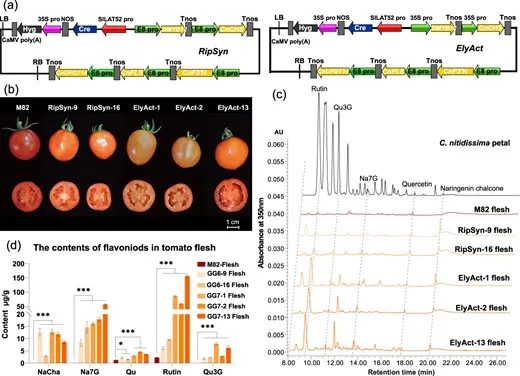
In a study published on November 7, 2024, researchers from Zhejiang University, Chinese Academy of Forestry, and Westlake University reproduced the biosynthetic pathway of flavonols from Camellia nitidissima in tomatoes. They identified five genes responsible for the formation of yellow pigments – including quercetin – and inserted them into the tomato genome.
Читай нас також у Viber та Telegram.
This resulted in a new variety with bright yellow flesh and increased antioxidant content.
Reported by Horti Daily
This allowed the fruits to have not only a new color but also a high content of flavonols – substances with powerful antioxidant properties. Researchers also found in the new tomatoes compounds unique to food crops, characteristic only of camellias – camelliasides A and C.
“This project combines the biology of ornamental plants with the improvement of food crops. By transferring the pigment pathway of camellias to tomatoes, we have shown how synthetic biology can awaken hidden metabolic potential and bring real health benefits,” said Professor Pengyan Fan, co-author of the study.
Scientists emphasize that such breeding opens the way to creating functional products of a new generation – with benefits not only for the eye but also for the body.
Views: 5
Теги: antioxidant content, bright yellow flesh, camelliasides A and C, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Chinese scientists, flavonols, food crops, functional products, genetic engineering, genetic modification, Health benefits, metabolic potential, ornamental plants, plant breeding, quercetin, synthetic biology, tomato genetics, Westlake University, yellow camellia genes, Zhejiang University