Afshin, A. et al. Health effects of dietary risks in 195 countries, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 393, 1958–1972 (2019).
Janmohamed, A. et al. Dietary quality and associated factors among women of reproductive age in six sub-Saharan African countries. Nutrients 16, 1115 (2024).
Stevens, G. A., Beal, T., Mbuya, M. N. N., Luo, H. & Neufeld, L. M. Micronutrient deficiencies among preschool-aged children and women of reproductive age worldwide: a pooled analysis of individual-level data from population-representative surveys. Lancet Glob. Health 10, e1590–e1599 (2022).
Headey, D., Hirvonen, K. & Hoddinott, J. Animal sourced foods and child stunting. Am. J. Agric Econ. 100, 1302–1319 (2018).
van Jaarsveld, P. et al. Nutrient content of eight African leafy vegetables and their potential contribution to dietary reference intakes. J. Food Compos. Anal. 33, 77–84 (2014).
Keats, E. C. et al. Effective interventions to address maternal and child malnutrition: an update of the evidence. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 5, 367–384 (2021).
Tan, X., Tan, P. Y., Gong, Y. Y. & Moore, J. B. Overnutrition is a risk factor for iron, but not for zinc or vitamin A deficiency in children and young people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Glob. Health https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjgh-2024-015135 (2024).
Reerink, I. et al. Experiences and lessons learned for delivery of micronutrient powders interventions. Matern. Child Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1111/mcn.12495 (2017).
Bloor, S. R., Schutte, R. & Hobson, A. R. Oral iron supplementation—gastrointestinal side effects and the impact on the gut microbiota. Microbiol. Res. 12, 491–502 (2021).
Gupta, S., Brazier, A. K. M. & Lowe, N. M. Zinc deficiency in low- and middle-income countries: prevalence and approaches for mitigation. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 33, 624–643 (2020).
Hall, A. G. & King, J. C. Zinc fortification: current trends and strategies. Nutrients 14, 3895 (2022).
Hombali, A. S., Solon, J. A., Venkatesh, B. T., Nair, N. S. & Peña-Rosas, J. P. Fortification of staple foods with vitamin A for vitamin A deficiency. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010068.pub2 (2019).
Kaur, N., Agarwal, A. & Sabharwal, M. Food fortification strategies to deliver nutrients for the management of iron deficiency anaemia. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 5, 2094–2107 (2022).
Carducci, B., Jägermeyr, J., Ruane, A. C. & Fanzo, J. Rising to the challenge: producing and sustaining a nutrient-dense and climate-resilient food basket for all. One Earth 6, 1443–1446 (2023).
Myers, S. S. et al. Increasing CO2 threatens human nutrition. Nature 510, 139–142 (2014).
Ebi, K. L. et al. Nutritional quality of crops in a high CO2 world: an agenda for research and technology development. Environ. Res. Lett. 16, 064045 (2021).
Walsh, C. A. & Lundgren, M. R. Nutritional quality of photosynthetically diverse crops under future climates. Plants People Planet 6, 1272–1283 (2024).
Ainsworth, E. A. & Long, S. P. 30 years of free-air carbon dioxide enrichment (FACE): what have we learned about future crop productivity and its potential for adaptation?. Glob. Change Biol. 27, 27–49 (2021).
Jägermeyr, J. et al. Climate impacts on global agriculture emerge earlier in new generation of climate and crop models. Nat. Food 2, 873–885 (2021).
Zabel, F. et al. Large potential for crop production adaptation depends on available future varieties. Glob. Change Biol. 27, 3870–3882 (2021).
Xia, Y. et al. Influences of extreme weather events on the carbon to nitrogen ratios of major staple crops. Sci. Total Environ. 969, 178943 (2025).
Mbow, C. et al. in Special Report on Climate Change and Land (eds Shukla, P. R. et al.) Ch. 5 (IPCC, 2019).
