of years to fully form,” NASA explains.
Studying these young stellar objects gives scientists a clearer picture of the early stages of star formation and the way stars like our Sun are created.
The Power of Gravitational Lensing
In addition to galaxy mergers, gravitational lensing is another cosmic phenomenon that often results in distorted and fascinating visuals. Gravitational lensing occurs when massive objects like galaxy clusters warp spacetime and magnify objects behind them. In the case of the “cosmic question mark,” gravitational lensing played a role in distorting the images of interacting galaxies. This process made the galaxies appear multiple times, tracing out the question mark shape across the sky.
The 2024 observation, captured by JWST, shows two distant galaxies interacting and being magnified by the gravitational lensing effect of a massive galaxy cluster.
“Two distant, interacting galaxies — a face-on spiral and a dusty red galaxy seen from the side — appear multiple times, tracing a familiar shape across the sky,” NASA explains.
This gravitational lensing effect adds a new layer of complexity and beauty to the cosmic question mark, revealing the potential for visual distortions that are both visually striking and scientifically important.
How JWST Unveils the Invisible Universe
The James Webb Space Telescope, with its ability to observe in infrared light, offers a new perspective on the universe that was not previously available. Infrared observations allow astronomers to peer deeper into space and observe objects that are too distant or faint to be seen with visible light. This capability is critical when studying the oldest galaxies, which emit light in infrared wavelengths due to their distance from Earth.
“Blue objects with diffraction spikes are stars, and the closer they are, the larger they appear. White-and-pink spiral galaxies sometimes appear larger than these stars, but are significantly farther away. The tiniest red dots, Webb’s infrared specialty, are often the oldest, most distant galaxies,” NASA explains.
JWST’s infrared observations provide crucial information about the origins of the universe, revealing galaxies that formed billions of years ago. These early galaxies, including the ones involved in the creation of the cosmic question mark, offer valuable insights into how galaxies, stars, and even the building blocks of life began to form in the early cosmos.
