Credit: Kampus Production from Pexels
Cannabis, also known as marijuana or weed, is widely consumed worldwide, whether for recreational or medicinal purposes. Over the past decades, the use of cannabis has been fully legalized or decriminalized in various countries worldwide, including Canada, many U.S. states, the Netherlands, Germany, Spain and Portugal.
While some studies have found that cannabis and especially cannabidiol (i.e., the non-intoxicating compound contained in it) can have medicinal effects, others have linked the abuse of its psychoactive variations (i.e., containing tetrahydrocannabinol or THC) with a greater risk of being diagnosed with psychiatric disorders.
As many individuals worldwide use cannabis on a regular basis, understanding the mechanisms that could link its consumption with psychiatric disorders could be highly valuable, as it might help to identify factors that increase the risk of developing specific disorders.
In a paper published in Nature Mental Health, researchers at Yale University School of Medicine, the Veterans Affairs Connecticut Healthcare System and Washington University School of Medicine shed new light on the genetic associations between cannabis use, cannabis use disorder (CanUD) and various psychiatric disorders.
CanUD is a mental health disorder characterized by a continued use of cannabis, difficulties experienced when trying to cut down its consumption or cease using it altogether, and an interference of the substance with daily activities, relationships or responsibilities.
“Increasing prevalence of cannabis use and CanUD may increase risk for psychiatric disorders,” wrote Marco Galimberti, Cassie Overstreet and their colleagues in their paper. “We evaluated the relationships between these cannabis traits and a range of psychiatric traits, running global and local genetic correlations, genomic structural equation modeling, colocalization analyses and Mendelian randomization analyses for causality.”
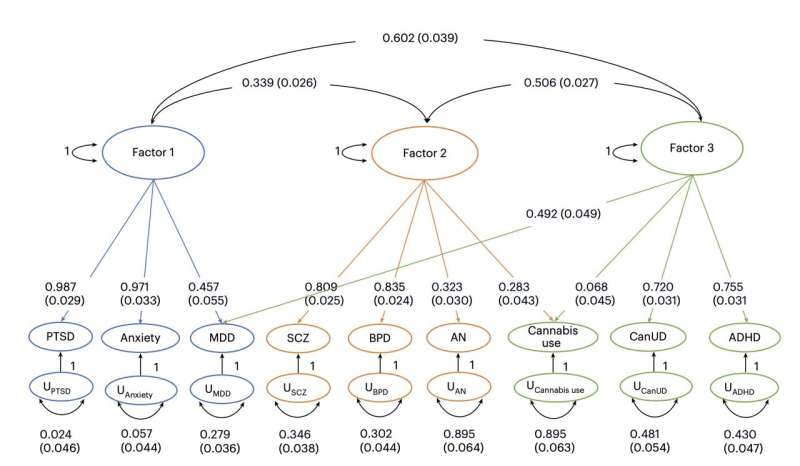
Genomic-SEM. Genomic-SEM analyses of cannabis traits (CanUD and cannabis use) and psychiatric disorders for a three-factor model. Credit: Galimberti et al. (Nature Mental Health, 2025).
The researchers analyzed genetic, psychiatric and psychological data collected as part of earlier studies, using various statistical techniques. First, they tried to detect genetic patterns that linked cannabis use with specific psychiatric and personality traits, using a technique known as genomic structural equation modeling.
Subsequently, they ran colocalization analyses, a statistical analysis that allowed them to uncover instances where two traits shared the same underlying genetic variant. Finally, they used a technique called Mendelian randomization to uncover causal relationships between traits, or in other words, if a sporadic or problematic use of cannabis caused specific disorders via genetic factors and vice versa.
“Global genetic analyses identified significantly different correlations between CanUD and cannabis use,” wrote Galimberti, Overstreet and their colleagues. “A variant in strong linkage disequilibrium to one regulating CHRNA2 was significantly shared by CanUD and schizophrenia in colocalization analysis and included in a significant region in local genetic correlations between these traits. A three-factor model from genomic structural equation modeling showed that CanUD and cannabis use partially map together onto a factor with major depressive disorder and ADHD.”
Interestingly, the researchers found that although cannabis use and CanUD are in some ways related, they had different genetic relationships with psychiatric disorders. In fact, they found that variations in the regulation of the gene CHRNA2, which has also been linked to nicotine consumption and dopamine signaling, were common to both schizophrenia and CanUD, but not to casual or general cannabis use.
“In terms of causality, CanUD showed bidirectional causal relationships with most tested psychiatric disorders, differently from cannabis use,” wrote Galimberti, Overstreet and their colleagues. “Increasing use of cannabis can increase rates of psychiatric disorders over time, especially in individuals who progress from cannabis use to CanUD.”
Overall, the findings of this recent study suggest that there is a bi-directional genetic relationship between the abuse of cannabis, specifically CanUD, and various psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, ADHD, depression, and bipolar disorder. In other words, it appears that CanUD could increase the risk of developing mental health disorders, and being diagnosed with some psychiatric disorders could also prompt abuse of cannabis.
This recent work could potentially inform the development of public health interventions aimed at monitoring or limiting people’s consumption of cannabis early, to reduce the risk that they will later develop psychiatric disorders. In addition, the analyses could inspire other research groups to delve deeper into the genetic associations they uncovered, potentially by analyzing a wider pool of genetic, psychological and medical data.
Written for you by our author Ingrid Fadelli,
edited by Gaby Clark
, and fact-checked and reviewed by Robert Egan —this article is the result of careful human work. We rely on readers like you to keep independent science journalism alive.
If this reporting matters to you,
please consider a donation (especially monthly).
You’ll get an ad-free account as a thank-you.
More information:
Marco Galimberti et al, The genetic relationship between cannabis use disorder, cannabis use and psychiatric disorders, Nature Mental Health (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s44220-025-00440-4.
© 2025 Science X Network
Citation:
Study explores genetic link between cannabis use and psychiatric disorders (2025, June 26)
retrieved 28 June 2025
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2025-06-explores-genetic-link-cannabis-psychiatric.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