Bezner Kerr, R. et al. in Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability (eds Pörtner, H.-O. et al.) 713–906 (IPCC, Cambridge Univ. Press, 2022).
McGrath, J. M. & Lobell, D. B. Reduction of transpiration and altered nutrient allocation contribute to nutrient decline of crops grown in elevated CO2 concentrations. Plant Cell Environ. 36, 697–705 (2013).
Uddling, J., Broberg, M. C., Feng, Z. & Pleijel, H. Crop quality under rising atmospheric CO2. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 45, 262–267 (2018).
Dusenge, M. E., Duarte, A. G. & Way, D. A. Plant carbon metabolism and climate change: elevated CO2 and temperature impacts on photosynthesis, photorespiration and respiration. N. Phytol. 221, 32–49 (2019).
Halpern, M., Yermiyahu, U. & Bar-Tal, A. in Advances in Agronomy Vol. 176 (ed. Sparks, D. L.) 1–34 (Academic Press, 2022).
Pérez, P., Morcuende, R., Martı́n del Molino, I. & Martı́nez-Carrasco, R. Diurnal changes of Rubisco in response to elevated CO2, temperature and nitrogen in wheat grown under temperature gradient tunnels. Environ. Exp. Bot. 53, 13–27 (2005).
Bunce, J. A. Effects of water vapor pressure difference on leaf gas exchange in potato and sorghum at ambient and elevated carbon dioxide under field conditions. Field Crops Res. 82, 37–47 (2003).
Dong, J., Gruda, N., Lam, S. K., Li, X. & Duan, Z. Effects of elevated CO2 on nutritional quality of vegetables: a review. Front. Plant Sci. 9, 924 (2018).
Triboi, E., Martre, P., Girousse, C., Ravel, C. & Triboi-Blondel, A.-M. Unravelling environmental and genetic relationships between grain yield and nitrogen concentration for wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 25, 108–118 (2006).
Wang, J. et al. Changes in grain protein and amino acids composition of wheat and rice under short-term increased [CO2] and temperature of canopy air in a paddy from East China. N. Phytol. 222, 726–734 (2019).
Wei, L. et al. Responses of rice qualitative characteristics to elevated carbon dioxide and higher temperature: implications for global nutrition. J. Sci. Food Agric. 101, 3854–3861 (2021).
Kong, X., Hou, R. & Yang, G. Effects of climatic warming on the starch and protein content of winter wheat grain under conservation tillage in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 238, 105995 (2024).
Martre, P. et al. Global needs for nitrogen fertilizer to improve wheat yield under climate change. Nat. Plants 10, 1081–1090 (2024).
He, M. & Dijkstra, F. A. Drought effect on plant nitrogen and phosphorus: a meta-analysis. N. Phytol. 204, 924–931 (2014).
Bista, D. R., Heckathorn, S. A., Jayawardena, D. M. & Boldt, J. K. Effect of drought and carbon dioxide on nutrient uptake and levels of nutrient-uptake proteins in roots of barley. Am. J. Bot. 107, 1401–1409 (2020).
Yang, R. et al. Implications of soil waterlogging for crop quality: a meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 161, 127395 (2024).
George, T. S. et al. Bottom-up perspective—the role of roots and rhizosphere in climate change adaptation and mitigation in agroecosystems. Plant Soil 500, 297–323 (2024).
Tian, Y. et al. Long-term soil warming decreases microbial phosphorus utilization by increasing abiotic phosphorus sorption and phosphorus losses. Nat. Commun. 14, 864 (2023).
Neumann, R. B., Seyfferth, A. L., Teshera-Levye, J. & Ellingson, J. Soil warming increases arsenic availability in the rice rhizosphere. Agric. Environ. Lett. 2, 170006 (2017).
Oishy, M. N. et al. Unravelling the effects of climate change on the soil–plant–atmosphere interactions: a critical review. Soil Environ. Health 3, 100130 (2025).
