Newswise — A study led by researchers from Zhejiang University and the Innovation Academy for Microsatellites of the Chinese Academy of Sciences designed new large-scale access protocols and technologies to address the characteristics and needs of satellite IoT, and explored the development trends of satellite IoT to encourage further research in this area by a wide range of scholars.
The study, led by Ph.D. Xiaoming CHEN, Assoc. Prof. Zhaobin XU, and Ph.D. Lin SHANG published a review paper titled “Satellite Internet of Things: challenges, solutions, and development trends” in Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering (FITEE) in 2023, Vol.24, Issue 7.
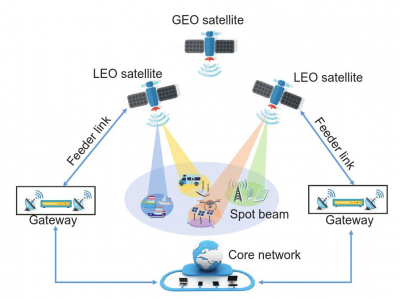
The network architecture of satellite IoT consists of IoT devices, gateways, access networks, and core networks. Low Earth orbit (LEO) satellites serve as access points and provide coverage using multi-beam techniques, but they face problems such as interference between beams and complex precoding. Geosynchronous orbit (GEO) satellites achieve high-speed data transmission through millimeter waves or lasers. The access network needs to handle the short-packet transmission of a large number of devices, and channel phase errors and resource allocation are the main challenges. Satellite IoT networks mainly provide machine-type communication services, which are characterized by sporadic traffic, small data volume, massive data packets, and diverse requirements. These characteristics are significantly different from traditional human-centric communication services and determine the uniqueness of satellite IoT design.
The challenges faced by satellite IoT are introduced as follows: 1) Massive connectivity – The number of IoT devices has increased dramatically. LEO satellites have high signaling overhead in identifying active devices, and traditional orthogonal multiple access techniques are difficult to meet the needs of simultaneously transmitting a large number of data packets. 2) Wide coverage – Multi-beam techniques have limitations in achieving wide coverage, such as limited beam numbers, complex propagation environments in different regions, difficult precoder design, and challenging robust precoding of beams. 3) High mobility – The high-speed movement of LEO satellites leads to fast time-varying channels, making the obtained channel state information possibly outdated. It is difficult to use complex wireless techniques to improve signal quality, and frequent handovers occur, reducing service performance. 4) Low power – LEO satellites have unstable energy acquisition and limited storage. IoT devices are difficult to replace batteries, and have strict requirements for power consumption. Low transmit power makes it difficult to ensure service quality. 5) Stringent latency – Compared with territorial IoT networks, satellite IoT has a large transmission delay. Some IoT services have strict requirements for delay, and it is necessary to reduce the latency.
The solutions to satellite IoT are pointed out as follows: 1) Access protocol – Abandon traditional grant-based random access protocols and adopt grant-free random access protocols to reduce signaling overhead and access delay. At the same time, active devices are detected through compressive sensing and covariance-based methods, and effective detection algorithms are designed to address the problems caused by short preambles. For some services, an unsourced random access protocol can be used to further reduce the delay. 2) Multiple access techniques – Orthogonal multiple access techniques and non-orthogonal multiple access techniques are introduced. The former improves the quality of received signals through a large number of narrow beams, but has high costs and power consumption. The latter allows a beam to admit transmissions from multiple devices, but generates co-channel interference and needs to be combined with interference mitigation schemes and successive interference cancellation techniques. Both have their advantages and disadvantages and should be selected according to requirements.
Finally, some development trends of satellite IoT are listed, including: 1) Satellite – territorial integrated IoT, which integrates the advantages of different IoT networks to achieve seamless global coverage; 2) Multi-LEO satellite cooperation, which improves performance and avoids service interruption; 3) Joint LEO and GEO satellite access, which meets the needs of different services; 4) Convergence of satellite IoT and deep-space communication networks, which constructs a high-throughput space network and expands the coverage from the Earth to space.
The paper “Satellite Internet of Things: challenges, solutions, and development trends” authored by Xiaoming CHEN, Zhaobin XU, and Lin SHANG. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1631/FITEE.2200648.