Ferdush, J., Paul, V., Varco, J., Jones, K. & Sasidharan, S. M. Consequences of elevated CO2 on soil acidification, cation depletion, and inorganic carbon: a column-based experimental investigation. Soil Tillage Res. 234, 105839 (2023).
Miner, G. L. et al. Global change impacts on mineral nutritional quality of cereal grains: coordinated datasets and analyses to advance a systems-based understanding. Field Crops Res. 310, 109338 (2024).
Rosenzweig, C. et al. The Agricultural Model Intercomparison and Improvement Project (AgMIP): protocols and pilot studies. Agric. For. Meteorol. 170, 166–182 (2013).
Ruane, A. C. et al. An AgMIP framework for improved agricultural representation in integrated assessment models. Environ. Res. Lett. 12, 125003 (2017).
Hoogenboom, G. et al. in Advances in Crop Modeling for a Sustainable Agriculture (ed. Boote, K. J.) 173–216 (Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing, 2019).
Jones, J. W. et al. The DSSAT cropping system model. Eur. J. Agron. 18, 235–265 (2003).
Dar, E. A., Hoogenboom, G. & Shah, Z. A. Meta analysis on the evaluation and application of DSSAT in South Asia and China: recent studies and the way forward. J. Agrometeorol. 25, 185–204 (2023).
Hopf, A. et al. Development and improvement of the CROPGRO-Strawberry model. Sci. Hortic. 291, 110538 (2022).
Hopf, A. et al. Dynamic prediction of preharvest strawberry quality traits as a function of environmental factors. HortScience 57, 1336–1355 (2022).
Tai, A. P. K., Sadiq, M., Pang, J. Y. S., Yung, D. H. Y. & Feng, Z. Impacts of surface ozone pollution on global crop yields: comparing different ozone exposure metrics and incorporating co-effects of CO2. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsufs.2021.534616 (2021).
Wang, X. & Mauzerall, D. L. Characterizing distributions of surface ozone and its impact on grain production in China, Japan and South Korea: 1990 and 2020. Atmos. Environ. 38, 4383–4402 (2004).
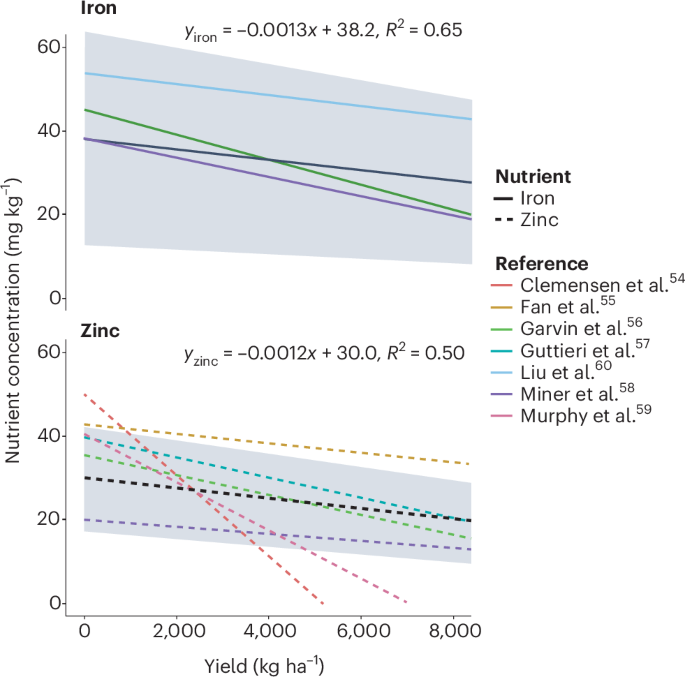
Clemensen, A. K. et al. Perennial forages influence mineral and protein concentrations in annual wheat cropping systems. Crop Sci. 61, 2080–2089 (2021).
Fan, M.-S. et al. Evidence of decreasing mineral density in wheat grain over the last 160 years. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 22, 315–324 (2008).
Garvin, D. F., Welch, R. M. & Finley, J. W. Historical shifts in the seed mineral micronutrient concentration of US hard red winter wheat germplasm. J. Sci. Food Agric. 86, 2213–2220 (2006).
Guttieri, M. J. et al. Variation for grain mineral concentration in a diversity panel of current and historical great plains hard winter wheat germplasm. Crop Sci. 55, 1035–1052 (2015).
Miner, G. L. et al. Wheat grain micronutrients and relationships with yield and protein in the U.S. Central Great Plains. Field Crops Res. 279, 108453 (2022).
Murphy, K. M., Reeves, P. G. & Jones, S. S. Relationship between yield and mineral nutrient concentrations in historical and modern spring wheat cultivars. Euphytica 163, 381–390 (2008).
Liu, H. et al. Grain iron and zinc concentrations of wheat and their relationships to yield in major wheat production areas in China. Field Crops Res. 156, 151–160 (2014).
Brunetti, G., Kodešová, R. & Šimůnek, J. Modeling the translocation and transformation of chemicals in the soil-plant continuum: a dynamic plant uptake module for the HYDRUS model. Water Resour. Res. 55, 8967–8989 (2019).
Office of Global Food Security The Vision for Adapted Crops and Soils (US Department of State, 2025); https://2021-2025.state.gov/the-vision-for-adapted-crops-and-soils/
Alae-Carew, C. et al. The impact of environmental changes on the yield and nutritional quality of fruits, nuts and seeds: a systematic review. Environ. Res. Lett. 15, 023002 (2020).
Scheelbeek, P. F. D. et al. Effect of environmental changes on vegetable and legume yields and nutritional quality. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 115, 6804–6809 (2018).
Hoogenboom, G. et al. in Improving Soil Fertility Recommendations in Africa Using the Decision Support System for Agrotechnology Transfer (DSSAT) (eds Kihara, J. et al.) 9–18 (Springer, 2012).
White, J. W. et al. Integrated description of agricultural field experiments and production: the ICASA Version 2.0 data standards. Comput. Electron. Agric. 96, 1–12 (2013).
Giulia, S. et al. The effect of climatic factors on nutrients in foods: evidence from a systematic map. Environ. Res. Lett. 15, 113002 (2020).
Chumley, H. & Hewlings, S. The effects of elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide [CO2] on micronutrient concentration, specifically iron (Fe) and zinc (Zn) in rice; a systematic review. J. Plant Nutr. 43, 1571–1578 (2020).
Fernando, N. et al. Wheat grain quality under increasing atmospheric CO2 concentrations in a semi-arid cropping system. J. Cereal Sci. 56, 684–690 (2012).
Hein, N. T. et al. Grain micronutrient composition and yield components in field-grown wheat are negatively impacted by high night-time temperature. Cereal Chem. 99, 615–624 (2022).
Högy, P. et al. Effects of elevated CO2 on grain yield and quality of wheat: results from a 3-year free-air CO2 enrichment experiment. Plant Biol.11, 60–69 (2009).
Hu, S. et al. Response of rice grain quality to elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration: a meta-analysis of 20-year FACE studies. Field Crops Res. 284, 108562 (2022).
Li, X., Jiang, D. & Liu, F. Dynamics of amino acid carbon and nitrogen and relationship with grain protein in wheat under elevated CO2 and soil warming. Environ. Exp. Bot. 132, 121–129 (2016).
Pour-Aboughadareh, A. et al. Effects of drought stress on some agronomic and morpho-physiological traits in durum wheat genotypes. Sustainability 12, 5610 (2020).
Sattar, A. et al. Individual and combined effect of terminal drought and heat stress on allometric growth, grain yield and quality of bread wheat. Pak. J. Bot. https://doi.org/10.30848/pjb2020-2(5) (2020).
Tomás, D., Rodrigues, J. C., Viegas, W. & Silva, M. Assessment of high temperature effects on grain yield and composition in bread wheat commercial varieties. Agronomy 10, 499 (2020).
Wang, Y., Frei, M., Song, Q. & Yang, L. The impact of atmospheric CO2 concentration enrichment on rice quality—a research review. Acta Ecol. Sin. 31, 277–282 (2011).
Zhu, C. et al. Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels this century will alter the protein, micronutrients, and vitamin content of rice grains with potential health consequences for the poorest rice-dependent countries. Sci. Adv. 4, eaaq1012 (2018).
Ziska, L. H., Namuco, O., Moya, T. & Quilang, J. Growth and yield response of field-grown tropical rice to increasing carbon dioxide and air temperature. Agron. J. 89, 45–53 (1997).
Emam, A. I. I. et al. Enriched grain minerals in Aegilops tauschii-derived common wheat population under heat-stress environments. Sci. Rep. 15, 5624 (2025).
Han, S., Liu, X., Makowski, D. & Ciais, P. Meta-analysis of water stress impact on rice quality in China. Agric. Water Manag. 307, 109230 (2025).
Lan, Y., Kuktaite, R., Chawade, A. & Johansson, E. Chasing high and stable wheat grain mineral content: mining diverse spring genotypes under induced drought stress. PLoS ONE 19, e0298350 (2024).
Yue, L. et al. The mechanism of manganese ferrite nanomaterials promoting drought resistance in rice. Nanomaterials https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13091484 (2023).
Zhou, R. et al. Effects of high temperature on grain quality and enzyme activity in heat-sensitive versus heat-tolerant rice cultivars. J. Sci. Food Agric. 104, 9729–9741 (2024).
Zahra, N. et al. Impact of climate change on wheat grain composition and quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 103, 2745–2751 (2023).
Galani, Y. J. H. et al. Effects of combined abiotic stresses on nutrient content of European wheat and implications for nutritional security under climate change. Sci. Rep. 12, 5700 (2022).
Nasiroleslami, E., Mozafari, H., Sadeghi-Shoae, M., Habibi, D. & Sani, B. Changes in yield, protein, minerals, and fatty acid profile of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) under fertilizer management involving application of nitrogen, humic acid, and seaweed extract. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 21, 2642–2651 (2021).
Castellari, M. P., Poffenbarger, H. J. & Van Sanford, D. A. Sulfur fertilization effects on protein concentration and yield of wheat: a meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 302, 109061 (2023).
Christensen, A. J., Srinivasan, V., Hart, J. C. & Marshall-Colon, A. Use of computational modeling combined with advanced visualization to develop strategies for the design of crop ideotypes to address food security. Nutr. Rev. 76, 332–347 (2018).
Huang, J. et al. Assimilation of remote sensing into crop growth models: current status and perspectives. Agric. For. Meteorol. 276—277, 107609 (2019).
Silva, J. V. & Giller, K. E. Grand challenges for the 21st century: what crop models can and can’t (yet) do. J. Agric. Sci. 158, 794–805 (2020).
Vos, J. et al. Functional–structural plant modelling: a new versatile tool in crop science. J. Exp. Bot. 61, 2101–2115 (2010).
Karageorgou, D. et al. Harmonising dietary datasets for global surveillance: methods and findings from the Global Dietary Database. Public Health Nutr. 27, e47 (2024).
Smith, M. R., Micha, R., Golden, C. D., Mozaffarian, D. & Myers, S. S. Global Expanded Nutrient Supply (GENuS) Model: a new method for estimating the global dietary supply of nutrients. PLoS ONE 11, e0146976 (2016).
Fredenberg, E. et al. Vision for Adapted Crops and Soils (VACS) Research in Action: Opportunity Crops for Africa (Rockefeller Foundation, 2024).